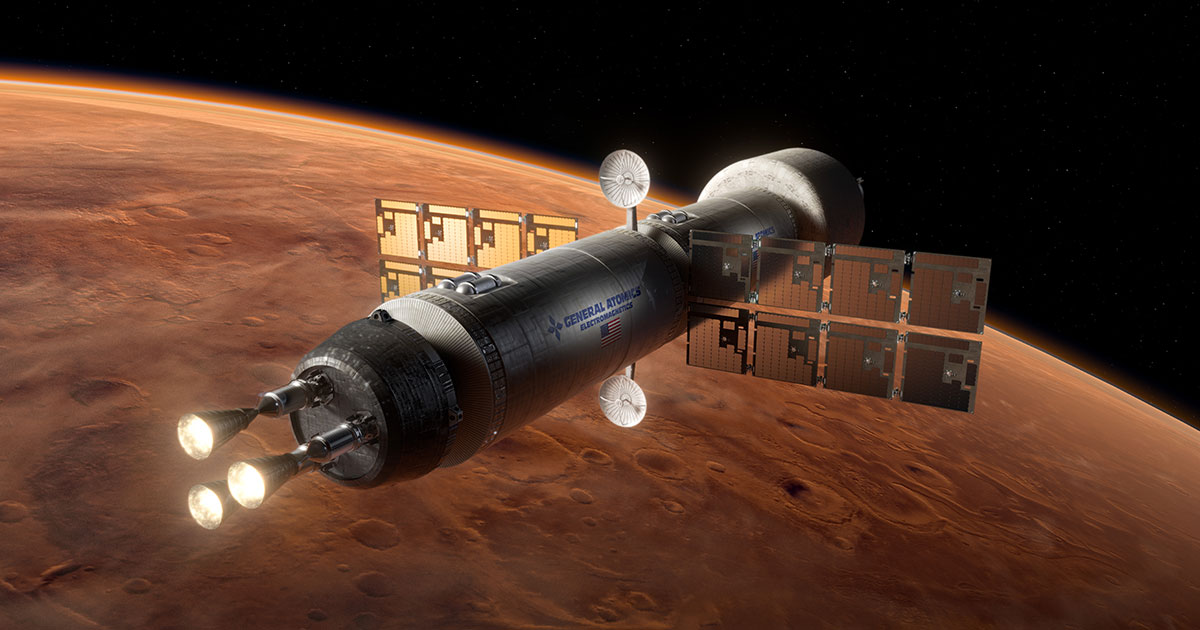

Efforts are underway to develop advanced propulsion systems that can reduce transit times to Mars and other locations in the Solar System. These include nuclear propulsion concepts, which NASA began researching again in 2016 for its proposed "Moon to Mars" mission architecture. In a recent paper, two aerospace innovators reviewed some key nuclear-electric propulsion concepts, their respective advantages, and challenges. In the end, they conclude that nuclear propulsion has the potential to revolutionize space exploration and make humanity "multiplanetary."
Continue reading
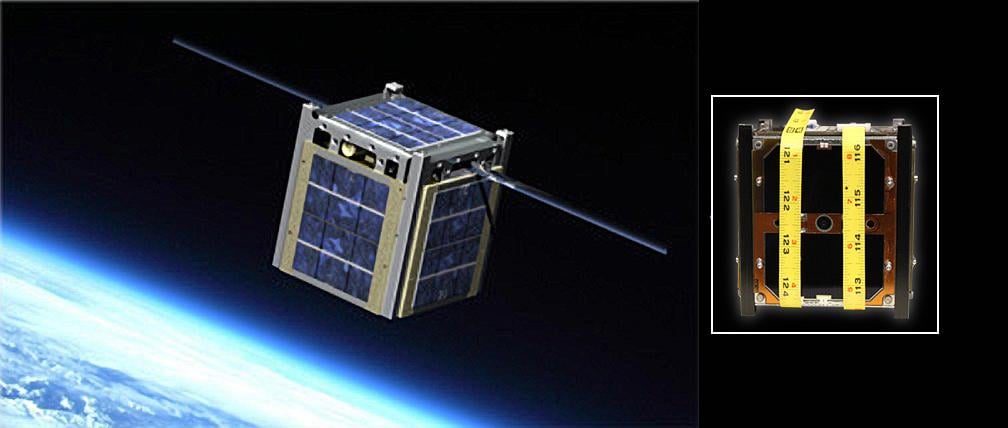

