
Continue reading

Continue reading
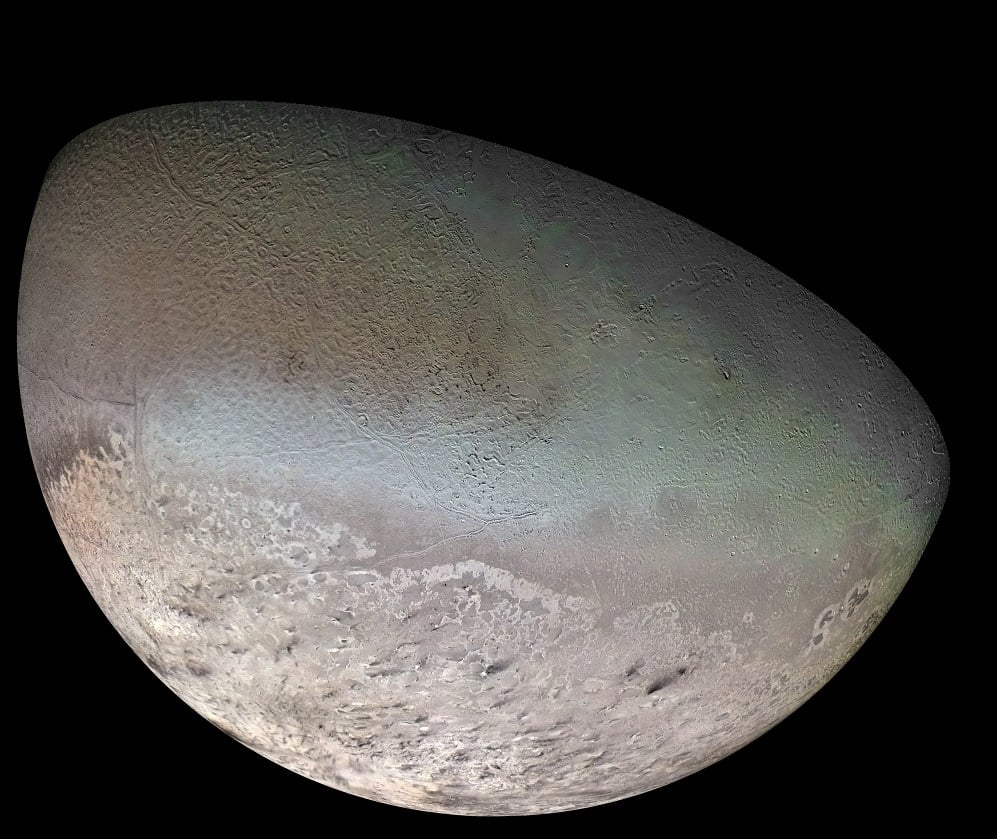
Continue reading
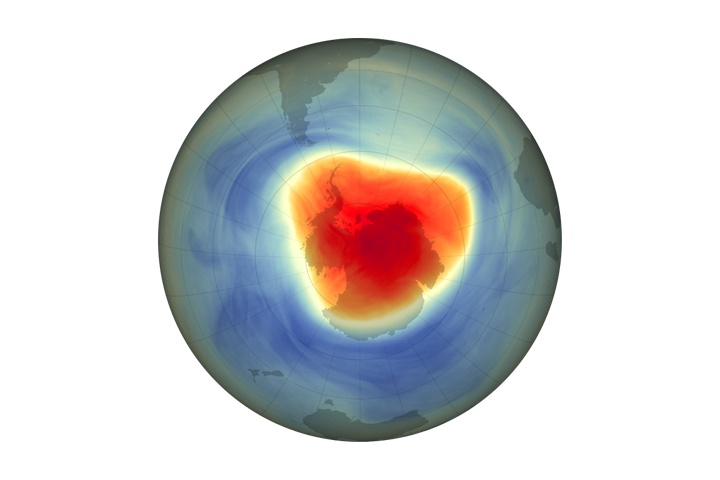
Continue reading
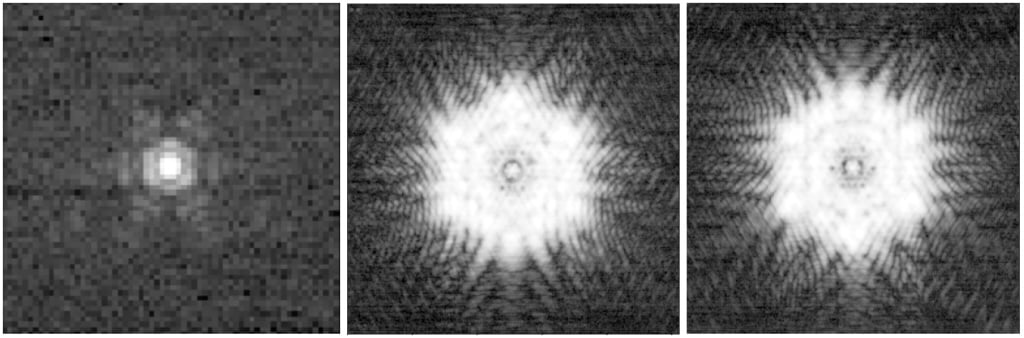
JWST's primary mirror consists of 18 individual segments, each of which can be moved on 6 different axes of freedom. This allows the telescope to maintain perfect focus, despite changing temperatures and micrometeorite strikes on its optics. The objective was 150 nanometers of wavefront error, but the current error is down to just 65 nanometers. In early October, engineers measured the telescope's jitter and refocused it again, bringing it to its perfect alignment
Continue reading

