Carolyn Collins Petersen
Carolyn Collins Petersen is a long-time science writer and former astronomy researcher. She writes about astronomy and space exploration and has written 8 books, countless articles, more than 60 documentaries for planetarium star theaters, and exhibits for Griffith Observatory, NASA/JPL, the California Academy of Sciences, the Shanghai Astronomical Museum, and the Lowell Observatory Dark Sky Planetarium. She is CEO of Loch Ness Productions. You can email Carolyn here.
Recent Articles
-

-

Siwarha's Wake Gives it Away at Betelgeuse
January 13, 2026Betelgeuse is the star that everybody can't wait to see blow up, preferably sooner than later. That's because it's a red supergiant on the verge of becoming a supernova and there hasn't been one explode this close in recorded human history. It's been changing its brightness and showing strange surface behavior, which is why astronomers track its activity closely. Are these changes due to its aging process? Do they mean it's about to blow up? Probably not.
-
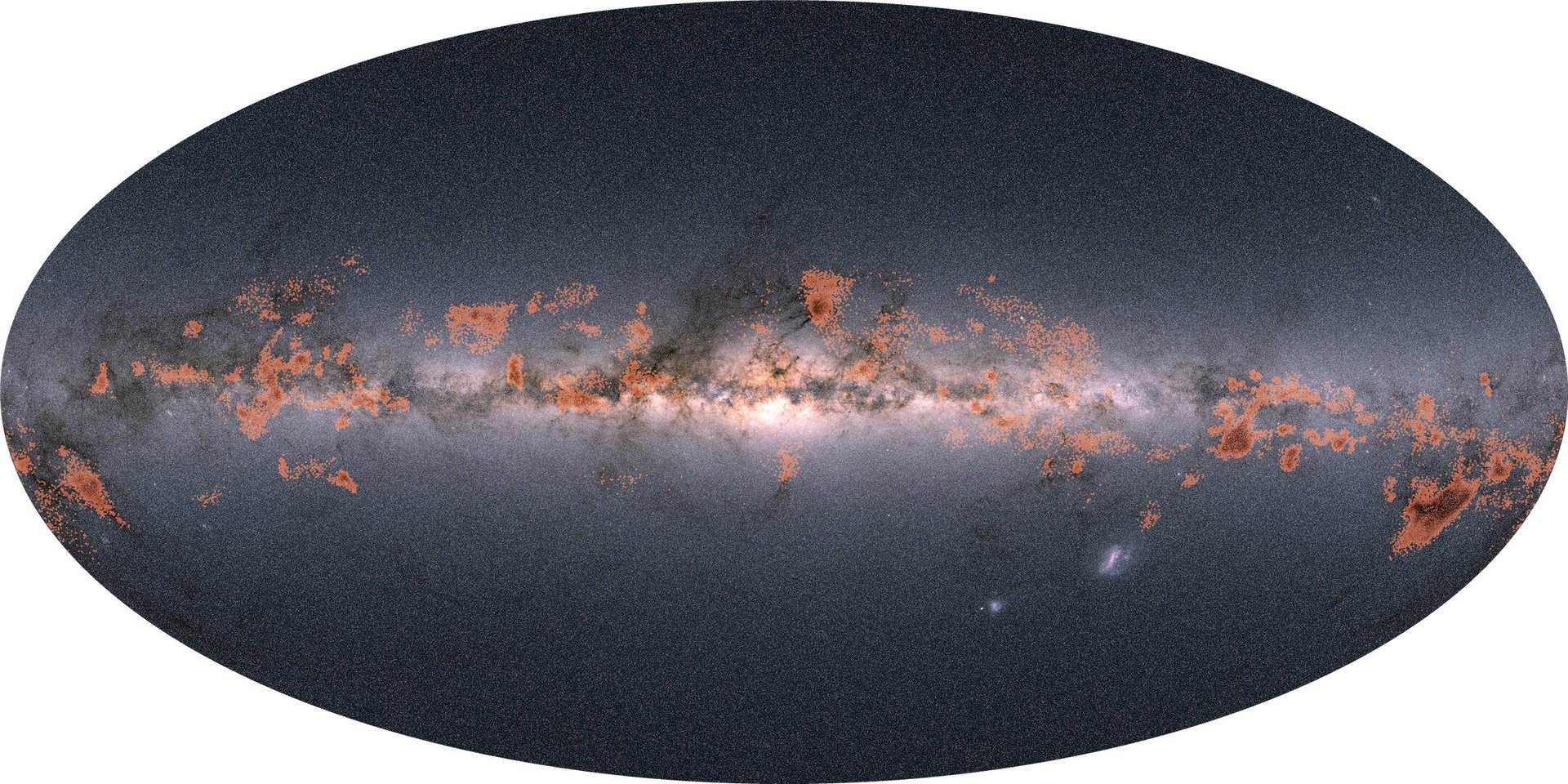