Deciding how to power a CubeSat is one of the greatest challenges when designing a modular spacecraft. Tradeoffs in solar panel size, battery size, and power consumption levels are all key considerations when selecting parts and mission architecture. To help with those design choices, a paper from researchers in Ethiopia and Korea describes a new machine-learning algorithm that helps CubeSat designers optimize their power consumption, ensuring these little satellites have a better chance of fulfilling their purpose.
Continue reading
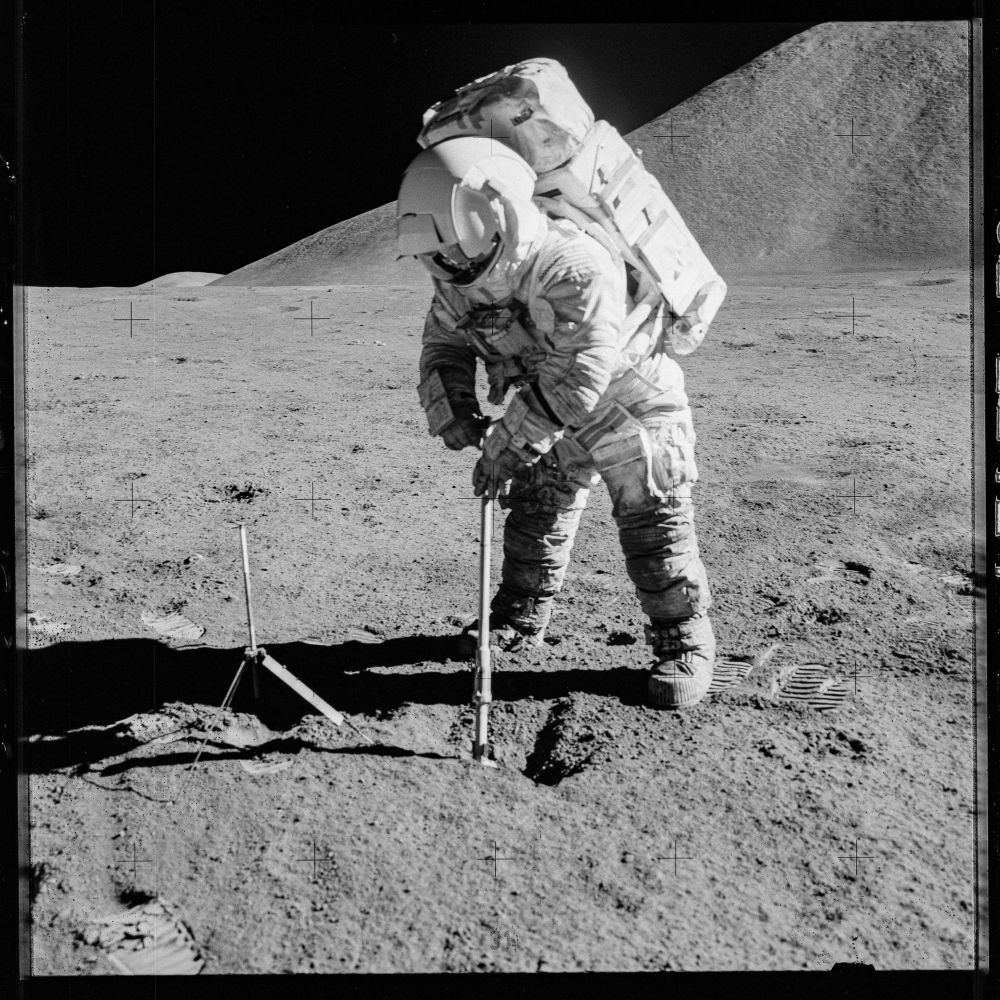

The hazards facing lunar astronauts are many. There's the radiation, the temperature extremes, the psychological challenges associated with isolation, and the risk of important equipment breaking down. But there's also the dust, which constitutes an ever-present background hazard.
Continue reading
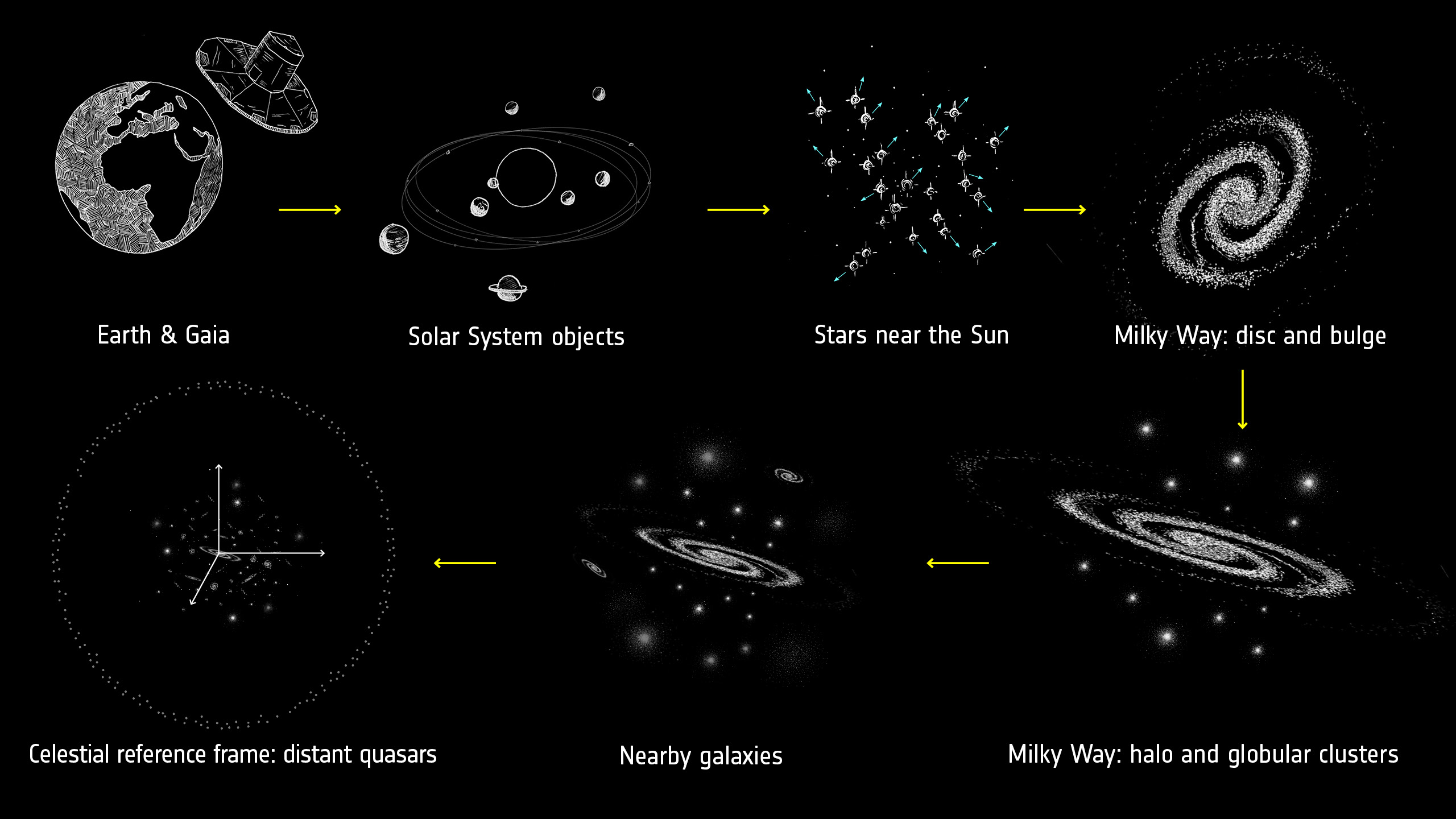
No matter where on Earth you stand, if you have a view of the night sky, and if it is dark enough, you can see the Milky Way. The Milky Way is our home, and its faint clouds of light and shadow have inspired human cultures across the globe. And yet, our view of the Milky Way is limited by our perspective. In many ways, we have learned more from other galaxies than from our own. But when the Gaia spacecraft launched in 2013, all of that changed.
Continue reading
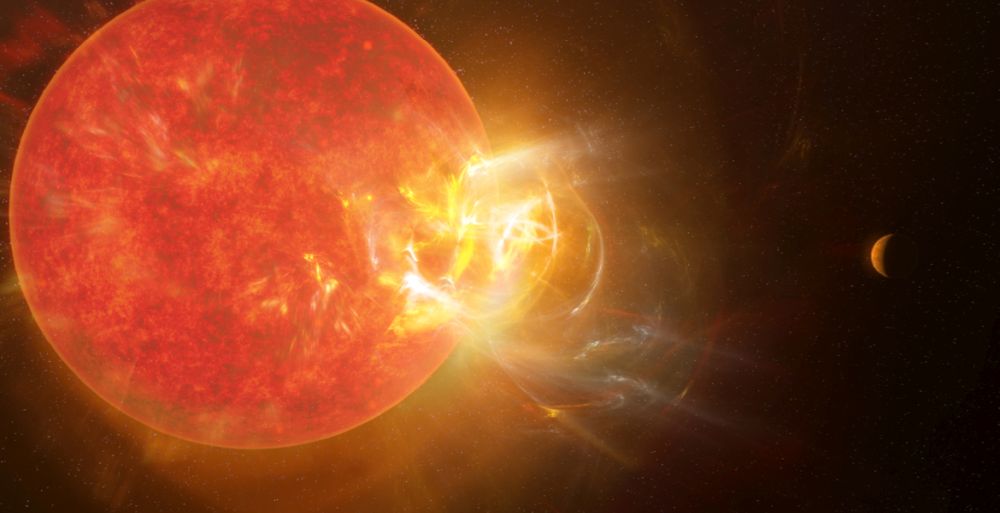