Continue reading
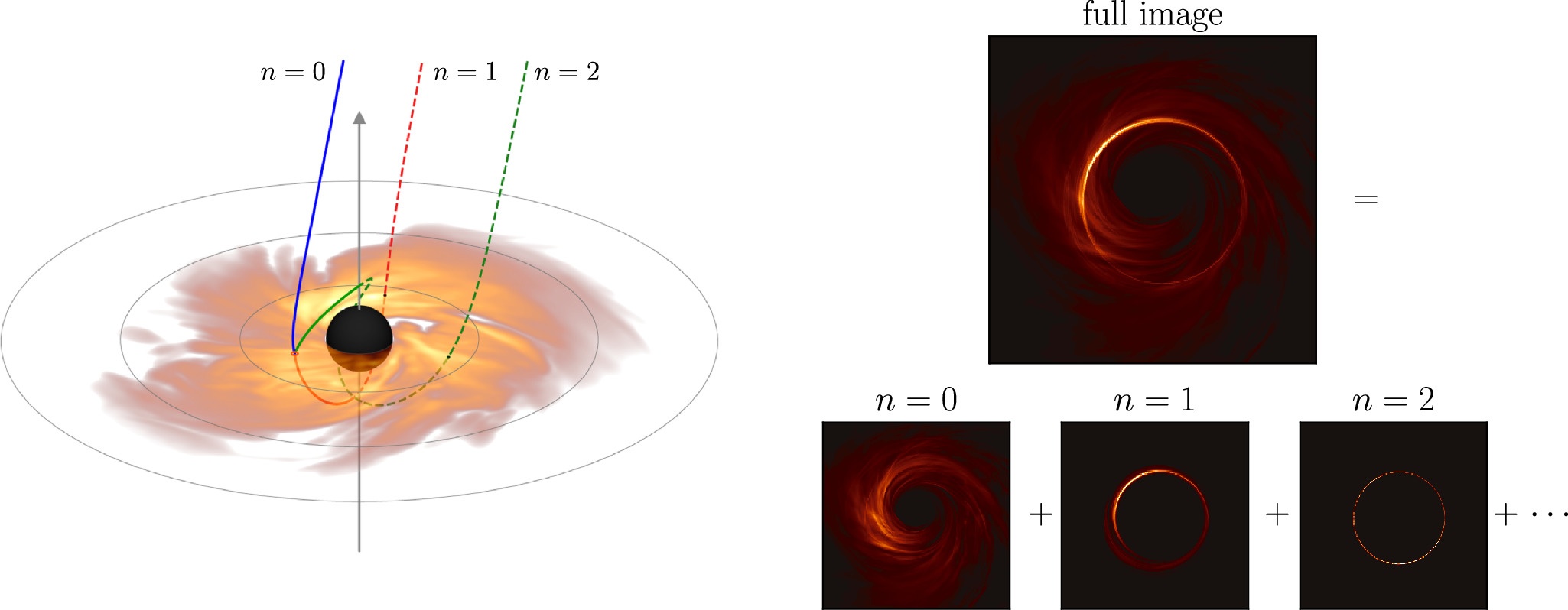
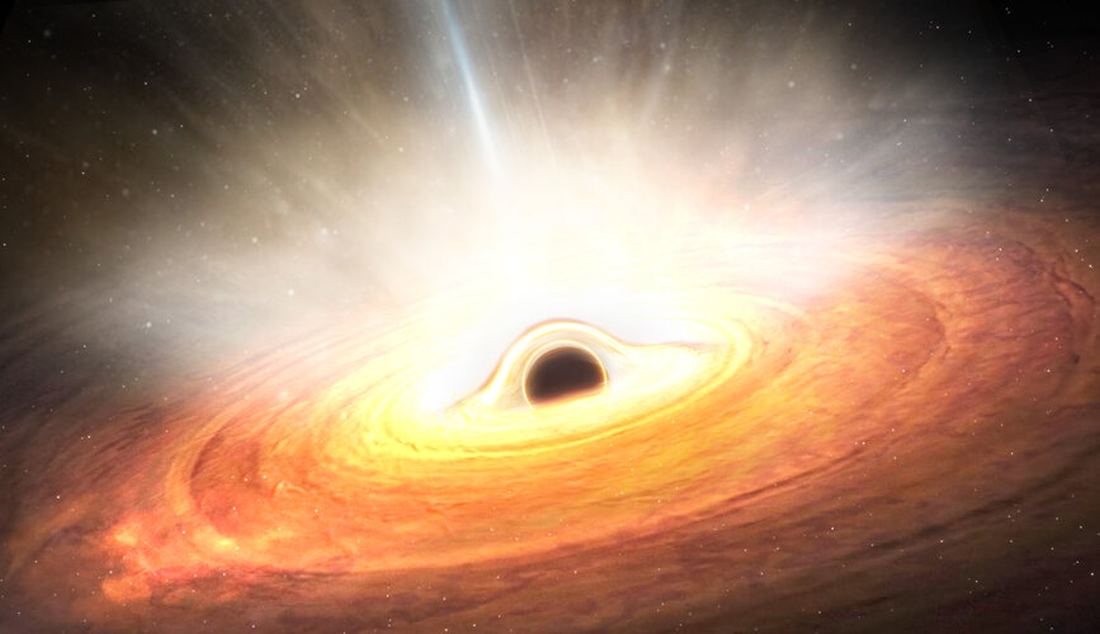
The speed of light gives astronomers a special trick when examining the tangled-up gravitational well around a black hole. Researchers have proposed that they can measure the spin of a black hole because of the bizarre path that photons take in their vicinity, released by accreting matter. Some photons blast straight out, while others are lensed indirectly, and some travel around the black hole twice before escaping, hinting at the black hole's rotation rate.
Continue reading
Continue reading
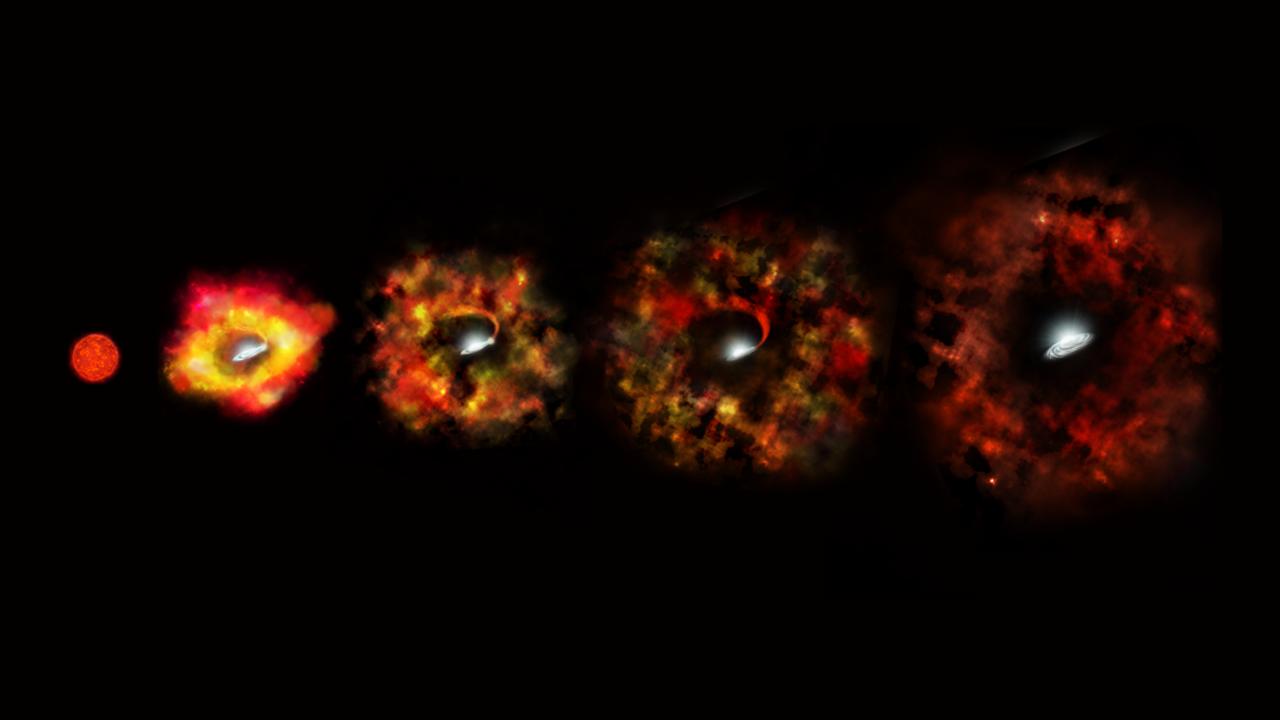
Continue reading