Clusters and Chains of Stars Reveal a Dynamic Milky Way
September 16, 2025Gaia Proves Our Skies Are Filled with Chains of Starry Gatherings Gaia Proves Our Skies Are Filled with Chains of Starry Gatherings https://www.esa.int/Science_Exploration/Space_Science/Gaia/Gaia_proves_our_skies_are_filled_with_chains_of_starry_gatherings
-
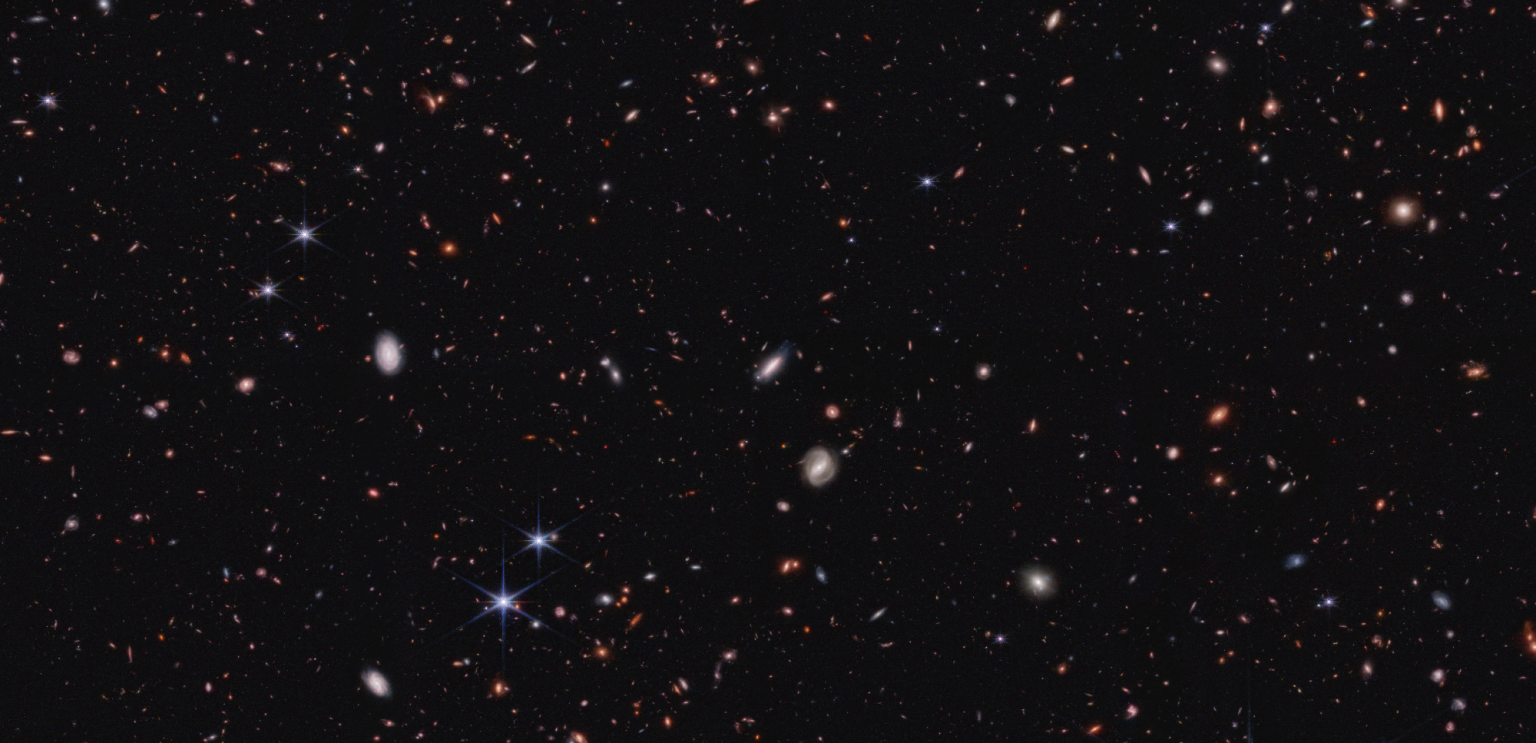

Mystery Objects in the Distant Universe Challenge Galaxy Formation Ideas
August 27, 2025The early Universe continues to spring surprises on astronomers. In a recent study of dim, distant objects, astronomers at the University of Missouri found at least 300 of them that look way too bright. That means they're forming stars much earlier than expected, or something else is going on. Whatever it is could affect our understanding of events in the infant cosmos.
-
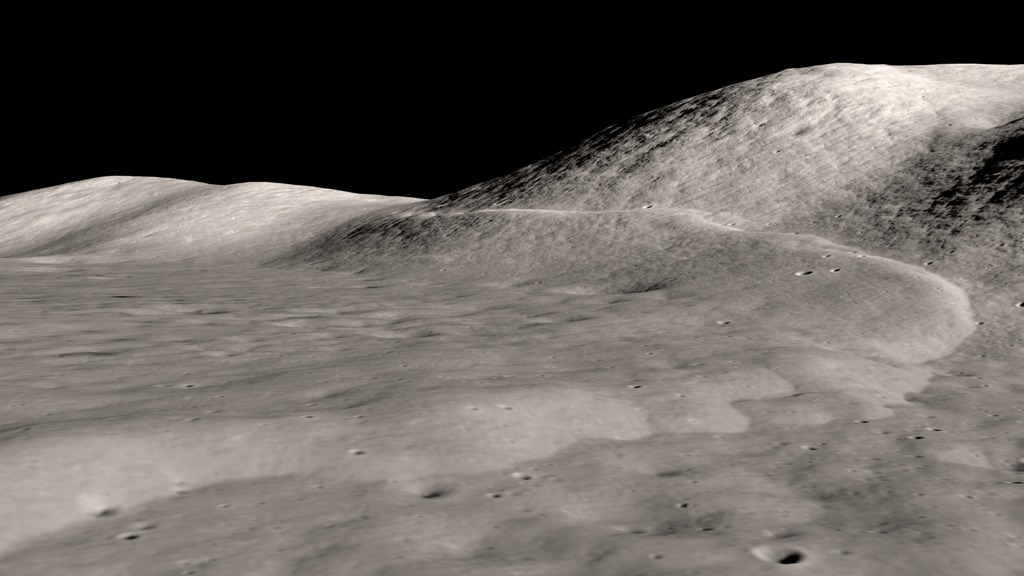
Moonquakes Will Pose Risks To Long-term Lunar Base Structures
August 14, 2025Our Moon is a seismically active world and its long history of quakes could affect the safety of permanent base structures there. That's one conclusion from a study of quakes along the Lee-Lincoln fault in the Taurus-Littrow valley where the Apollo 17 astronauts landed in 1972. “The global distribution of young thrust faults like the Lee-Lincoln fault, their potential to be still active and the potential to form new thrust faults from ongoing contraction should be considered when planning the location and assessing stability of permanent outposts on the Moon,” said Smithsonian senior scientist emeritus Thomas R. Watters, lead author of the paper.
-
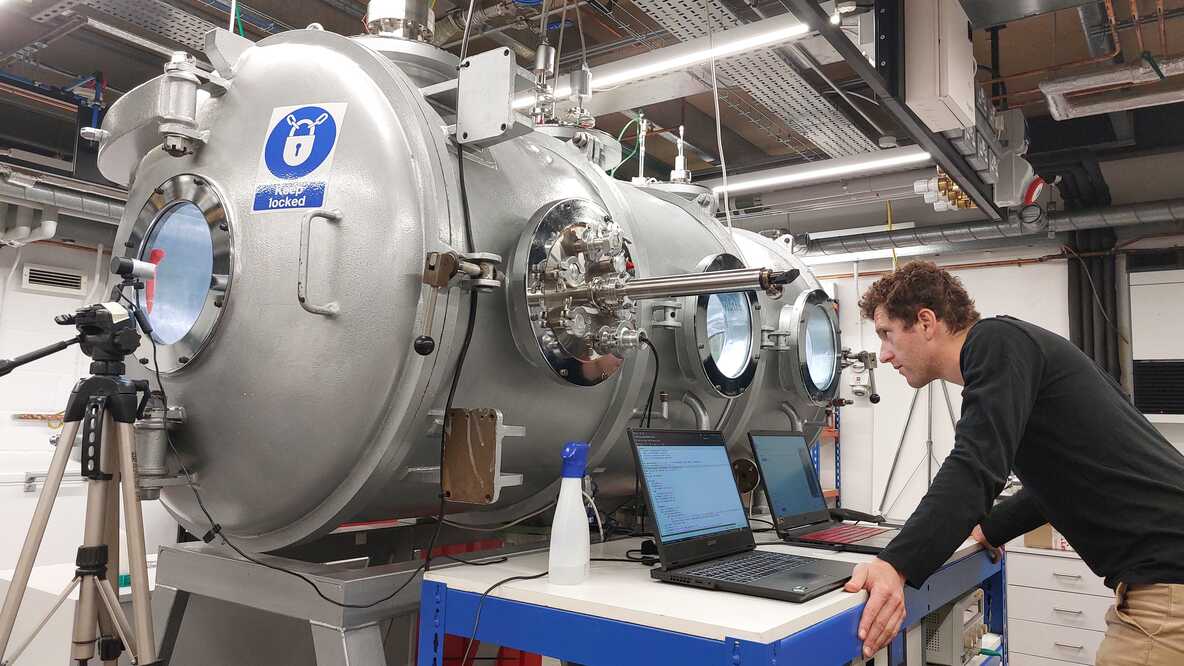