In this age of exoplanet discovery, the flaring of red dwarf stars (M-dwarfs) has taken on new importance. M-dwarfs are known to host many terrestrial planets in their putative habitable zones. The problem is the flaring could make their habitable zones uninhabitable.
Continue reading
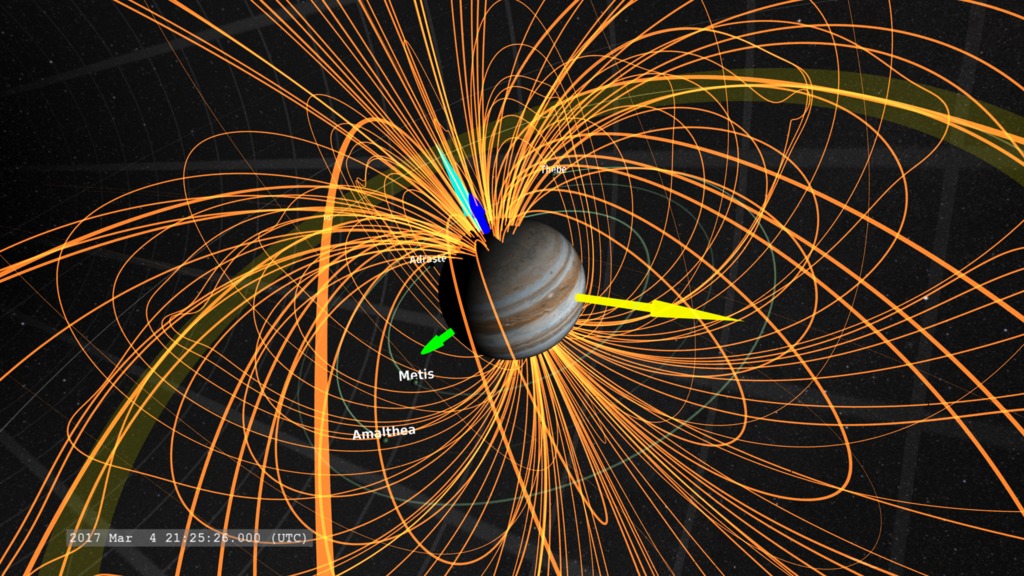
There are a number of ways that exoplanets have been discovered over recent years but a team of astronomers have been exploring other ways. One particular exciting method is to hunt for them by finding their magnetospheres! Earth and Jupiter are a great example of planets that are surrounded by strong magnetospheres that interact with solar activity and when they do, they release radio emissions. The team of researchers have been demonstrating just how they could detect Jupiter's radio emissions using simulated data. Not only would they be able to detect it, but they could also measure its rotation and even detect interactions with its moons!
Continue reading
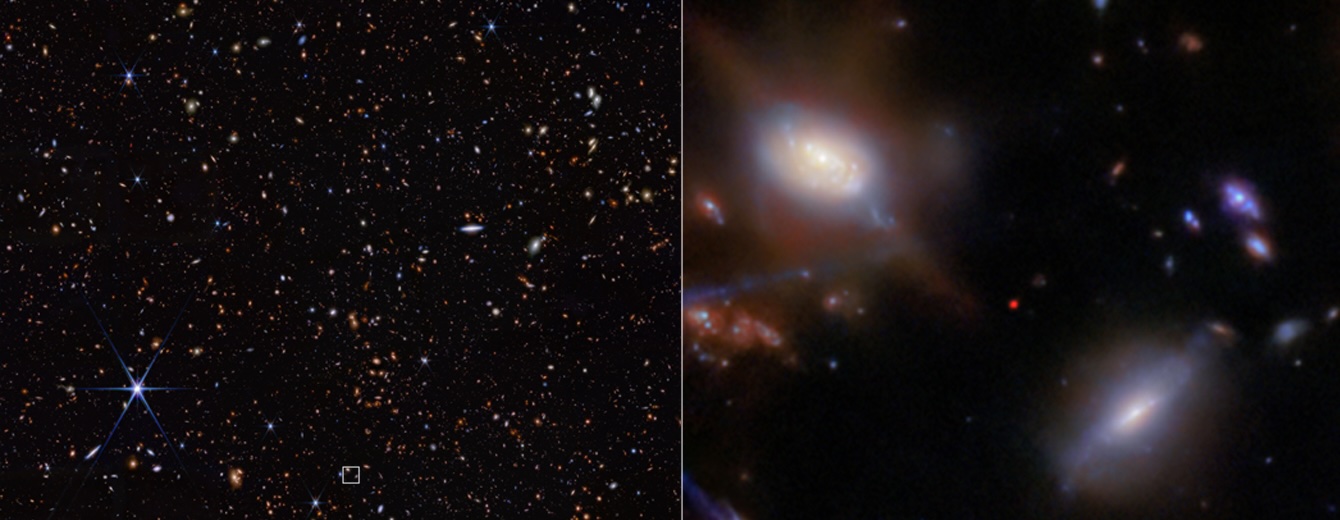

