
Continue reading
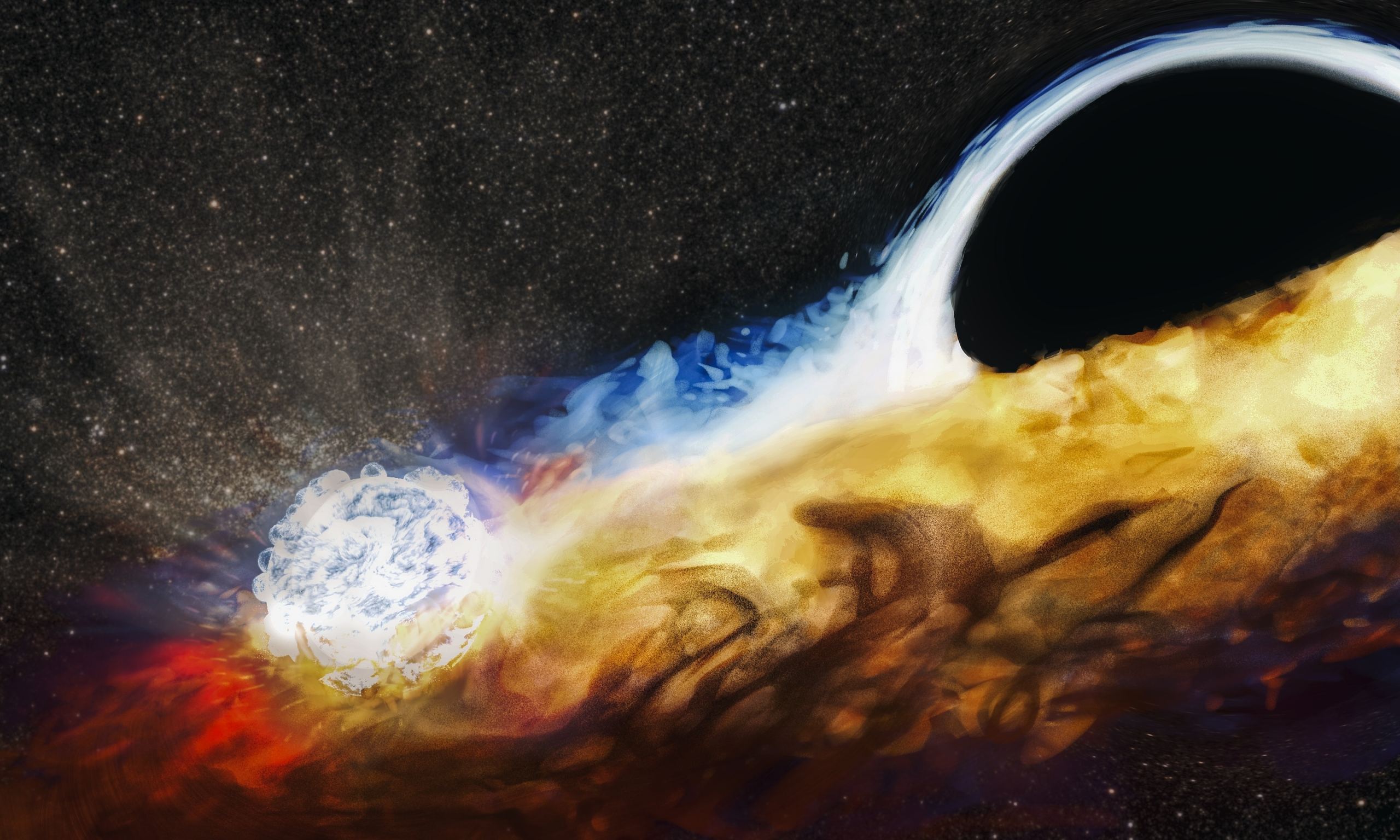

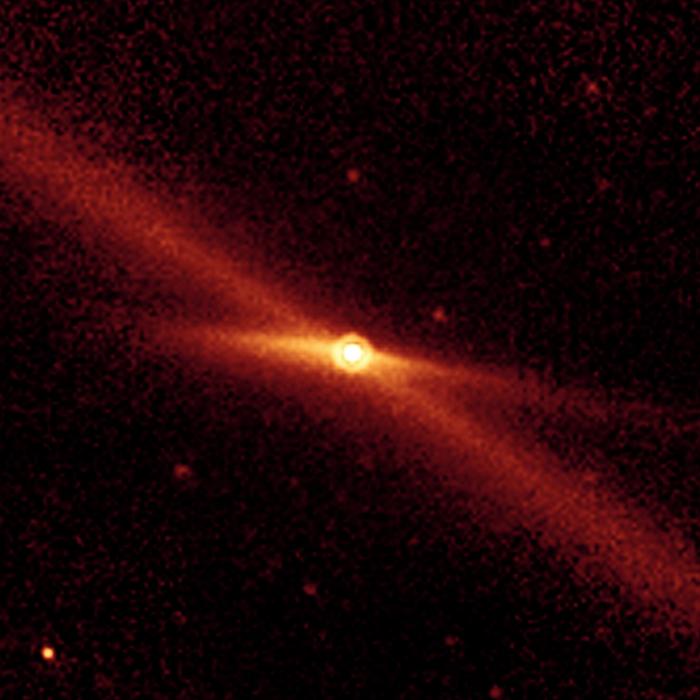
Astronomers have discovered the telltale signature of a supermassive black hole that recently tore a star apart that came too close. This is known as a tidal disruption event, and it causes a flash of X-ray radiation that's detectable from our space telescopes. The expanding debris cloud from the shredded star has drifted into the path of another star, which is now repeatedly crashing through the cloud every 48 hours, sending out additional flares.