Continue reading
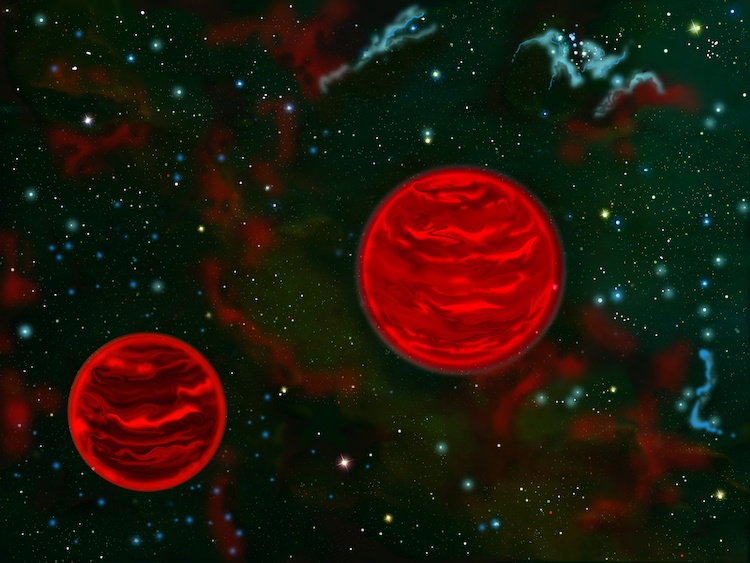

WST recently turned up hundreds of free-floating rogue planets in the Orion Nebula, 42 in binary configurations. How two Jupiter-mass objects could end up orbiting one another has puzzled astronomers, but now a team of researchers thinks they know it happens. Large, hot stars in the Orion Nebula blasted the outer layers of smaller stars, eroding them away and preventing them from gaining enough mass to ignite fusion in their cores - even binary stars.
Continue reading
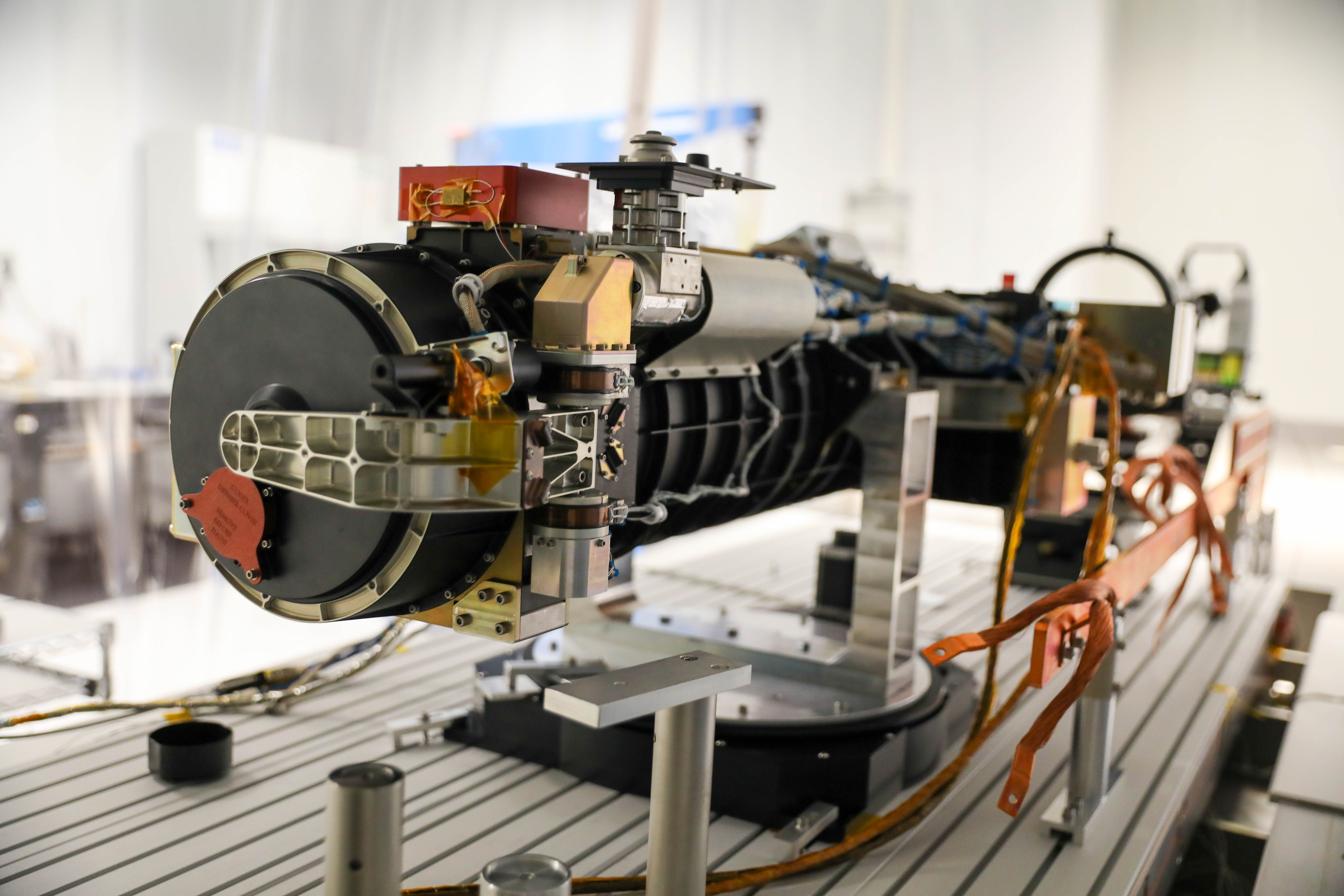
A new space-based telescope aims to address a key solar mystery.
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading
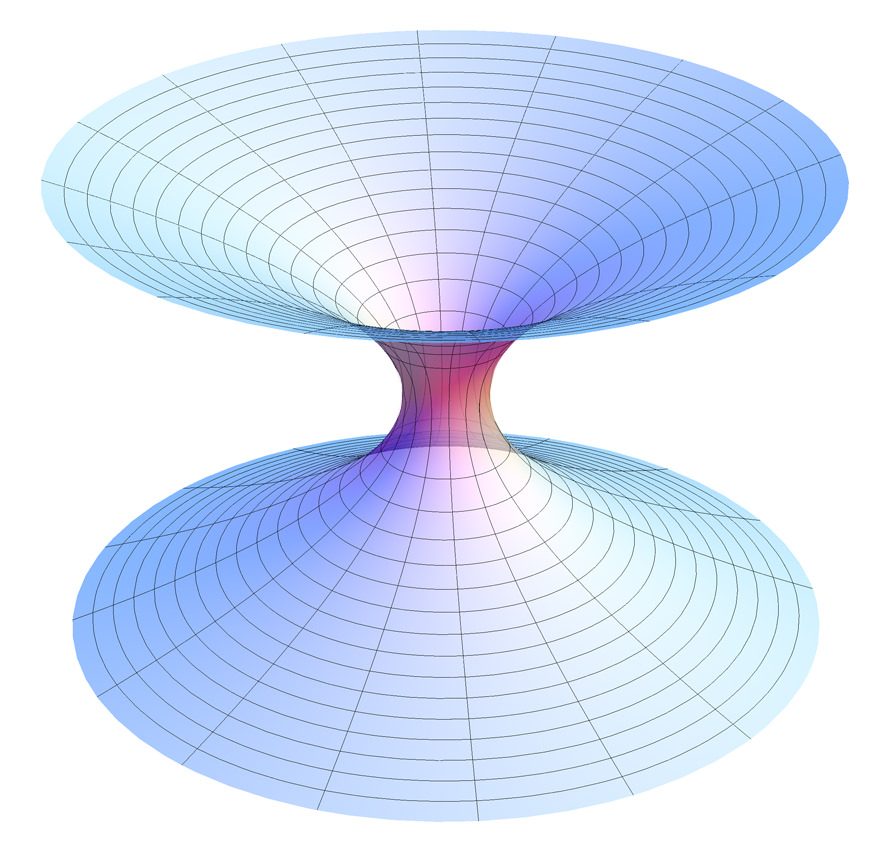
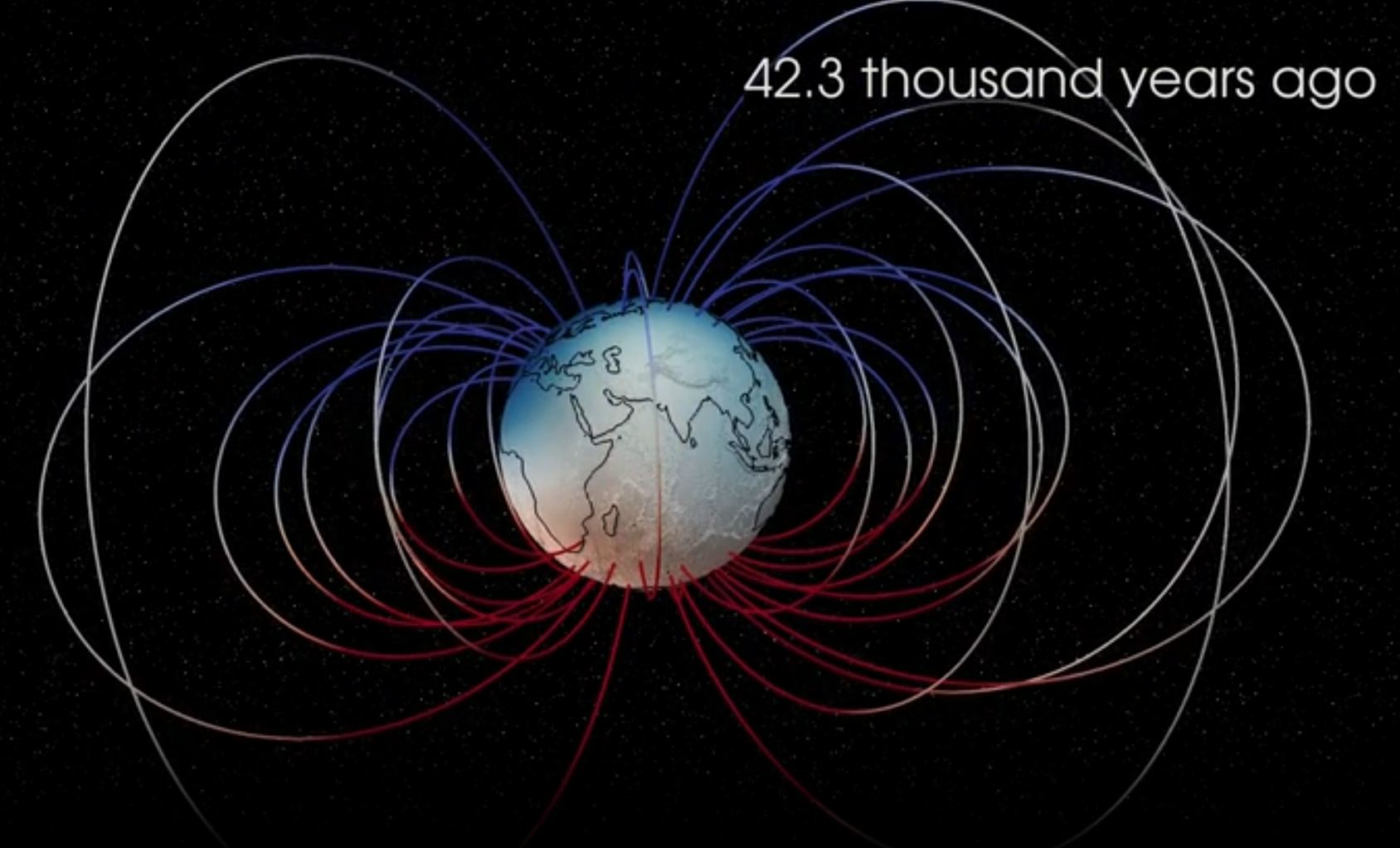
The theory of black holes has several mathematical oddities. Recent research shows our understanding of rotating black holes might not be as strong as we thought.
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading
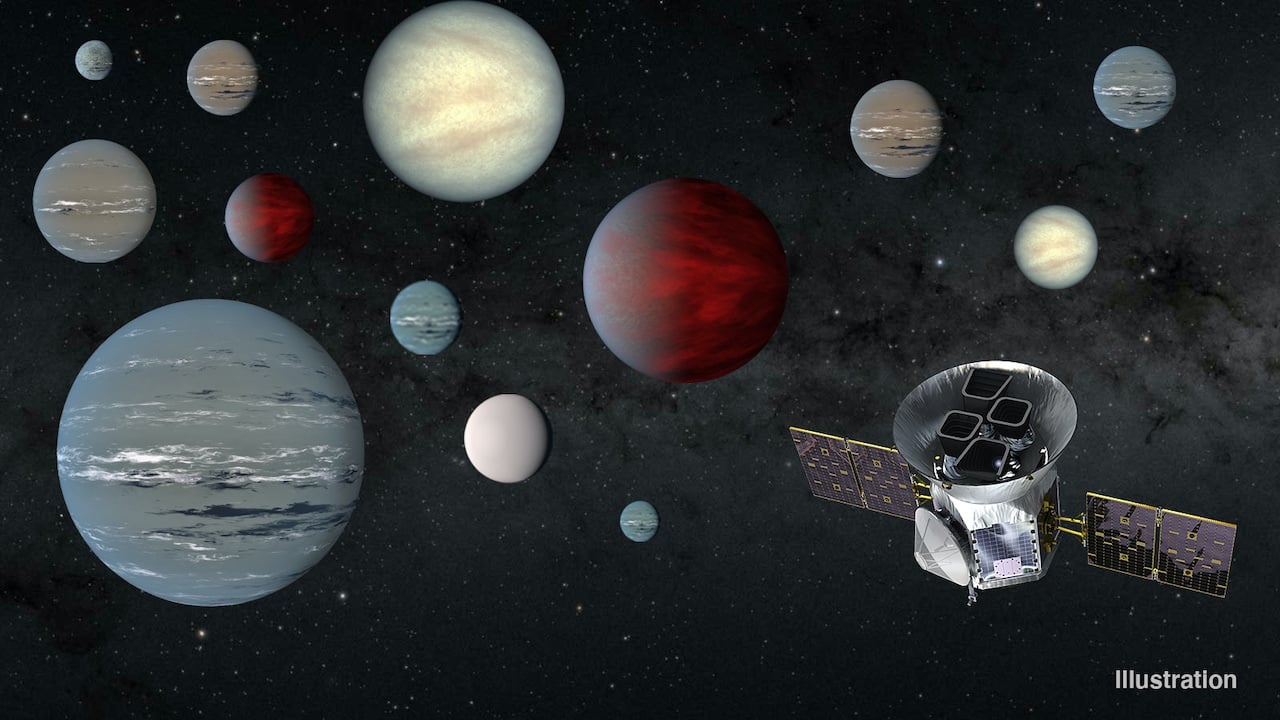