When the James Webb Space Telescope was launched in December 2021, one of its primary purposes was to see the first galaxies in the Universe forming just a few million years after the Big Bang. In true JWST style though, it has surpassed all expectations and now, a team of astronomers think they have gone even further back, seeing one galaxy clearing the early fog that obscured the Universe! The image represents a point in time 330 million years after the Big Bang and reveals a bright hydrogen emission from the fog surrounding a galaxy. It was somewhat unexpected though as current models predict it would have been blown away long ago!
Continue reading
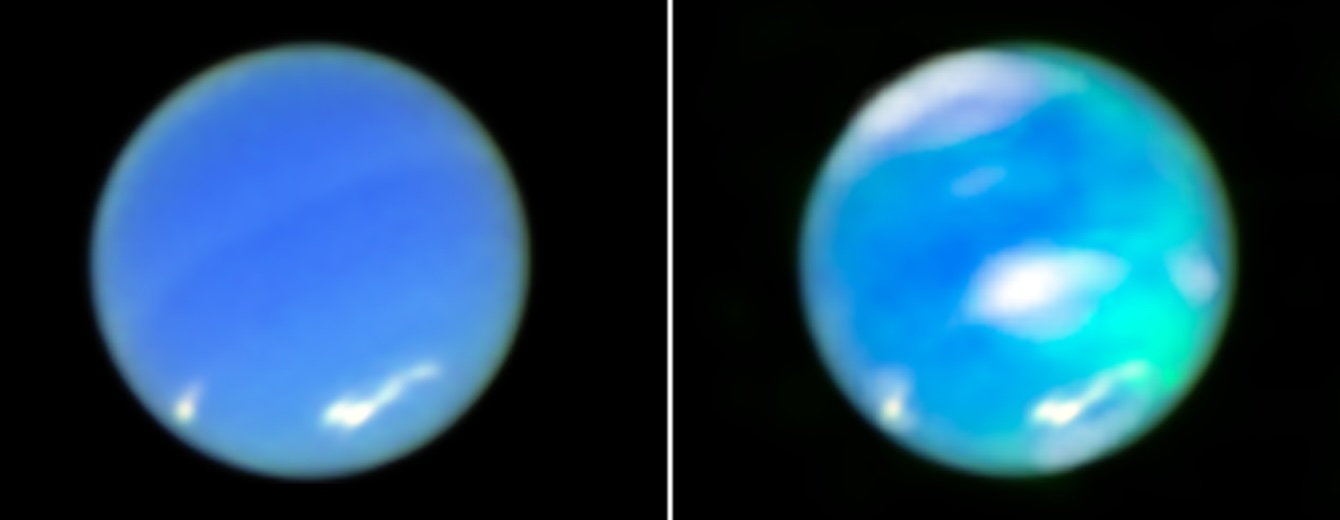
The outer planets remain somewhat of a mystery and Neptune is no exception. Voyager 2 has been the only probe that has visited the outermost planet but thankfully the James Webb Space Telescope is powerful enough to reveal it in all its glory. With its cameras regularly fixed on Neptune it has even picked up auroral activity in some of its latest images. The data was gathered back in 2023 using Webb's Near-Infrared spectrograph which detected the tell tale sign of auroral activity, an emission line of trihydrogen cation. The element appears on other giant planets too when aurora are present.
Continue reading
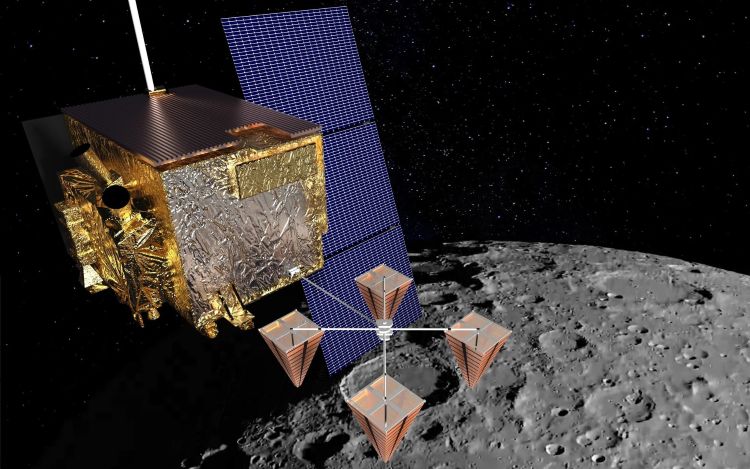