Continue reading

Continue reading
Continue reading
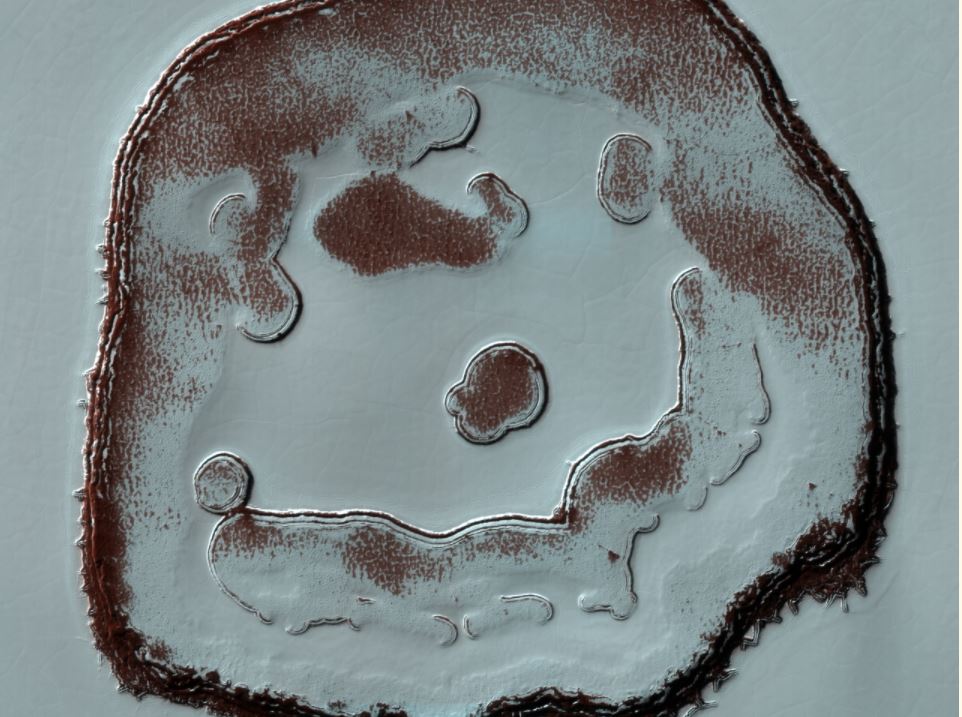
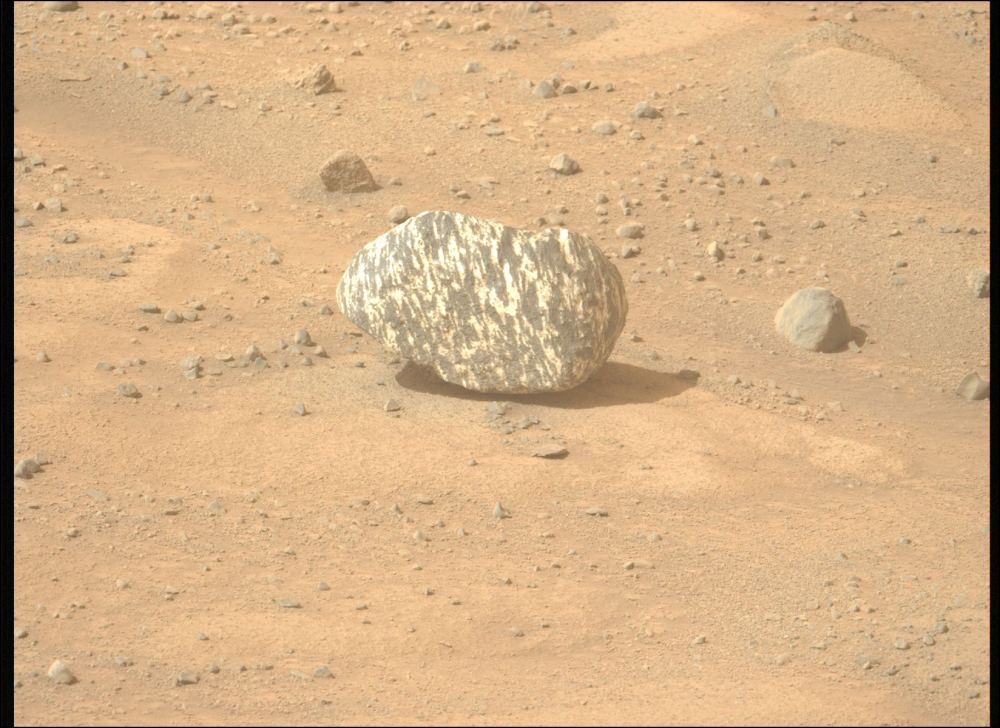
We've learned a tremendous amount about Mars because samples from the Red Planet have already been delivered to Earth: meteorites. Scientists have studied the composition of Martian meteorites and tracked down the specific craters on Mars where many of them came from. It's believed that Mars has been struck hard enough to produce meteorites about ten times in recent history. Some of these craters have yet to be matched with meteorites, but the rocks could be out there.