Simulating Ice Worlds in the Lab
August 04, 2025Many objects in the outer Solar System contain large amounts of water ice, leading to a thick icy shell surrounding an ocean of liquid water. This water behaves like lava on Earth, reshaping their surfaces through a process called cryovolcanism. To better understand this process, researchers have created a low-pressure chamber that simulates the near-vacuum conditions on the surfaces of worlds like Europa and Enceladus. They could watch water create features we see across the Solar System.
-
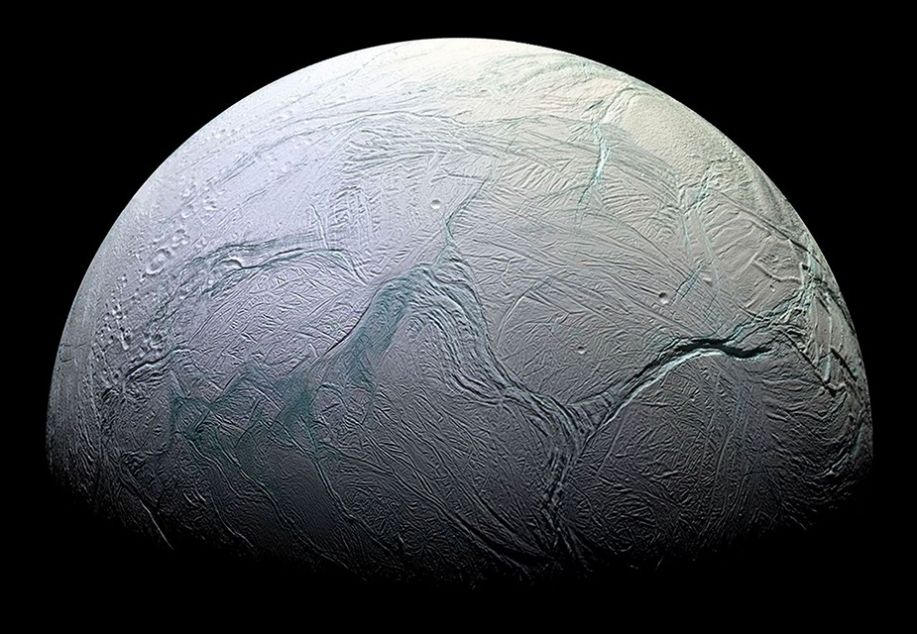

Cosmic Rays Could Support Life Just Under the Ice
July 31, 2025If you've ever dreamed of traveling through space as an explorer, you know there'll be some serious "downside dangers". One of them is cosmic rays. These high-speed particles slam through anything, including our bodies, damaging DNA and ripping molecules apart. As dangerous as they sound to unprotected spacefarers, they could actually help microscopic life survive hiding under the icy surfaces of places like Europa or Enceladus.
-
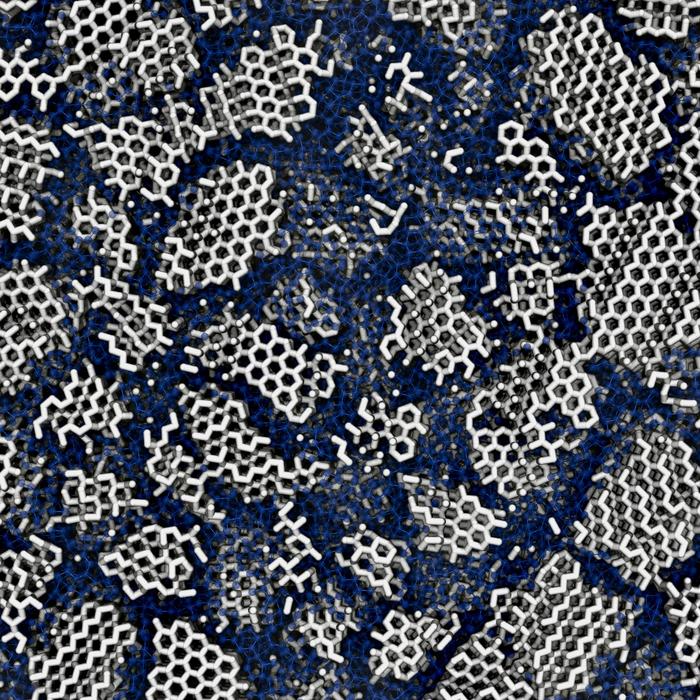
Ice in Space Isn't the Same as Ice on Earth
July 25, 2025Next time you're drinking a frosty iced beverage, think about the structure of the frozen chunks chilling it down. Here on Earth, we generally see it in many forms: cubes form, sleet, snow, icicles, slabs covering lakes and rivers, and glaciers. Water ice takes all these fascinating forms, thanks to its hexagonal crystal lattice. That makes it less dense than nonfrozen water, which allows it to float in a drink, in a lake, and on the ocean.
-