Can the cosmic rays bombarding the lunar surface be used to identify subsurface water ice deposits? This is what a recent study and iposter presented at the 56th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (LPSC) hopes to address as a team of researchers developed a novel method called the Cosmic Ray Lunar Sounder (CoRaLS) capable of detecting subsurface lunar water ice deposits that are elusive to current radar systems. This study has the potential to help expand the human presence on the Moon since water ice deposits are currently being focused on the permanently shadowed regions (PSRs) of the Moon for the upcoming Artemis missions.
Continue reading
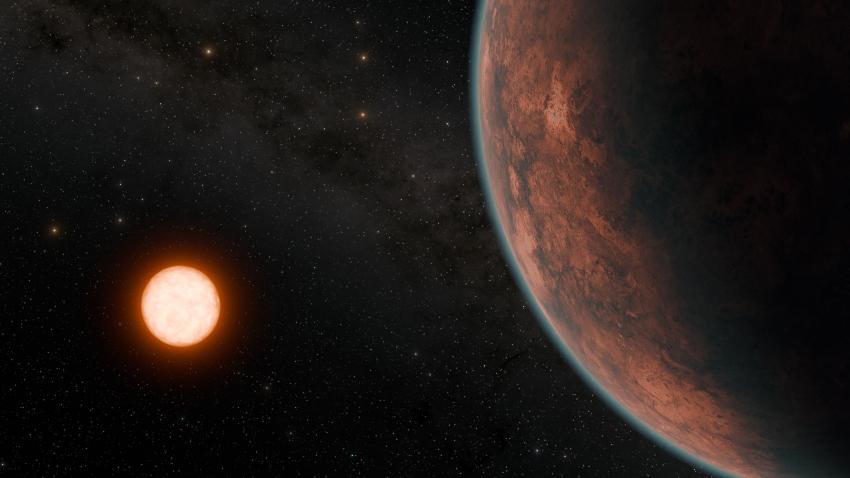

What can Venus-like exoplanets, also known as exoVenuses, teach us about our own solar system and potentially finding life beyond Earth, and how can the planned Habitable Worlds Observatory (HWO) provide these insights? This is what a recent study presented at the 56th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (LPSC) hopes to address as a team of scientists discussed the difficulties of studying exoVenuses and how HWO can help alleviate these challenges by directly imaging them. This study has the potential to help astronomers develop advanced methods for better identifying and understanding potentially life-harboring exoplanets throughout the cosmos.
Continue reading
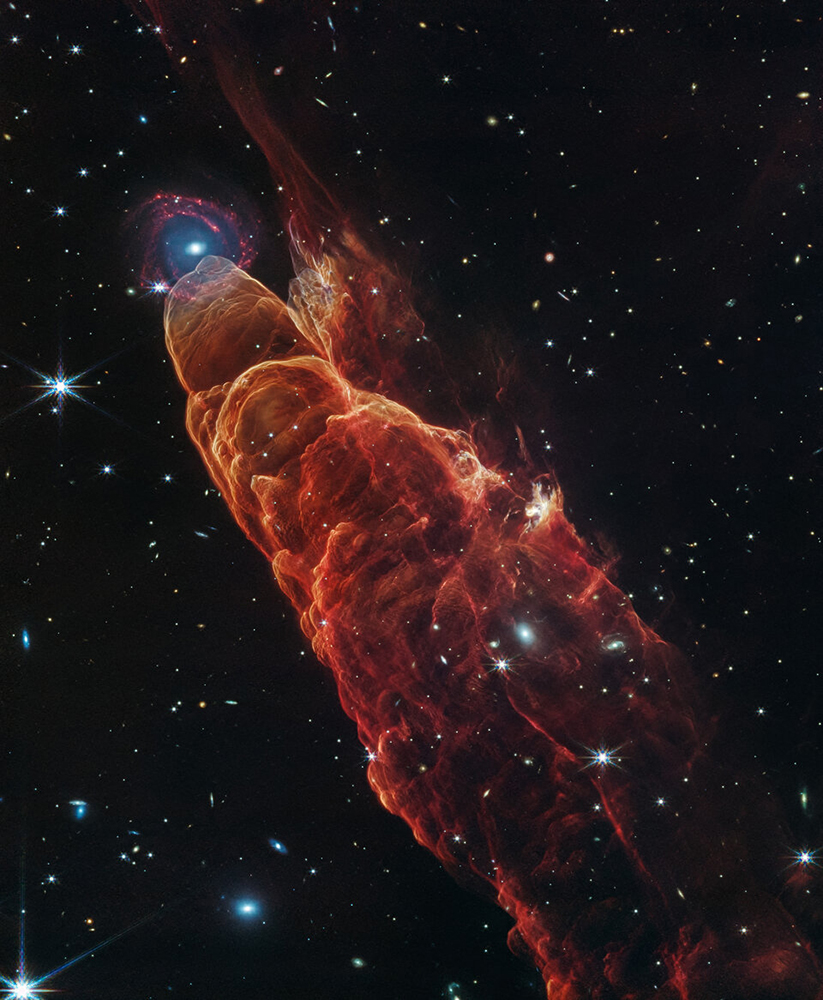