NASA's TESS mission has turned up thousands of exoplanet candidates in almost as many different star systems. But if one or two planets show up in a system, that means it's aligned with Earth, and that means we should be able to see even more in the same system. In a new paper, astronomers calculate which planetary systems have room for more exoplanets, creating a list of priority targets for further study.
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading
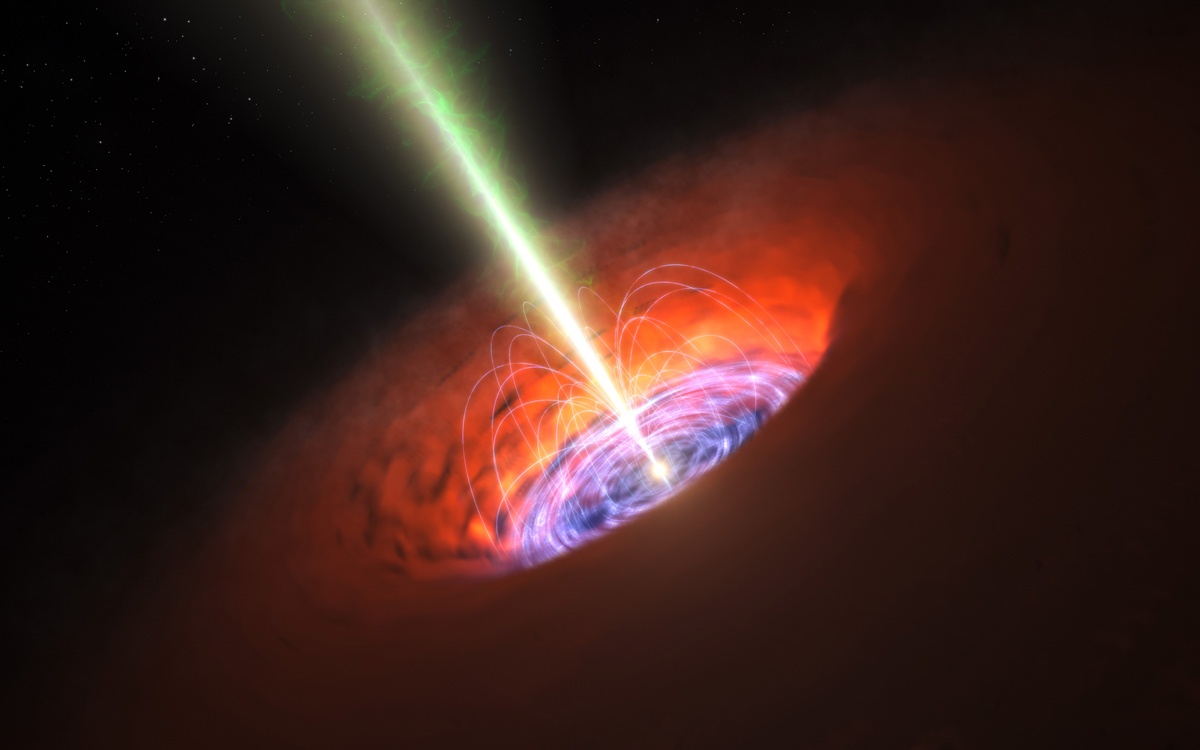

Black holes are incredible powerhouses, but they might generate even more energy thanks to an unusual effect known as frame dragging.
Continue reading

Continue reading
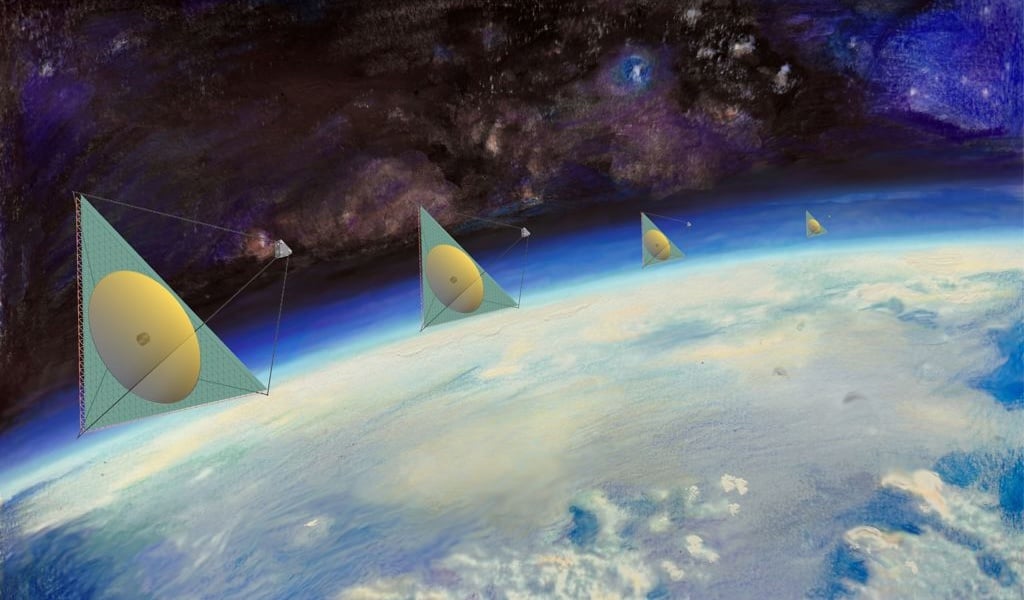

As we saw with JWST, it's difficult and expensive to launch large telescope apertures, relying on origami techniques to unfold the full mirror. A new paper proposes that telescope mirrors could be made out of a thin polymer that's only 200 micrometers thick. It could be rolled up inside a rocket fairing and then unrolled once it gets to space. This could allow apertures vastly larger than anything currently in space, with several working together as an interferometer.
Continue reading