New Horizons Could Find Its Way to Proxima Centauri if it Wanted
July 21, 2025The New Horizons spacecraft is humanity's fastest-moving spacecraft and headed to interstellar space. Since its exploration of Pluto 10 years ago and subsequent flyby of Arrokoth in 2019, it's been traversing and studying the Kuiper Belt while looking for other flyby objects. That's not all it's been doing, however. New Horizons also has an extended program of making heliophysics observations. The mission science team has also planned astrophysical studies with the spacecraft's instruments. Those include measuring the intensity of the cosmic optical background and taking images of stars such as Proxima Centauri. As the spacecraft moves, the apparent positions of its stellar navigation targets have changed, but that hasn't bothered New Horizons one bit. It knows exactly where it is thanks to 3D observations of those nearby stars.
-
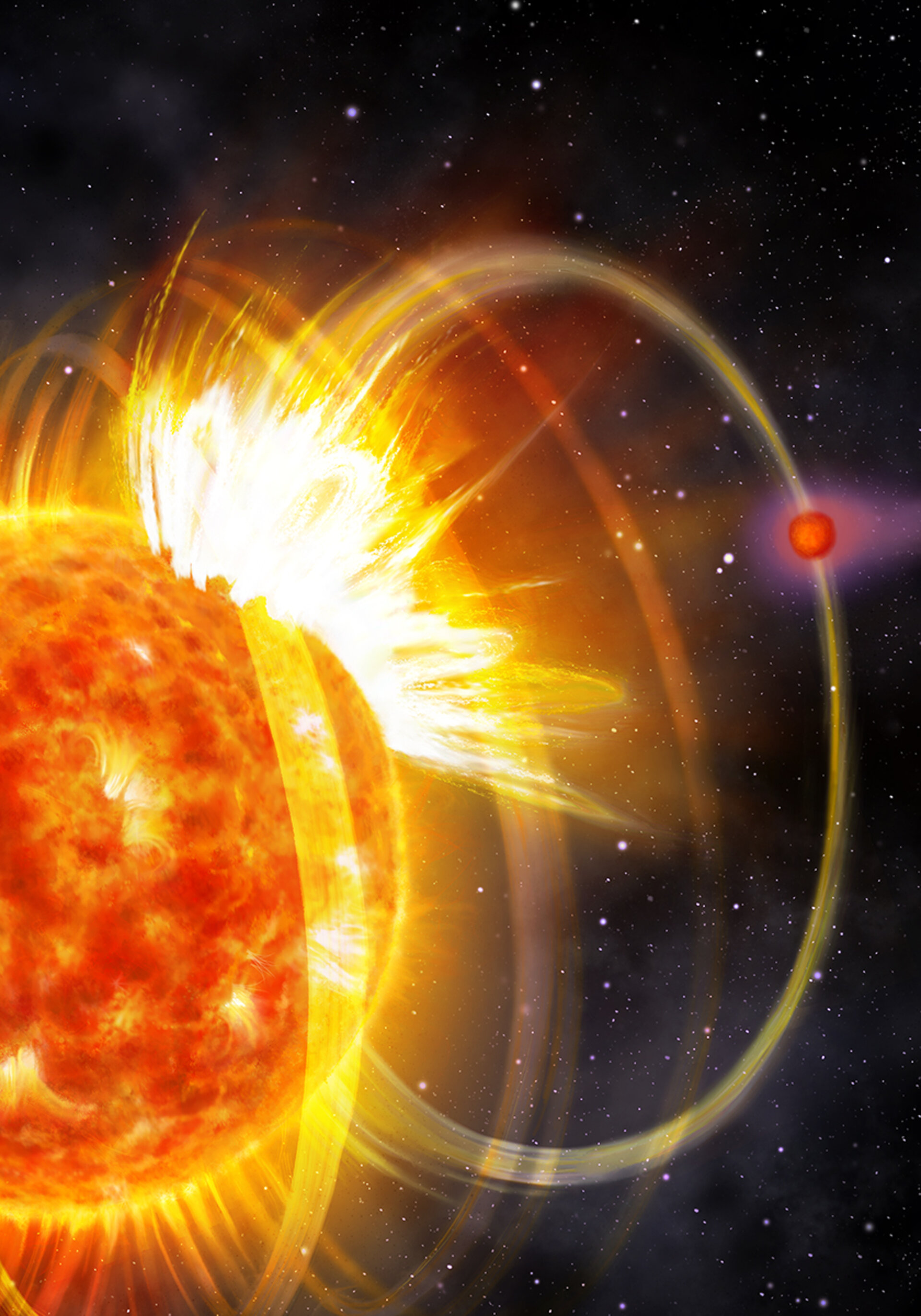
Planets Can Trigger Damaging Flares
July 08, 2025We all know what it's like when Earth is on the receiving end of a solar flare. Things get spicy in the upper atmosphere, and the outbursts have the potential to disrupt technology here at home. Catastrophic flares of radiation devastate planets around other stars, too. Now it looks like scientists have found that planets orbiting close to their stars can trigger the flares that threaten to harm them.
-