Way back in 2006, the Spitzer Space Telescope (SST) took an infrared look at a strange object called Herbig-Haro 49/50. It's a jet flowing away from a hot young star. The Spitzer image showed a fuzzy blob at the end of the jet. Was it part of the jet, or something more distant? Recently, the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) focused its infrared eye on the same object and sent home a fantastic snapshot of this cosmic tornado. It also answered the question about the blob: it turns out to be a distant galaxy, itself bursting with hot young stars.
Continue reading
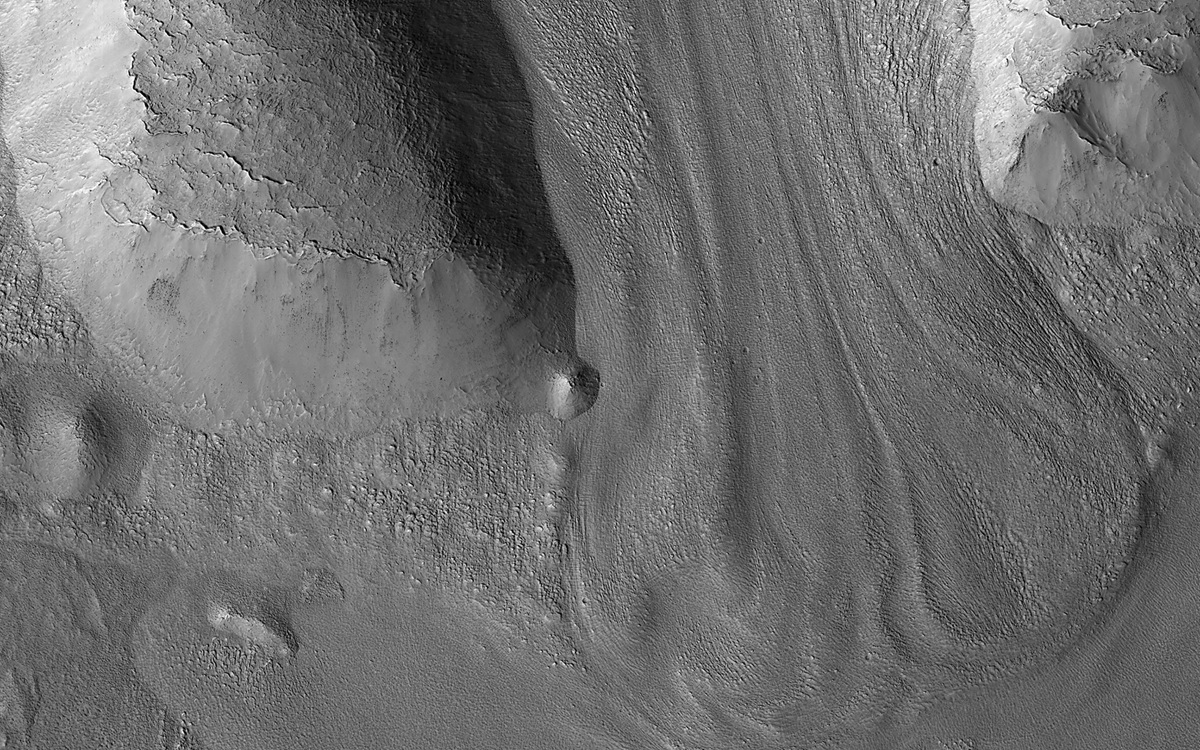

Mars is cold and dry, but long ago, it was warmer and wetter. Today, its geology is driven by wind and sand, but it was also shaped by water and maybe even glaciers. Glacial activity on Mars was long assumed to be dry, with glaciers frozen right to their beds, scouring the landscape of the Red Planet. But now, researchers think they've found evidence of subglacial melting, where a layer of water forms under the glacier, helping to form various features on Mars.
Continue reading
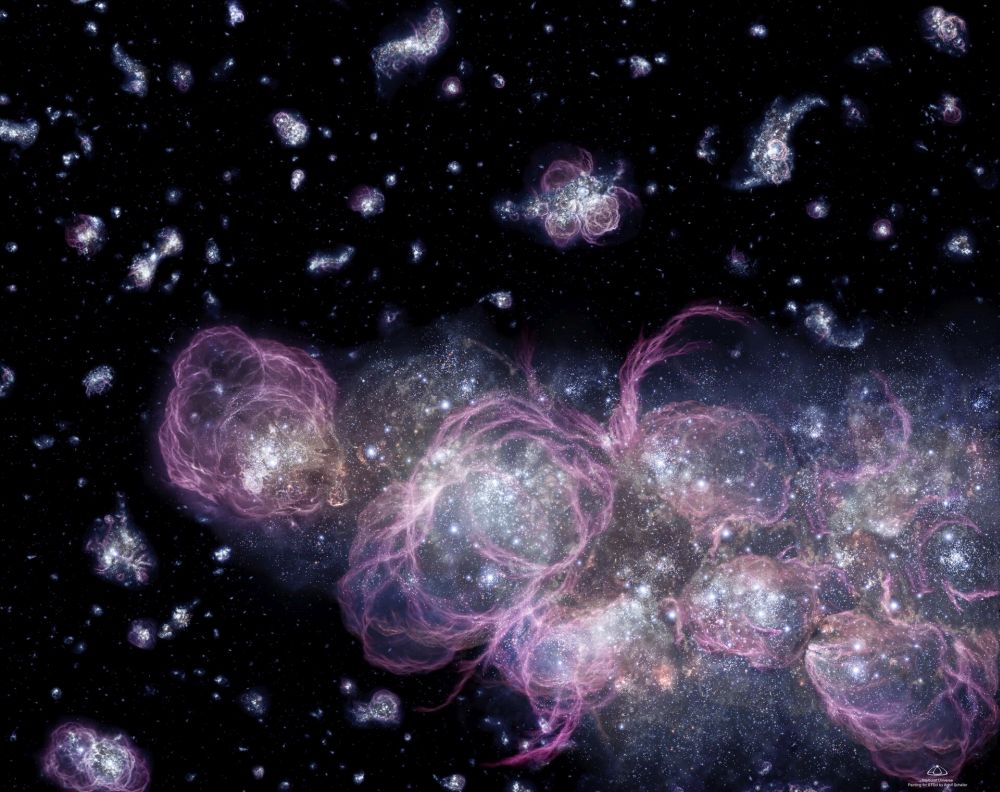