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading
Continue reading
Continue reading
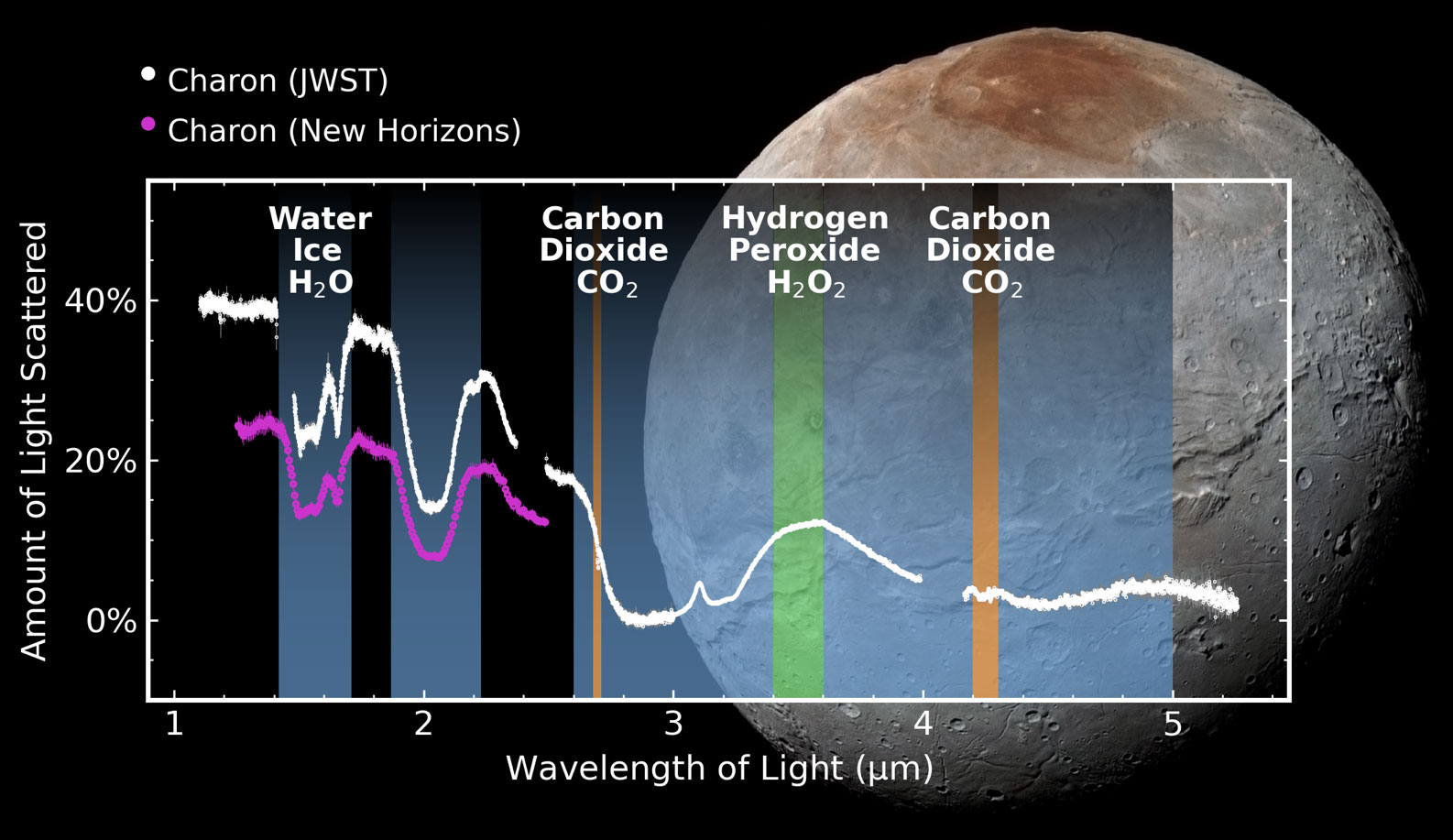
Continue reading

Continue reading
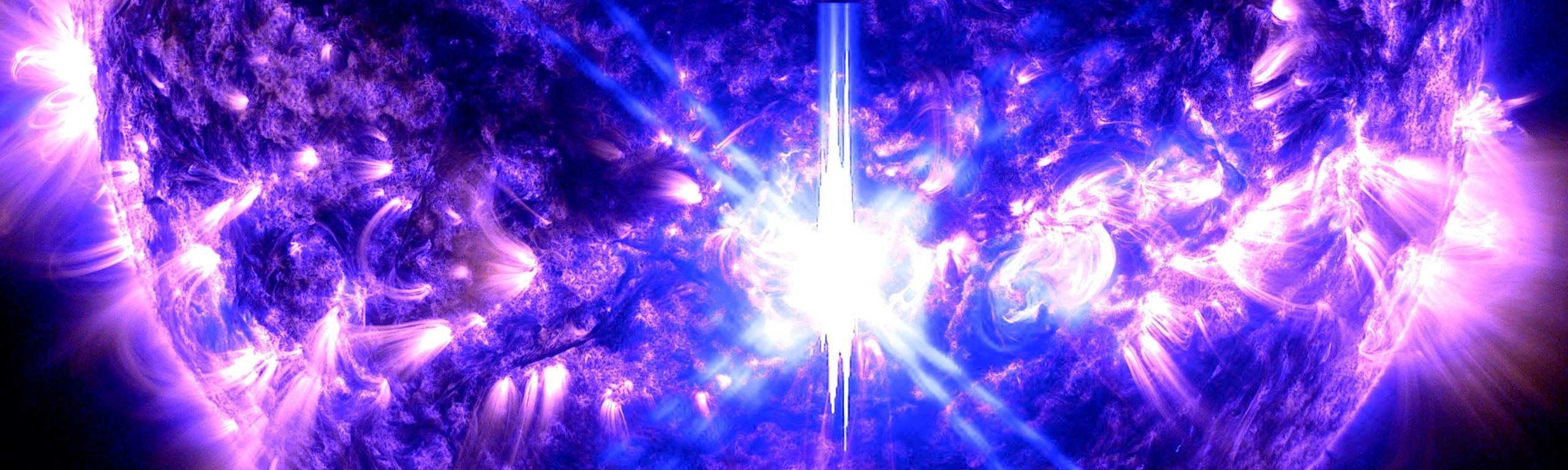

As we approach the peak of Solar Cycle 25, we can expect more and more activity on the Sun. And on October 3rd, the Sun released its most powerful Earth-directed flare of the current cycle, registering as an X9.0. Of course, this means an increase in aurora activity here on the planet, with visibility at lower latitudes. So, if you're hoping to see auroras this cycle, the next couple of days could be your best chance. Good luck!