Webb Refines the Bullet Cluster's Mass
July 06, 2025One of the most iconic cosmic scenes in the Universe lies nearly 3.8 billion light-years away from us in the direction of the constellation Carina. This is where two massive clusters of galaxies have collided. The resulting combined galaxies and other material is now called the Bullet Cluster, after one of the two members that interacted over several billion years. It's one of the hottest-known galaxy clusters, thanks to clouds of gas that were heated by shockwaves during the event. Astronomers have observed this scene with several different telescopes in multiple wavelengths of light, including X-ray and infrared. Those observations and others show that the dark matter makes up the majority of the cluster's mass. Its gravitational effect distorts light from more distant objects and makes it an ideal gravitational lens.
-
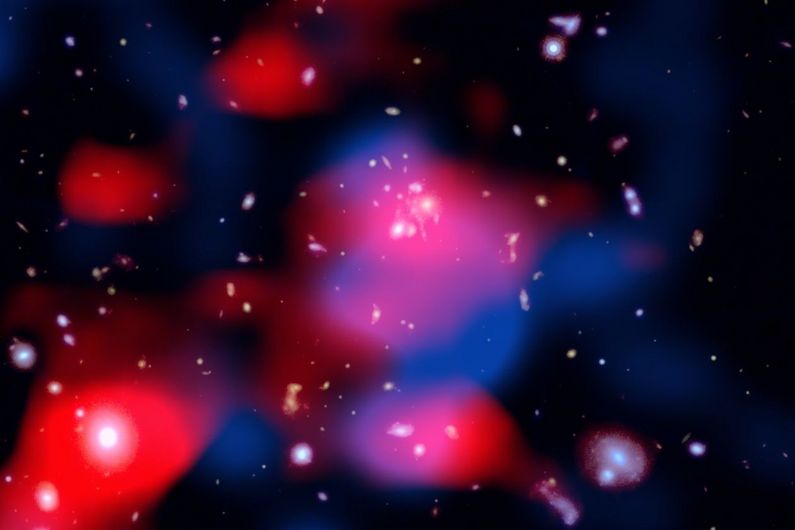

Galaxy Clusters Have Been Surrounded by High-Energy Particles for Almost Their Entire History
June 30, 2025If you could see the Universe through a radio-wave "eye", you'd detect mini-halos of relativistic particles creating radio emissions around some galaxy clusters. Astronomers long figured those halos are relative "recent" happenings in the nearby Universe and didn't occur in the early epochs of cosmic history. That's all changed now that the Low Frequency Array (LOFAR) radio observatory in Europe has revealed newborn galaxies in the early Universe already surrounded by a halo of particles. It's a rare look at what such clusters were like soon after they formed.
-
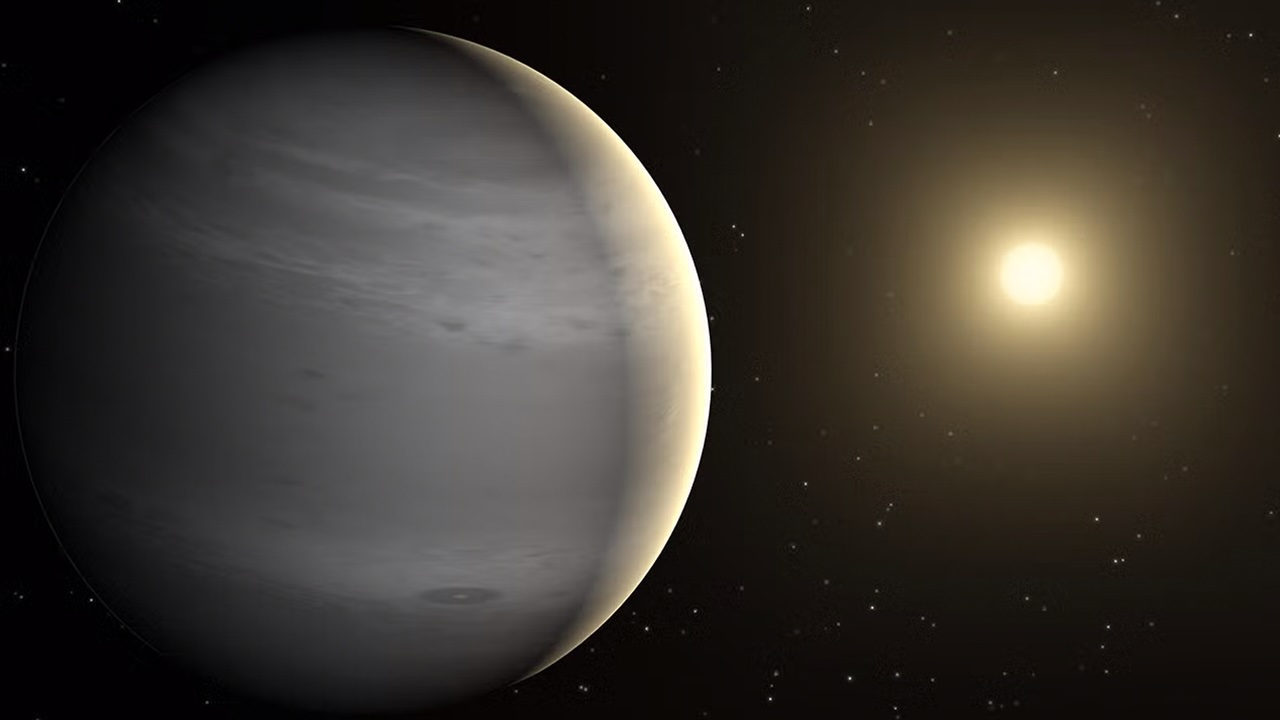

Worldwide Team of Citizen Scientists Help Confirm a Tricky Exoplanet
June 29, 2025Distant exoplanets can be dodgy to spot even in the best of observations. Despite the challenges, a team of astronomers just reported the discovery of a gas giant exoplanet that lies about 400 light-years from Earth. It's called TOI-4465 b and it takes 12 hours to transit across the face of its star during its 102-day orbit.
-