Dark matter is a confounding concept that teeters on the leading edges of cosmology and physics. We don't know what it is or how exactly it fits into the Standard Cosmological Model. We only know that its unseen mass is a critical part of the Universe.
Continue reading

The search for evidence of life on Mars just got a little more interesting with the discovery of large organic molecules in a rock sample. The Mars Curiosity Rover, which is digging in the Martian rock beds as it goes along, tested pieces of its haul and found interesting organic compounds inside them.
Continue reading
Suppose humanity was faced with an extinction-level event. Not just high odds, but certain-sure. A nearby supernova will explode and irradiate all life, a black hole will engulf the Earth, a Mars-sized interstellar asteroid with our name on it. A cataclysm that will end all life on Earth. We could accept our fate and face our ultimate extinction together. We could gather the archives from libraries across the world and launch them into space in the hopes that another civilization will find them. Or we could build a fleet of arks containing life from Earth. Not people, but bacteria, fungi and other simple organisms. Seed the Universe with our genetic heritage. Of all of these, the last option has the greatest chance of continuing our story. It's an idea known as directed panspermia, and we will soon have the ability to undertake it. But should we?
Continue reading

What drives us to send probes throughout the Solar System and rovers and landers to Mars? It's not cheap, and it's not easy. It's because we live inside a big, natural puzzle, and we want to understand it. That's one reason. But the main reason for space exploration is to search for life beyond Earth. That our planet could be the only planet to host life is a disquieting thought.
Continue reading
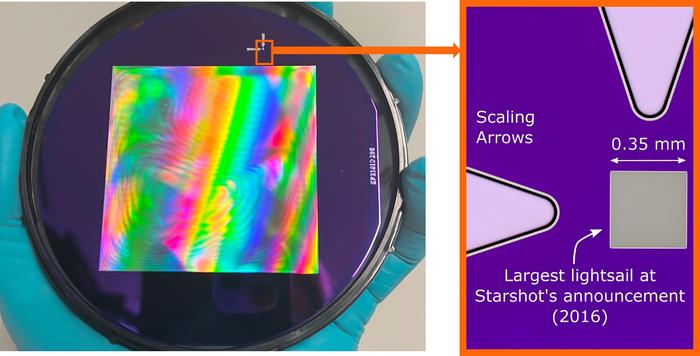
It's been almost 10 years since Breakthrough Starshot began funding research into interstellar missions. Back then, state of the art meant a tiny lightsail just 0.25mm across, skip forward to today and, following their funded research, a new prototype has been revealed measuring 60mm x 60mm and just 200 nanometres thick! We are not quite able to use it to hop to Proxima Centauri but the technology keeps advancing until that day arrives.
Continue reading
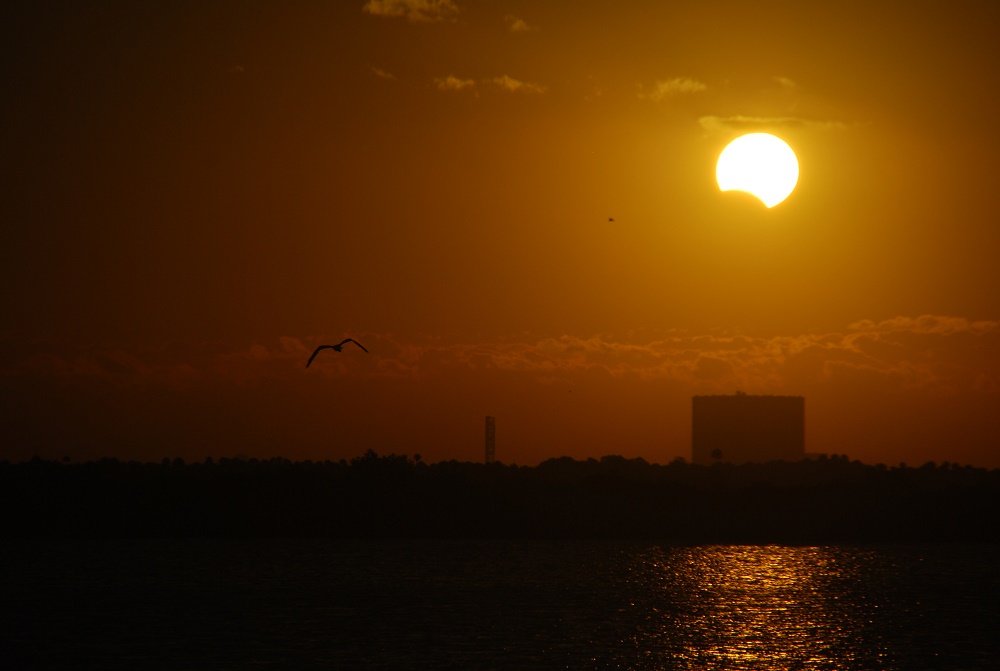