Continue reading

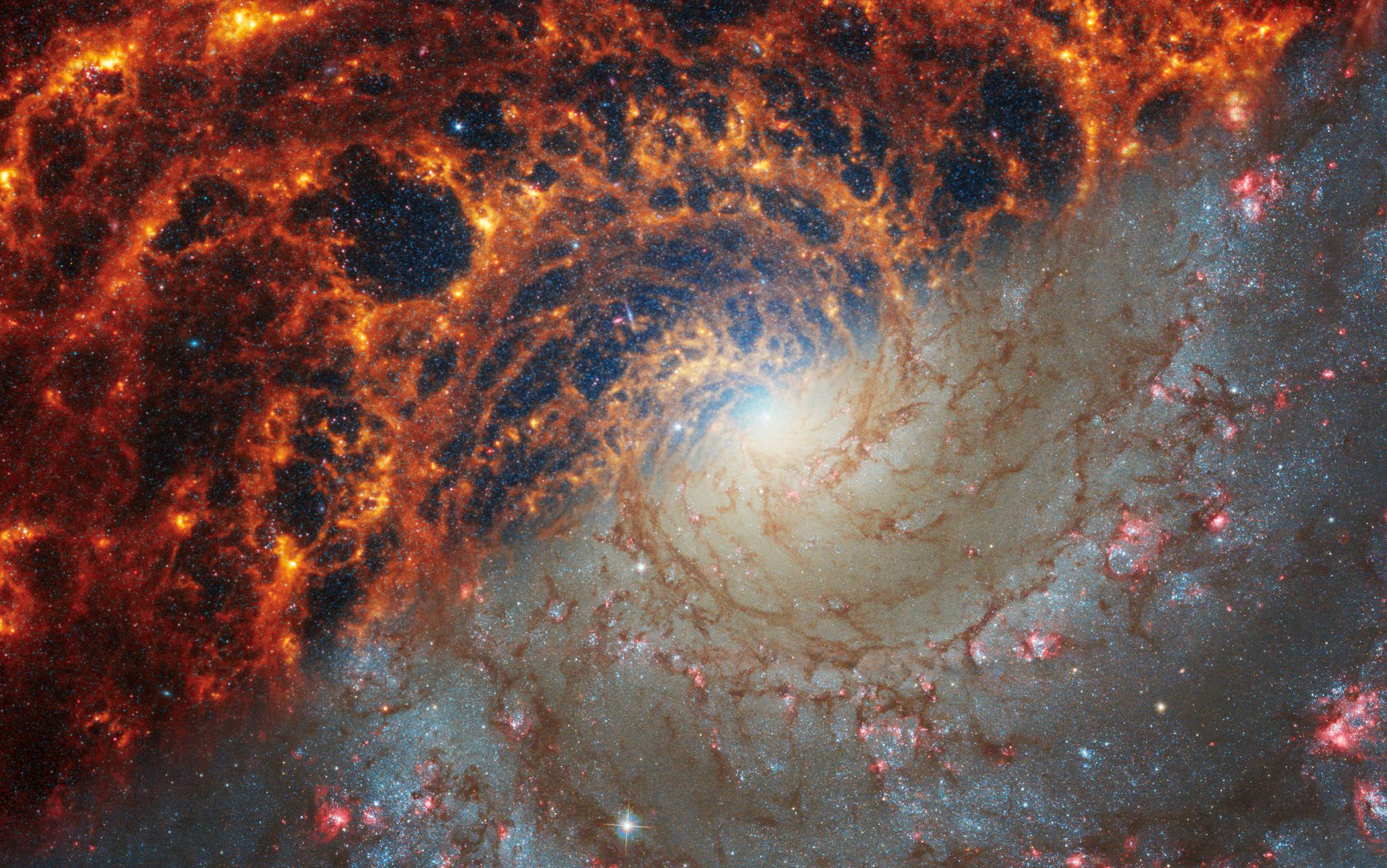
The spectra of distant galaxies shows that dying sun-like stars, not supernovae, enrich galaxies the most.
Continue reading
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading
Continue reading
Continue reading

Continue reading

Freeman Dyson proposed that advanced civilizations might eventually harvest all the energy coming from their stars by surrounding them with a swarm of solar-collecting satellites. But other astronomers have proposed that we might see all that rock go into the construction of artificial planets instead, surrounding a star with dozens of habitable worlds and captured rogue planets. If we detect a star system with a surprising number of planets, they could be artificial.
Continue reading
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading
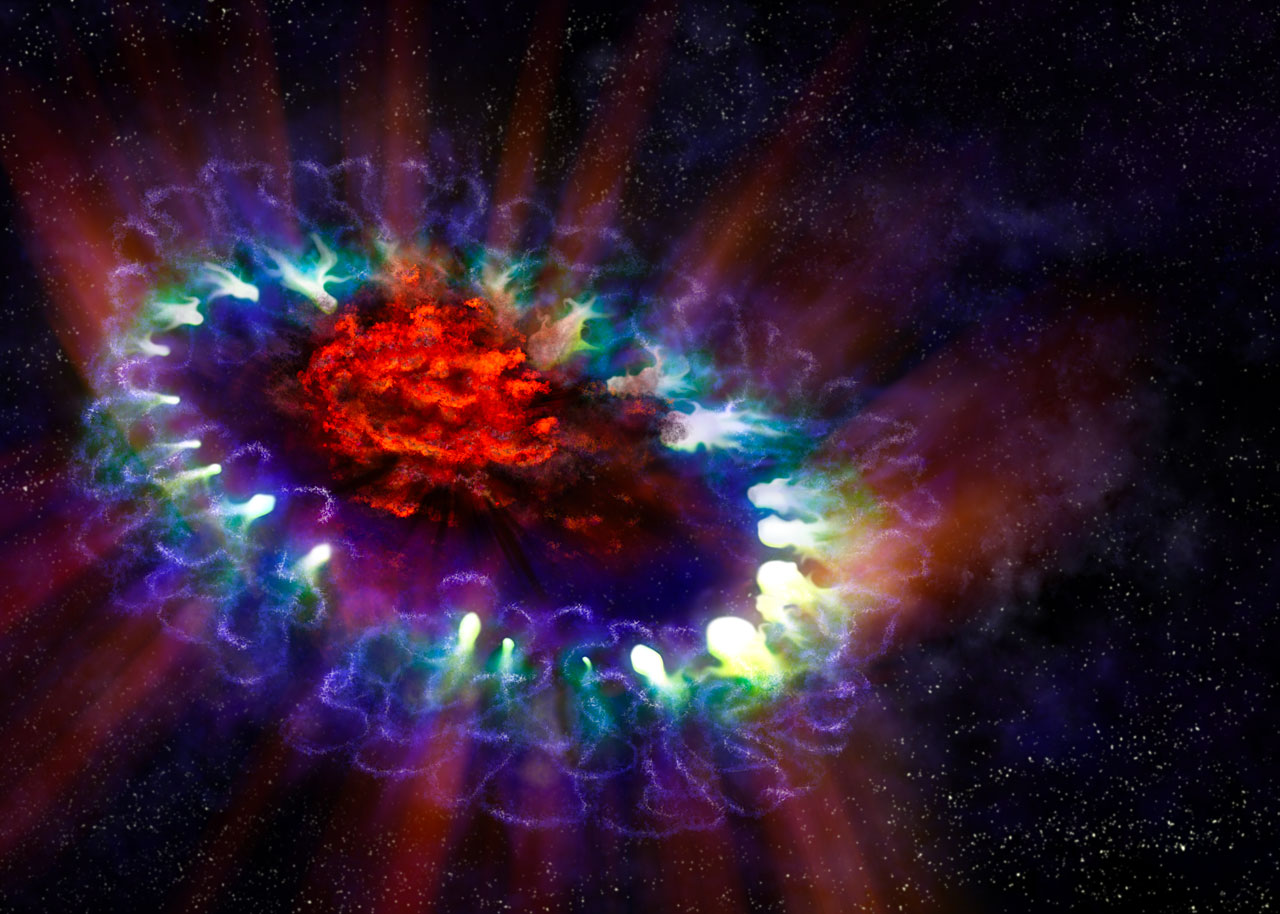