Astronomers Explore Different Physics on Simulated Clones of the Milky Way
June 27, 2025How do you search for a substance that doesn't give off any kind of light, but its gravitational influence shapes galaxies? That's the challenge researchers face as they try to find and explain the mysterious substance called dark matter. They're wrestling with an invisible "something" that appears to make up much of all matter in the Universe.
-
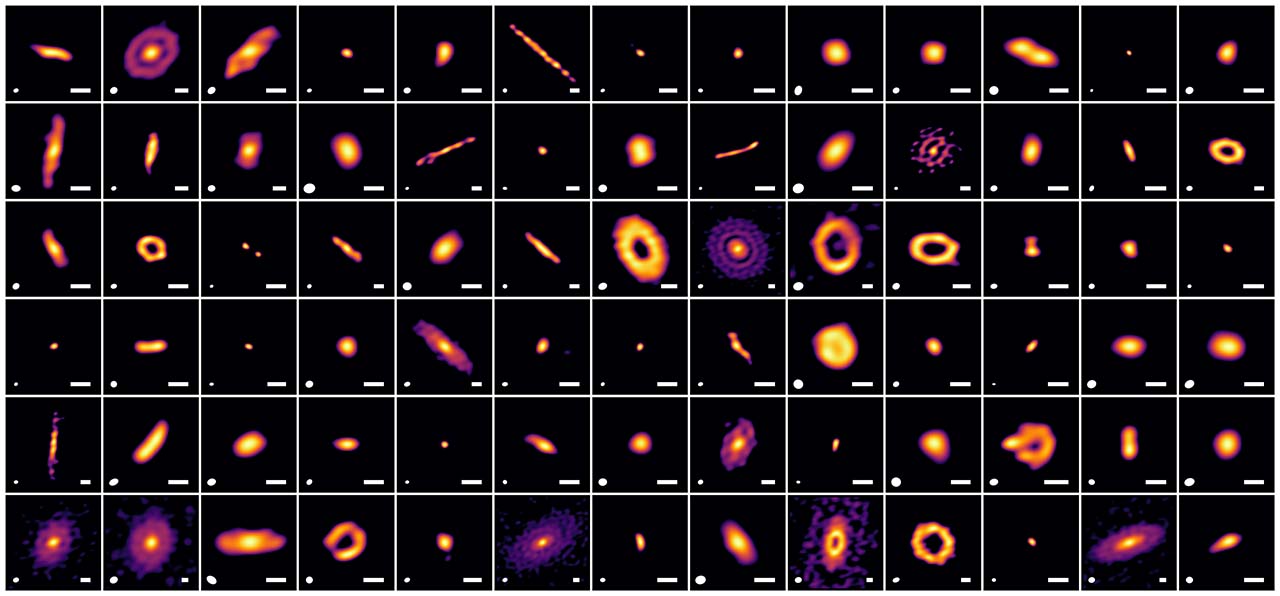

Planets Form Earlier Than Thought Around Baby Stars
June 27, 2025The Sun and its planets formed out of the solar nebula, around 4.6 billion years ago. But what was the delay between the Sun's formation and the planets? Astronomers have surveyed 78 protoplanetary disks in the Ophiuchus star-forming region and seen examples of every step in the planetary formation process. They found that the planets start forming much earlier than previously believed, when the disk is still filled with gas and dust, growing together with their host stars.
-
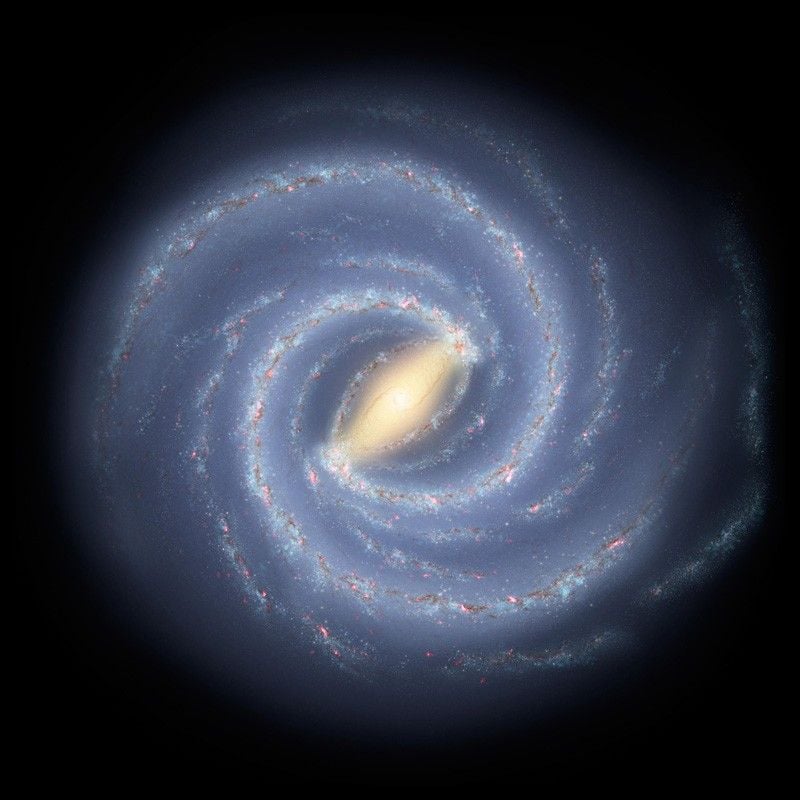