Got clear skies this weekend? If clouds cooperate, observers in the North Atlantic and surrounding regions may witness a rare spectacle: a partial solar eclipse. This is the second eclipse of 2025, and bookends the first eclipse season of the year. The season started with March 14th total lunar eclipse. Depending where you are observing from, this is a shallow to a deep partial, 'almost' total solar eclipse.
Continue reading
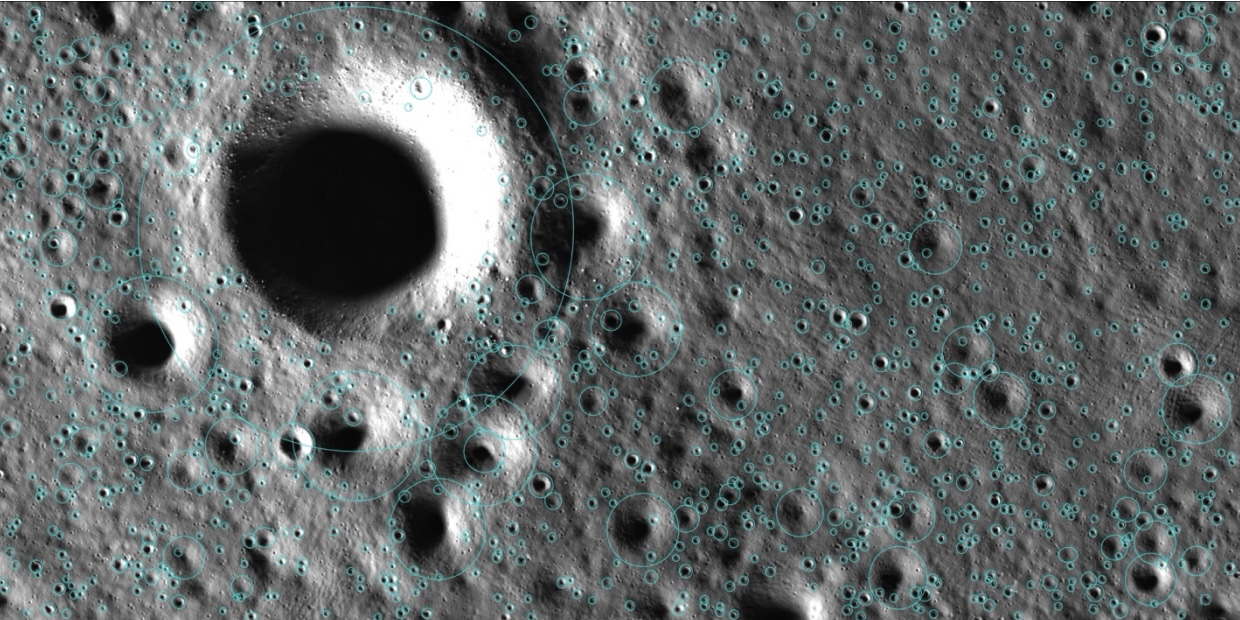

The focus is all on the Moon at the moment as we strive to establish a permanent lunar base. At the south polar region there are permanently shadowed craters protecting pockets of water ice. Korea's Pathfinder Lunar Orbiter (KPLO) has been capturing images of these craters using its ShadowCam instrument. Now, using that data, planetary scientists are using a machine learning algorithm to identify over a billion impact craters in the region, deep inside the shadowed craters and each is at least 16 metres in diameter.
Continue reading
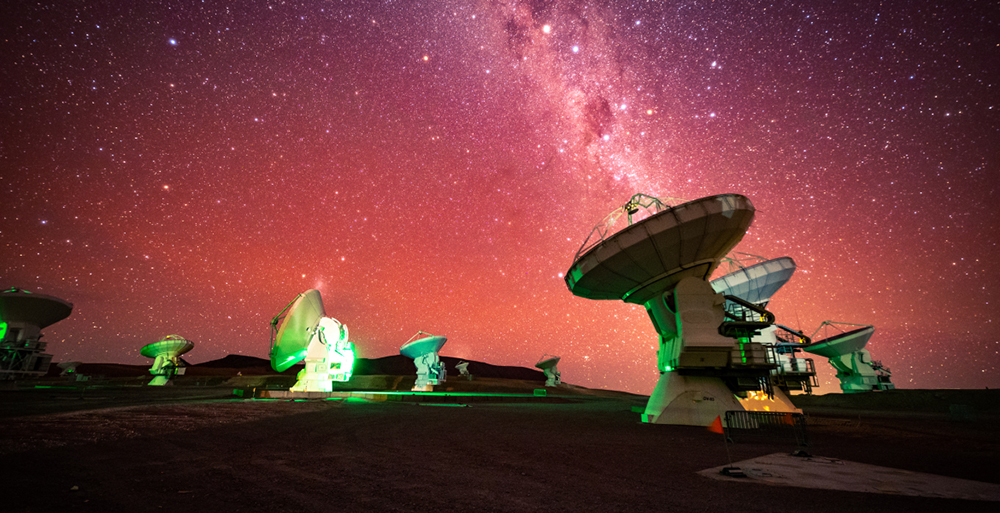

What happens when you mix clouds of gas and dust, strong outflows, and energetic shock waves at the core of the Milky Way Galaxy? Space tornadoes. At least, that's how researchers using the Atacama Large Millimeter Array in Chile to study the galaxy's heart described what they found.
Continue reading

 Universe Today
Universe Today


