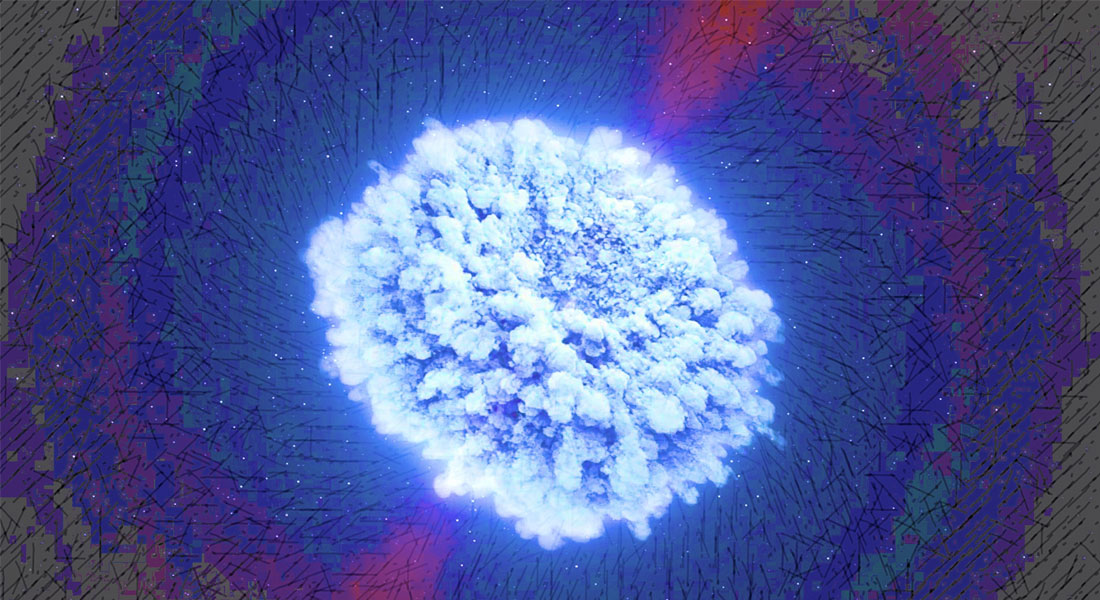
Dust grains older than the Sun can tell us about how supernovae enriched the cosmos with heavy elements, but the details are subtle and require more study.
Continue reading
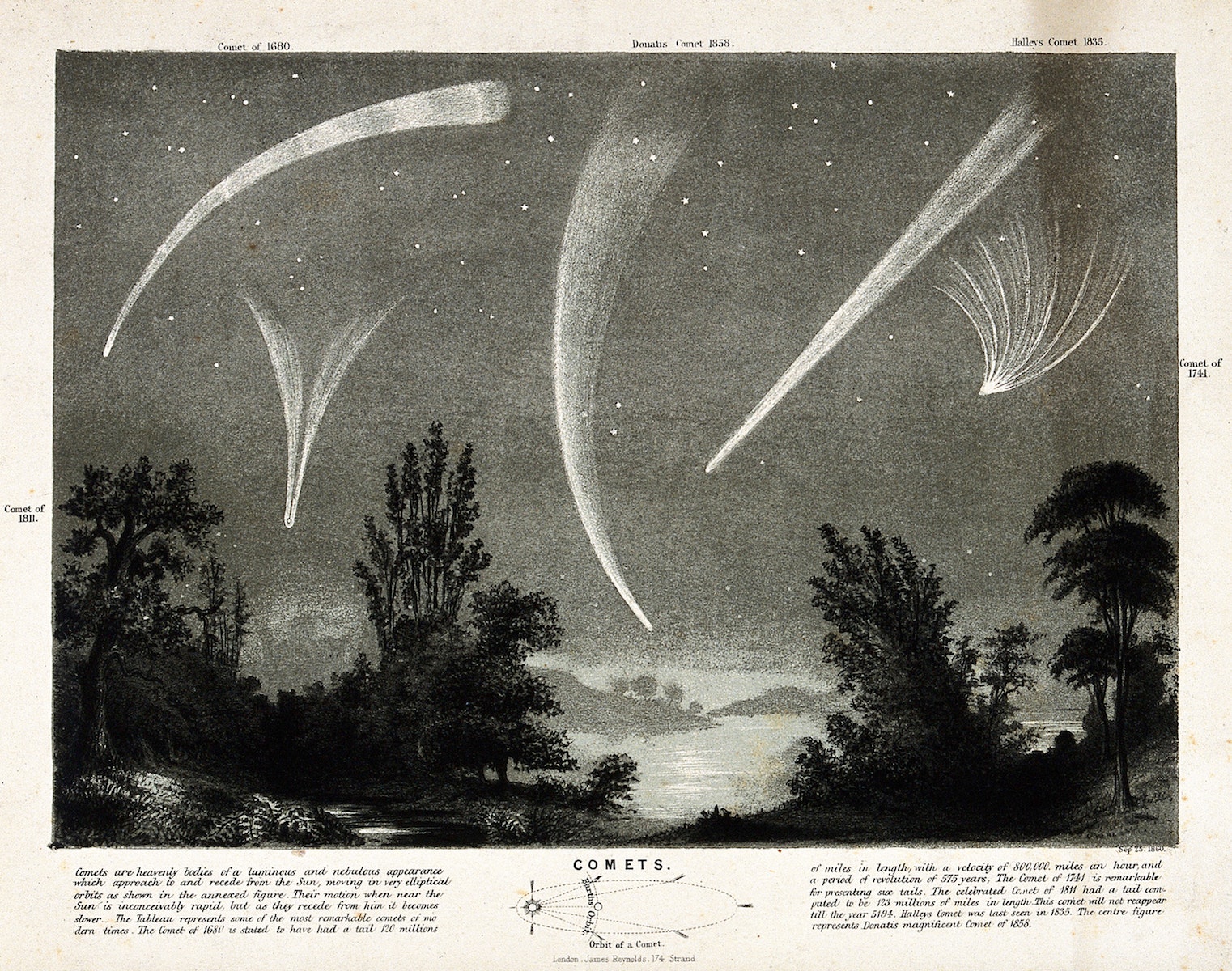