The Milky Way is More Clumpy than Astronomers Thought
June 24, 2025Astronomers have found a new way of accurately mapping the outer gas disk of the Milky Way using the positions of young stars. In the process, they've also discovered that our galaxy's structure is more complex than everyone thought, complete with tufty-looking "flocculent" gas clouds.
-
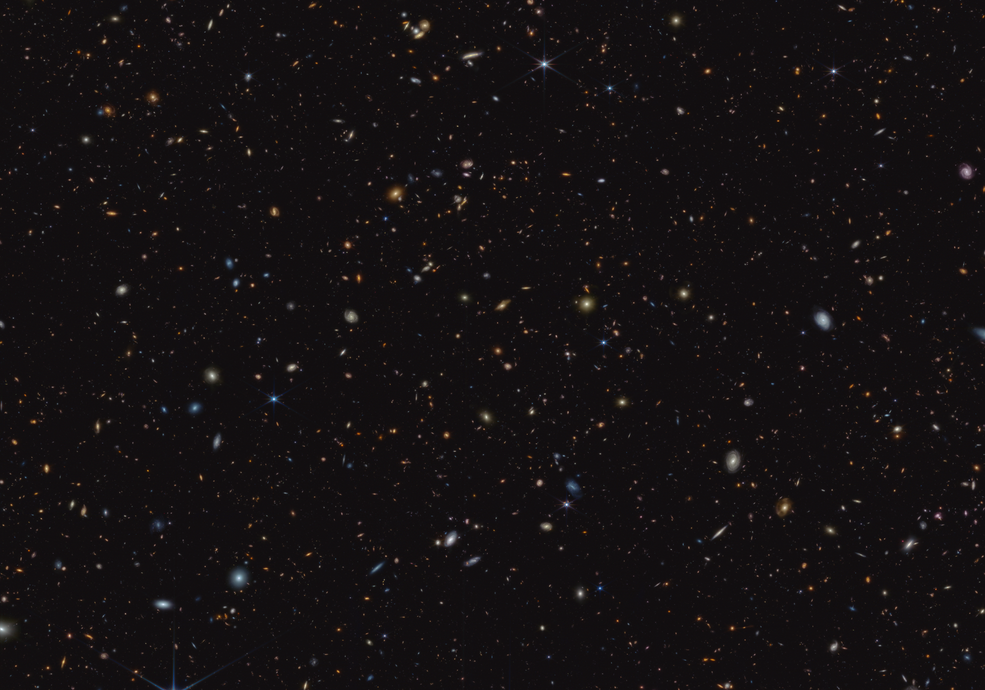

Superdense Star Factories Tell a Tale of Starbirth in the Early Universe
June 20, 2025The early Universe was a busy place some 13 billion years ago. That's when countless young galaxies began to evolve and birthed stars at a prodigious rate. The hearts of those very distant galaxies show turbulent, lumpy disks studded with even thicker clumps of dust and gas that spawned huge batches of stars. Astronomers want to understand what's driving the clumping, so they've turned to recent surveys of closer galaxies in the "local Universe" that contain similar lumpy regions.
-
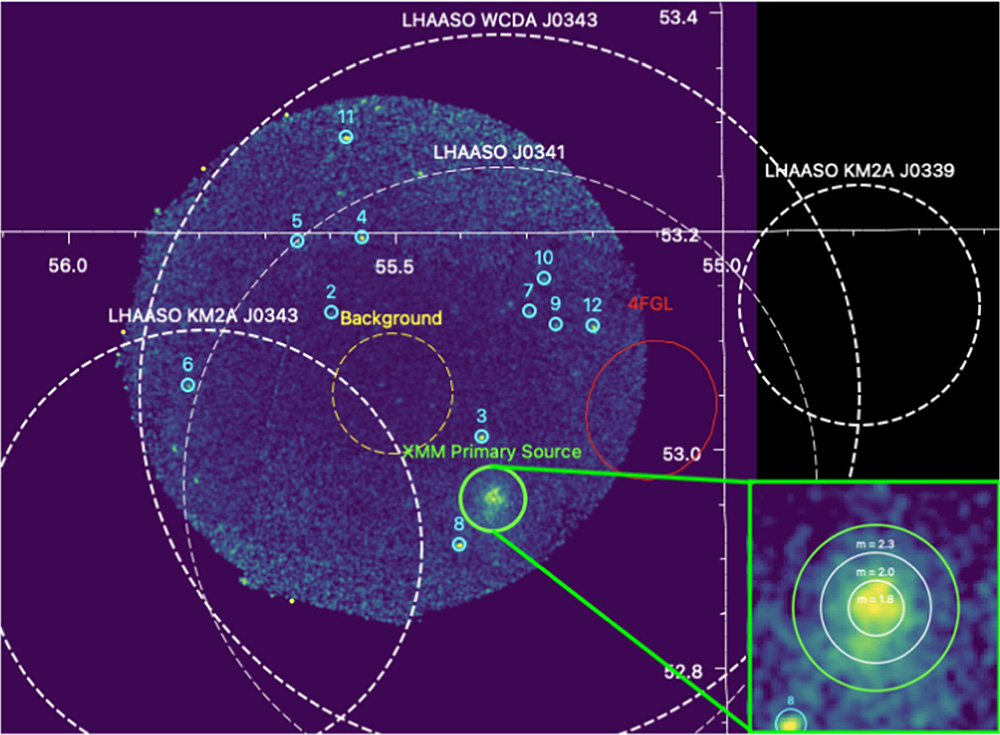
Astronomers are Closing in on the Source of Galactic Cosmic Rays
June 17, 2025In 1912, astronomer Victor Hess discovered strange, high-energy particles called "cosmic rays." Since then, researchers have hunted for their birthplaces. Today, we know about some of the cosmic ray "launch pads", ranging from the Sun and supernova explosions to black holes and distant active galactic nuclei. What astronomers are now searching are sources of cosmic rays within the Milky Way Galaxy. One such source is a pulsar wind nebula sending high-energy particles out to space.
-
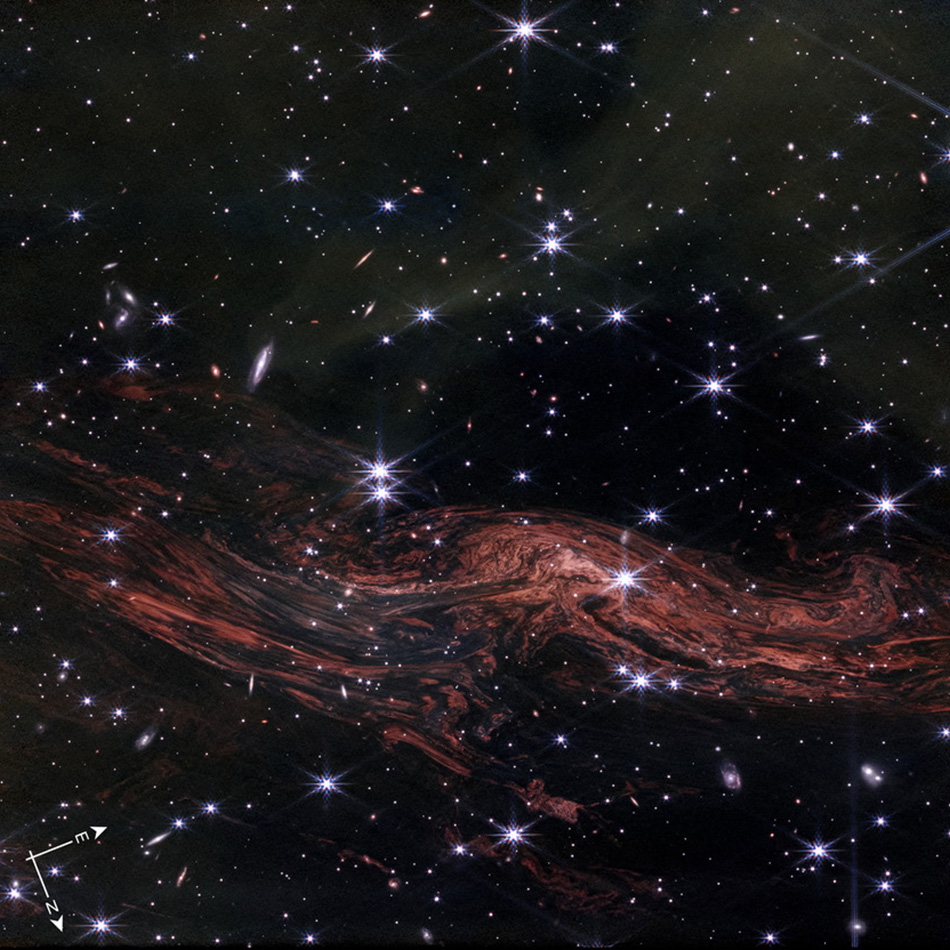