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading
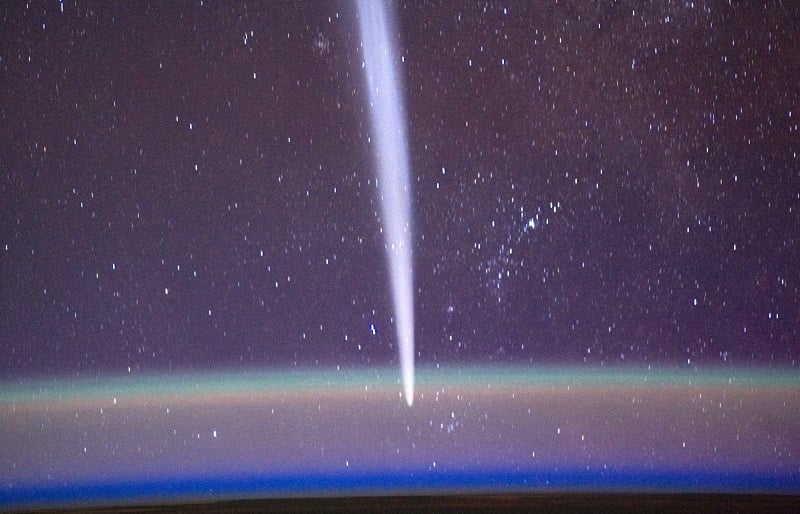

A new sungrazing comet with potential may grace our skies in late October.
Continue reading
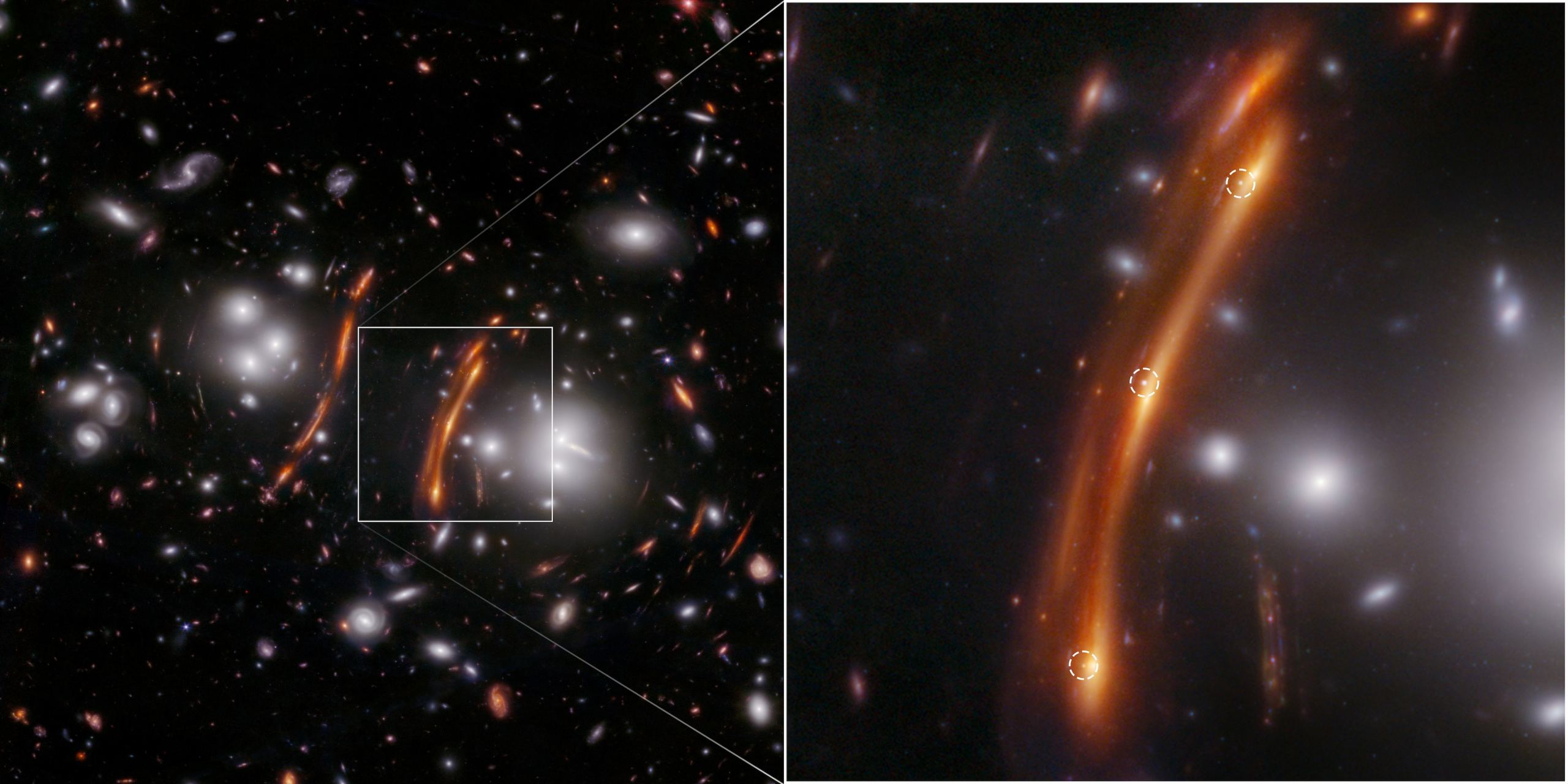

Astronomers want new ways to measure distance in the Universe, working to calculate its rate of expansion. A new image from JWST contains a gravitational lens of a background galaxy. And in that galaxy are three versions of the same Type 1a supernova, one of the most distant ever seen. With this supernova, astronomers are able to extend their distance ladder out by billions of years, and yet, it doesn't resolve the famous Hubble Tension; it only confirms it.