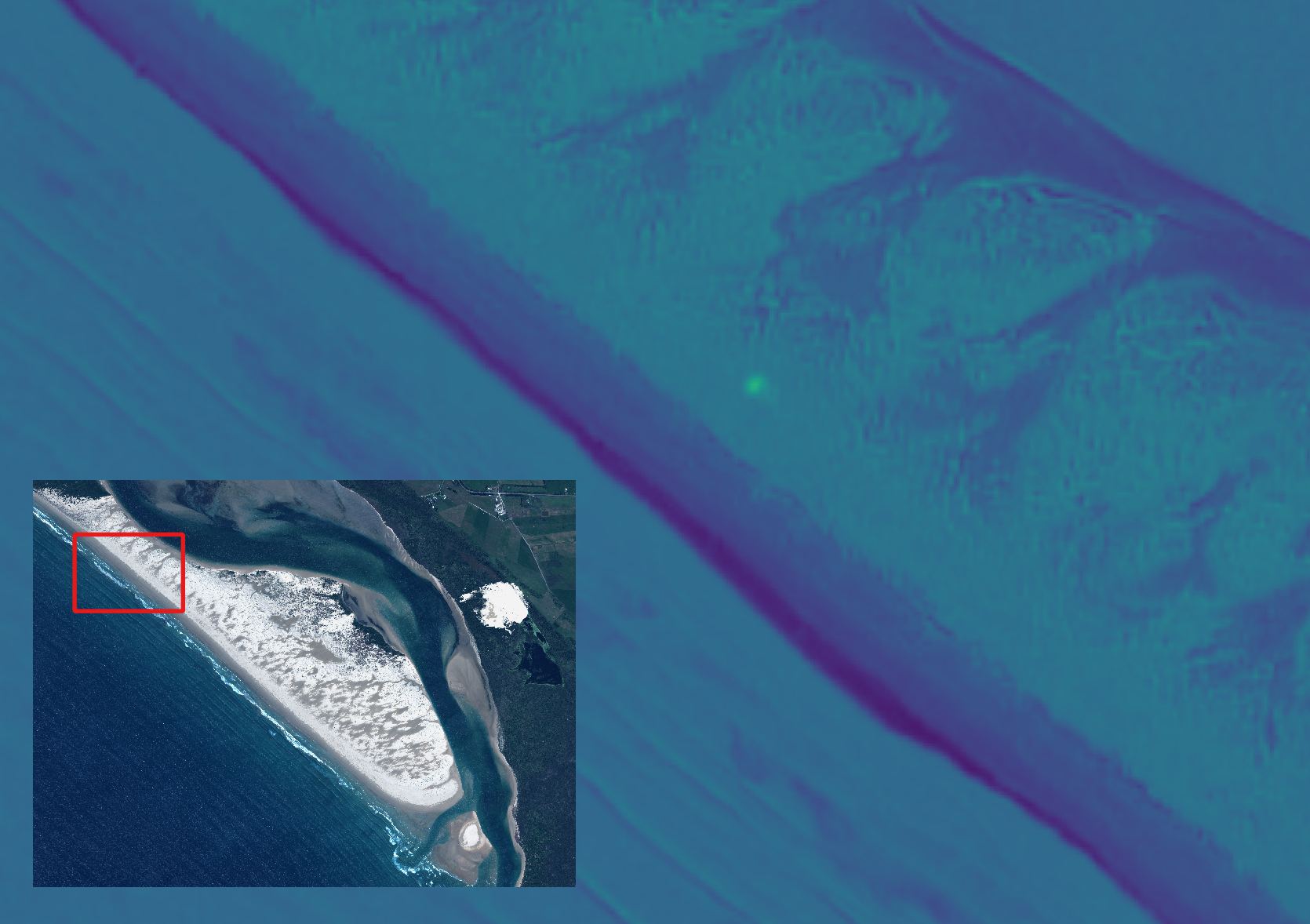
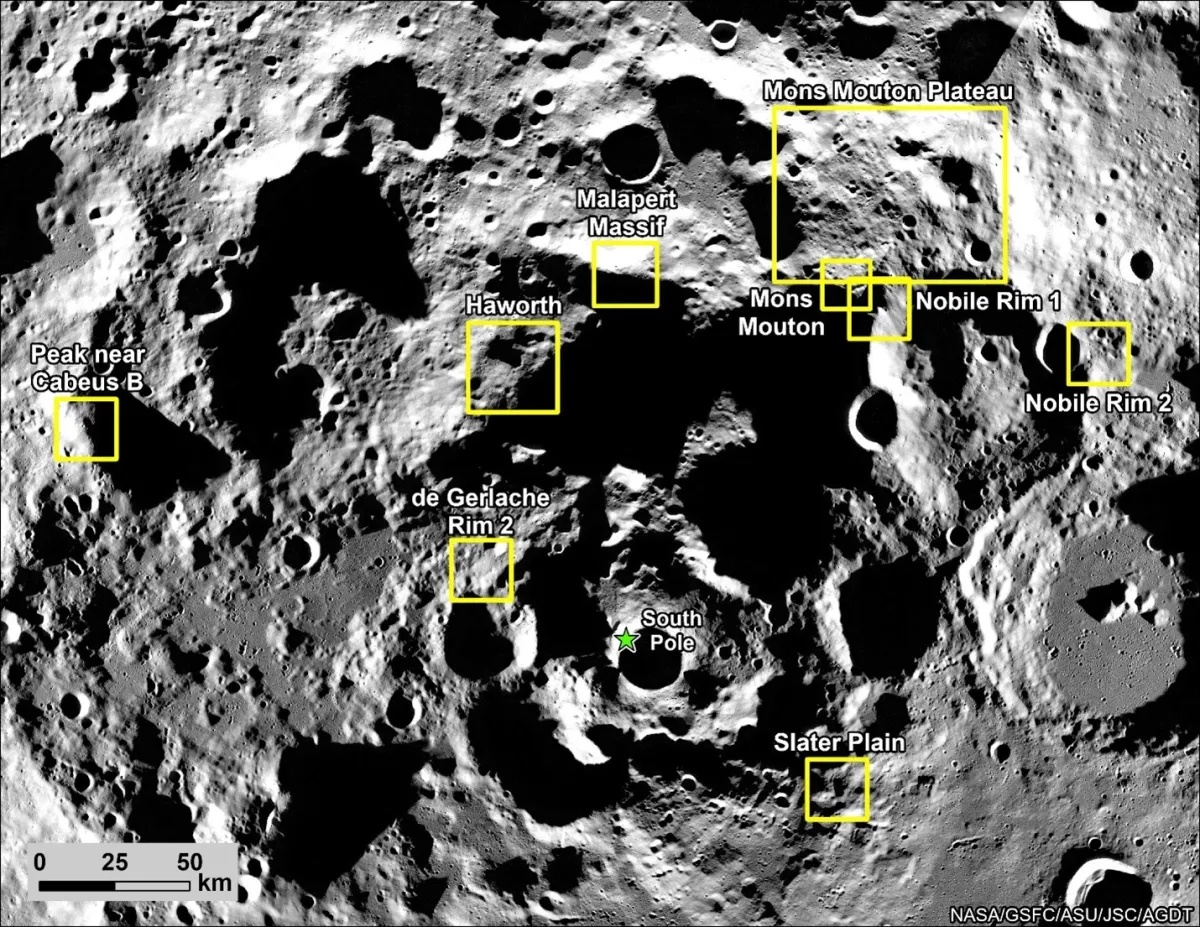
Long-period comets can have orbits that can take hundreds of years before they return to the inner Solar System and sometimes come dangerously close to Earth. To search for potentially hazardous comets, astronomers have used meteor showers as a historical record. When the Earth passes through a meteoroid stream left by a comet, we see a meteor shower. From these showers, they can calculate the orbit of the comet and predict when it will come back to our neighborhood.
Continue reading
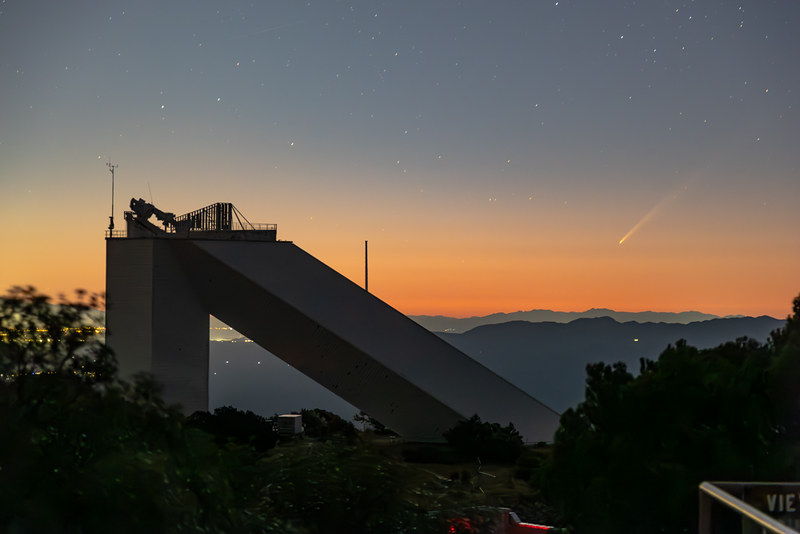

Comet C/2023 A3 Tsuchinshan-ATLAS survived perihelion to become a fine dusk object for northern hemisphere observers.
Continue reading