Distant Galaxy Has Similar Icy Dust to the Milky Way. So, Similar Planets?
June 12, 2025For most of us, dust is just something we have to clean up. For astronomers, interstellar dust is a hindrance when they want to study distant objects. However, recent James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) observations of a distant galaxy are changing that. This infrared-sensitive observatory is letting them find a way to use dust to understand the evolution of early galaxies. In addition, it uncovered a special property of that galaxy's ice-covered dust, indicating it could be similar to the materials that formed our Solar System.
-
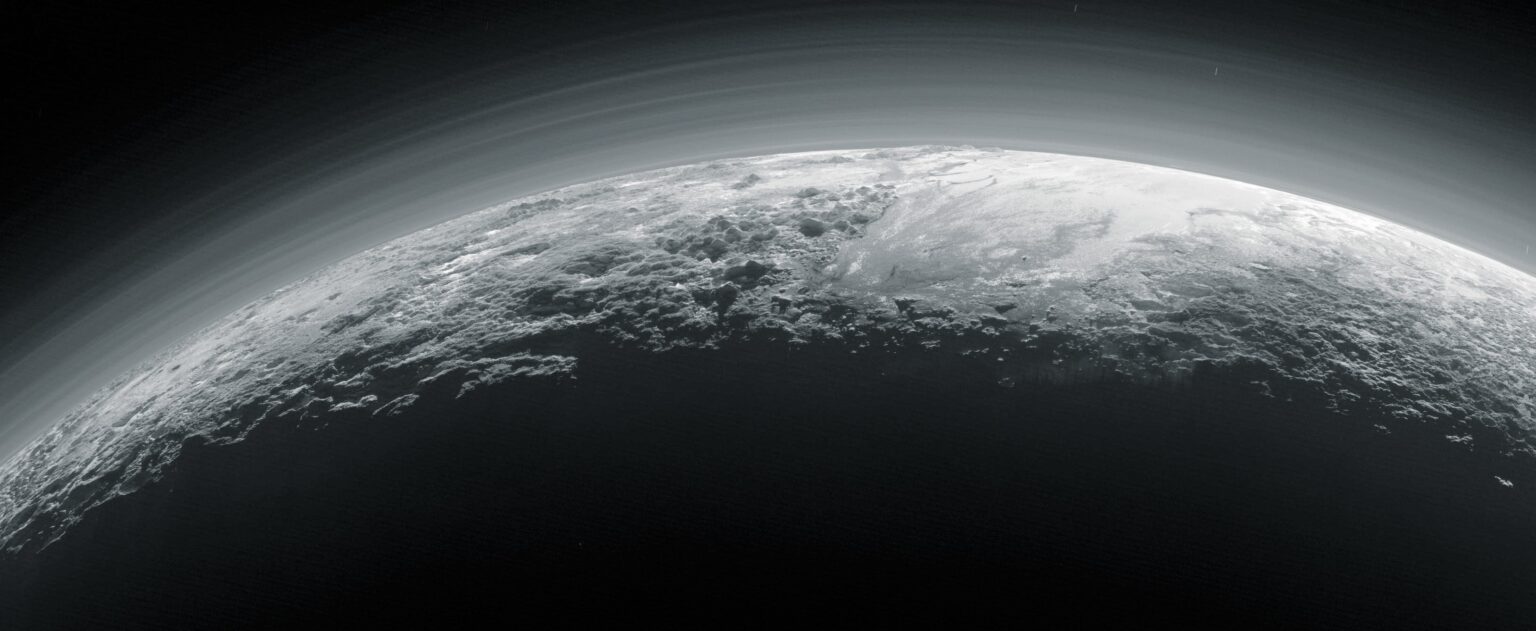
Webb Watches Haze Rise and Fall in Pluto's Atmosphere
June 04, 2025When the New Horizons spacecraft swept past Pluto and Charon in 2015, it revealed two amazingly complex worlds and an active atmosphere on Pluto. Those snapshots redefined our understanding of the system. Now, new observations using the James Webb Space Telescope taken over the space of a week, show that Pluto's atmosphere is completely different from any other one in the Solar System.
 Universe Today
Universe Today