Continue reading
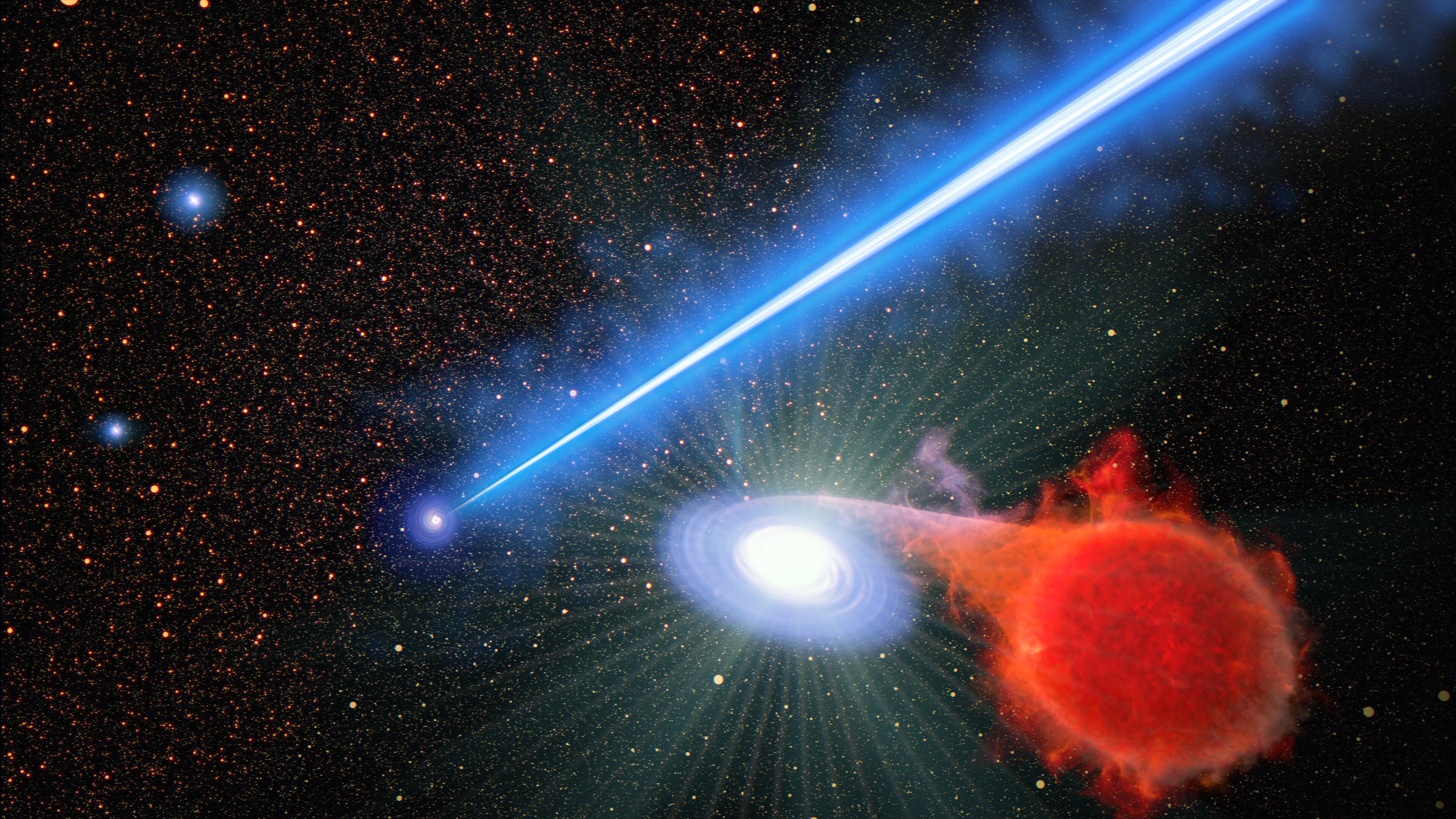
Continue reading

Continue reading
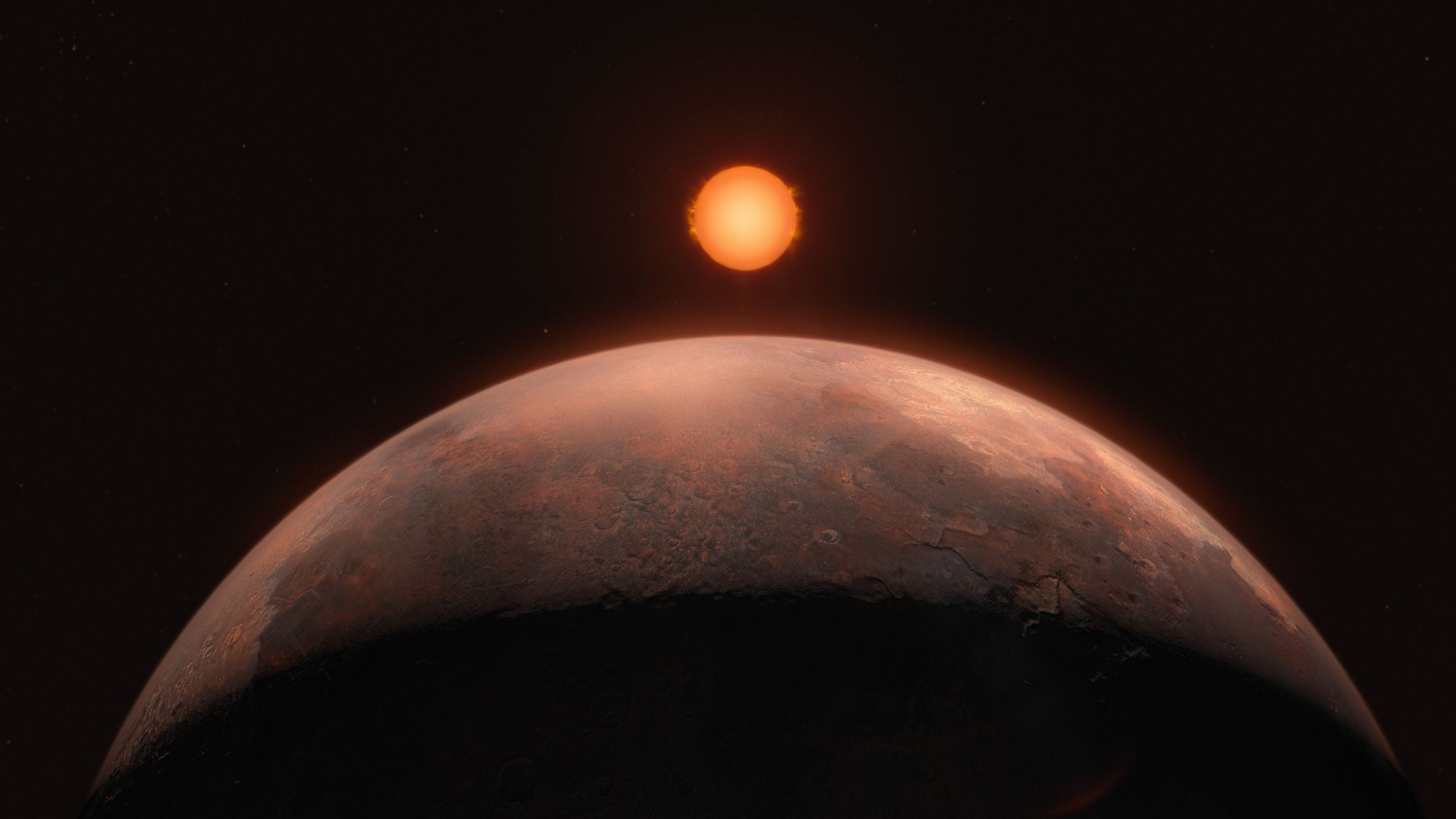

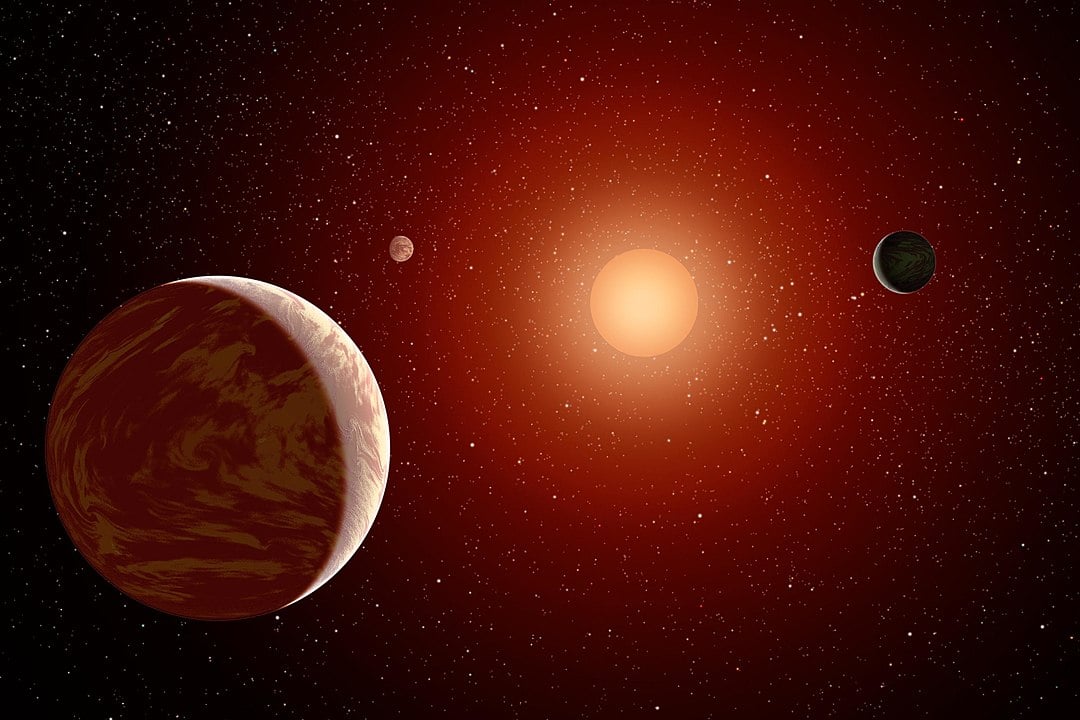
The red dwarf Barnard's Star is the closest single star to the Sun, only six light-years away. Astronomers have announced the discovery of a planet with half the mass of Venus, orbiting the star every three days. This puts it too close to be in the habitable zone, with a surface temperature of 125 °C. The team also found a hint of three additional planets in the system but will require further observations to pin down their sizes and orbits.