Continue reading
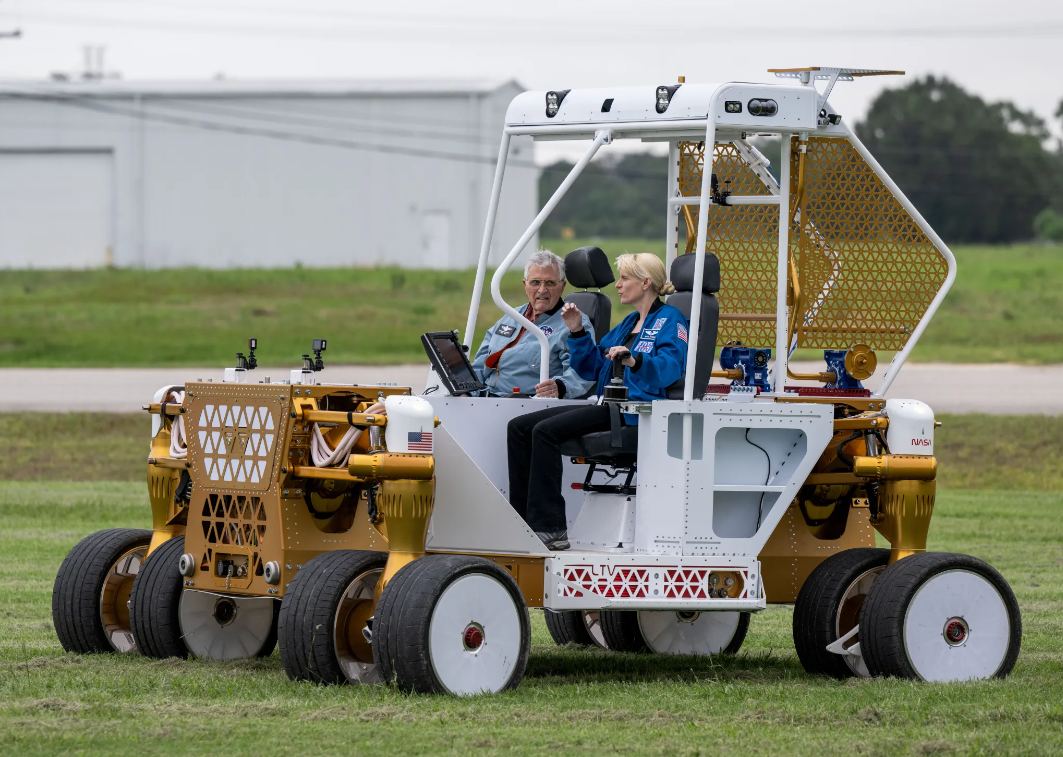

Continue reading
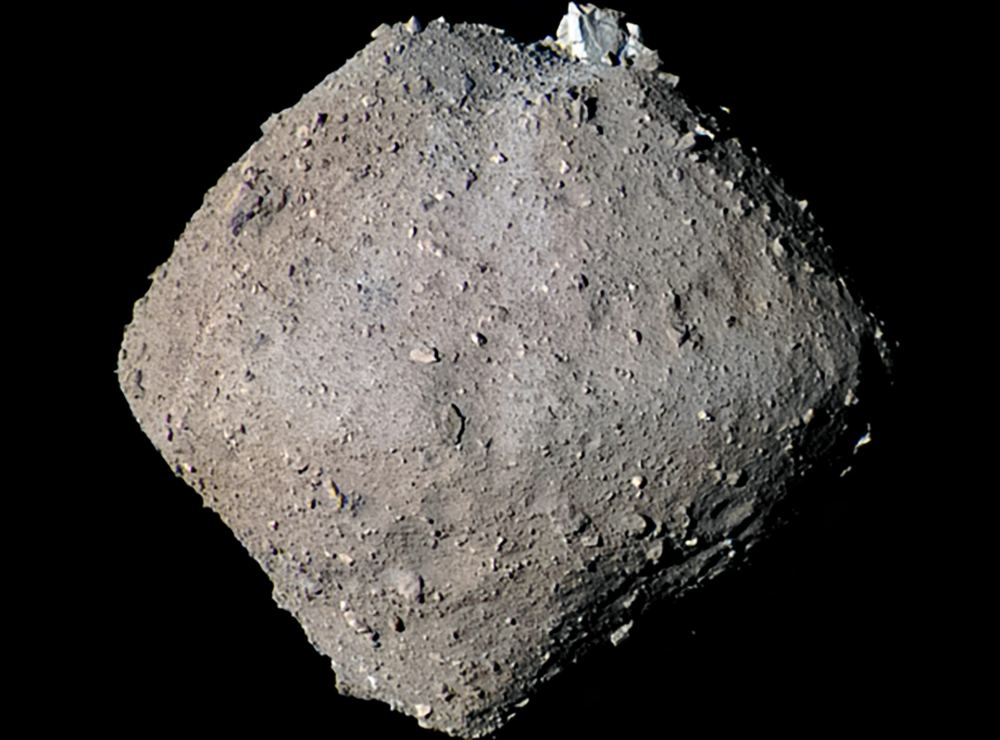

Continue reading
In 2005 astronomers found a pulsar rotating at 716 times a second. Now a team studying an X-ray binary has found another neutron star spinning at that rate.
Continue reading
Continue reading
Continue reading
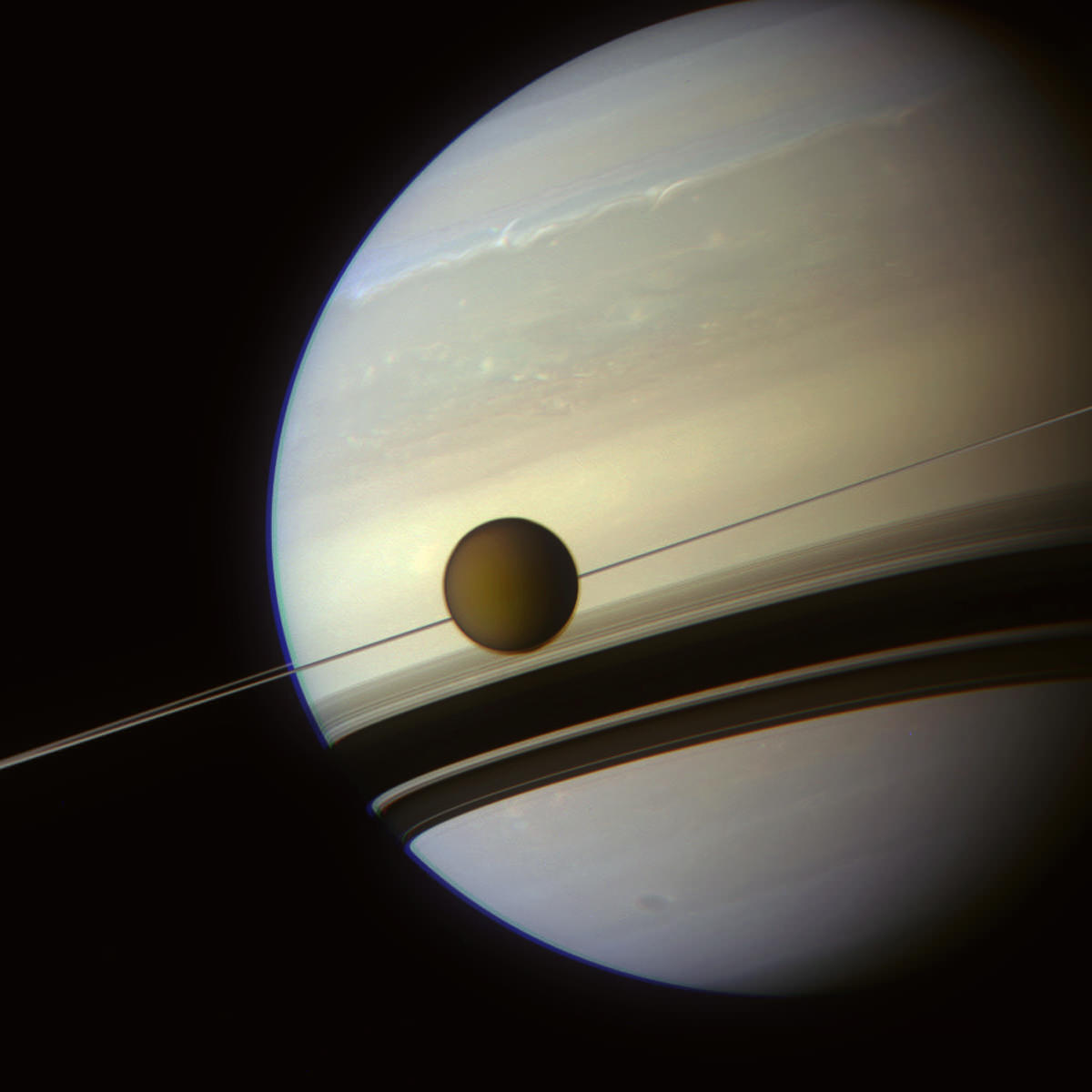

Continue reading
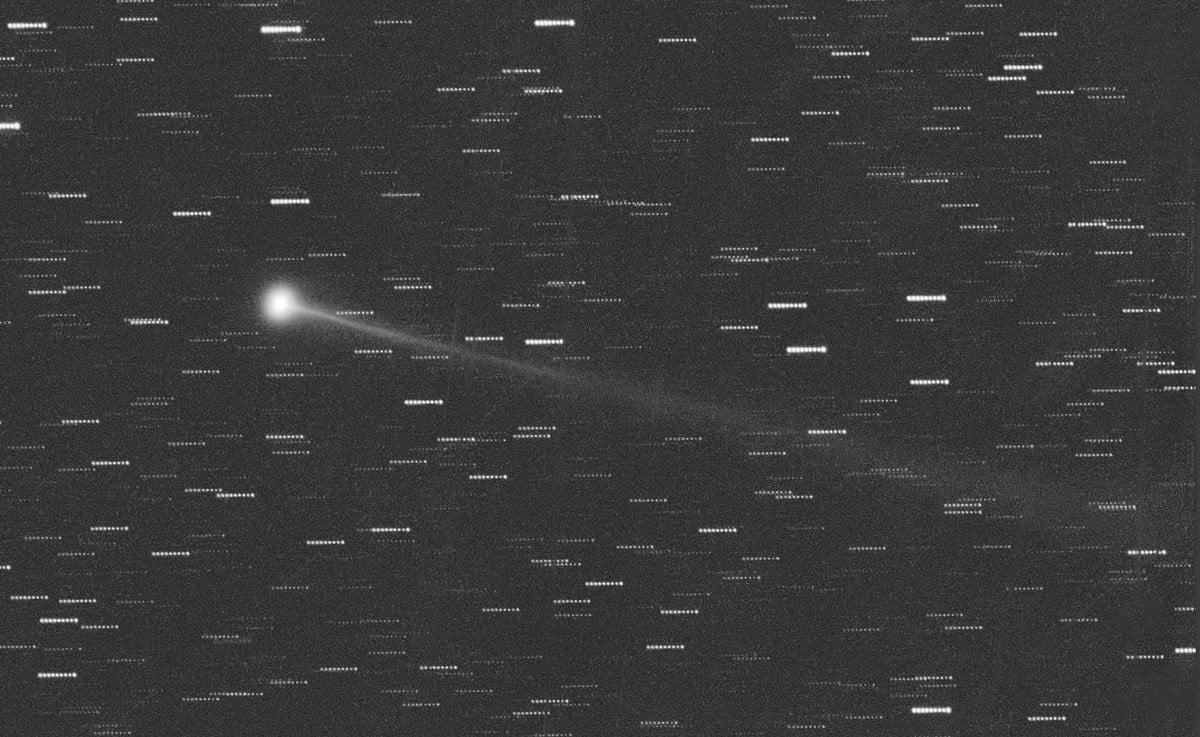

Sungrazer C/2024 S1 ATLAS breaks apart at perihelion.
Continue reading


















