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading
Continue reading
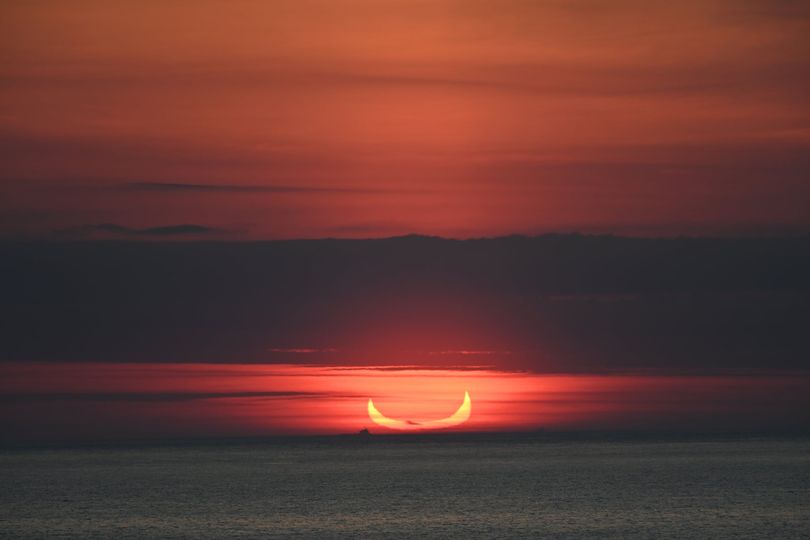

A remote annular solar eclipse bookends the final eclipse season for 2024.
Continue reading
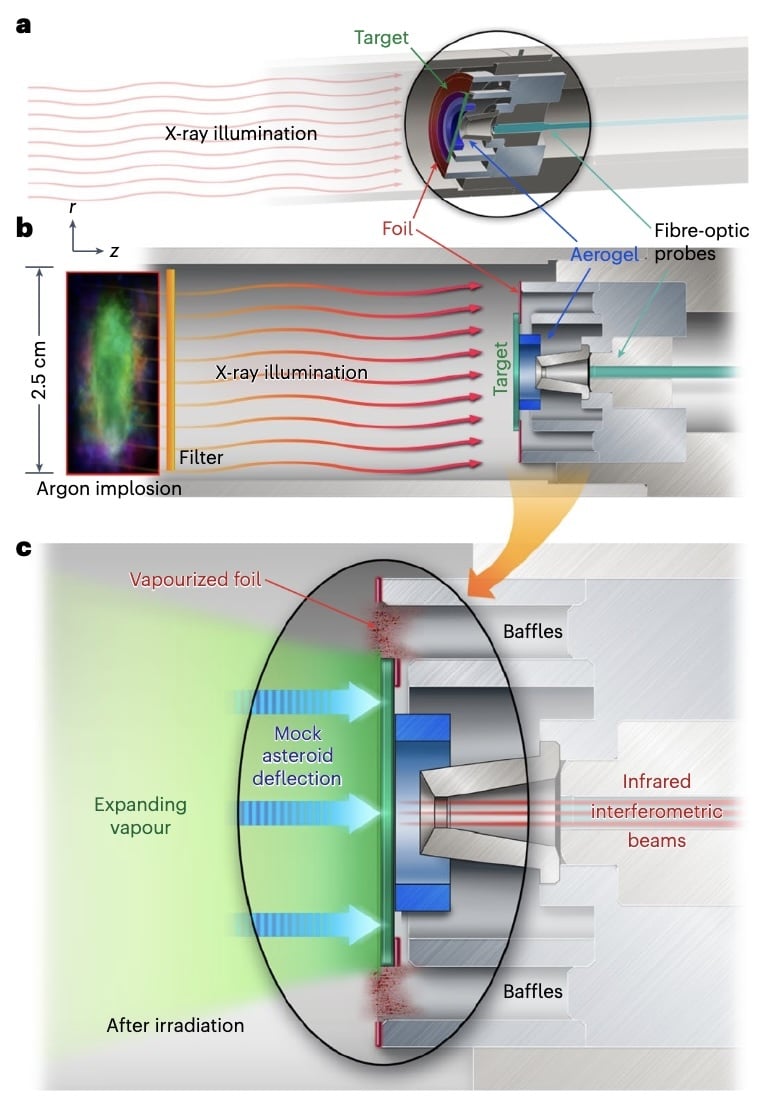
Continue reading

Continue reading

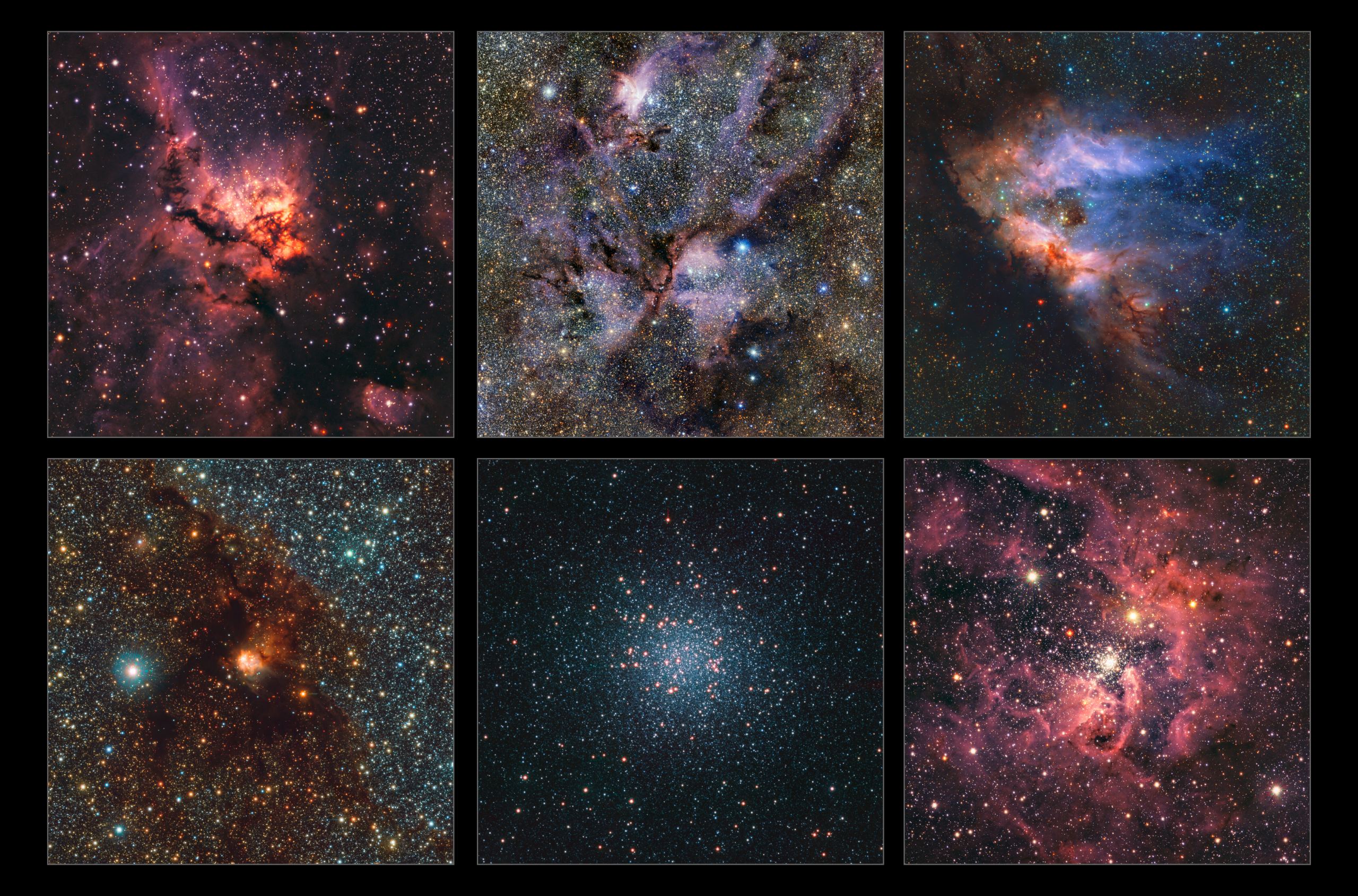
Looking out into the universe, astronomers have identified countless spiral galaxies similar to the Milky Way. But is our home galaxy normal? A 10+ year survey called Satellites Around Galactic Analogs (SAGA) has been measuring galaxy systems like the Milky Way, including the companion satellite galaxies that surround them. They found that the Milky Way has fewer satellite galaxies than others with roughly the same size and mass.
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

We know that Mars was once a warmer, wetter world with a thicker atmosphere, but now it has 1% of the atmospheric density of Earth. Where did it all go? One theory is that billions of years of interaction with the solar wind have buffeted it off into space. New research suggests that the atmosphere might still be there, just bound up in the clay-covered material that forms the crust of Mars. Trickling water could have drawn CO2 out of the atmosphere and locked it away.
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Dark matter seems to be an invisible particle that only interacts with regular matter (or itself) through gravity. But in a new study, based on data gathered by Hubble, researchers think they've found evidence of interactions with regular matter beyond just gravity. They recorded the structure of a low-mass galaxy, measured the concentrations of dark matter, and then compared that to simulations where dark matter only interacts through gravity and found a discrepancy.
Continue reading
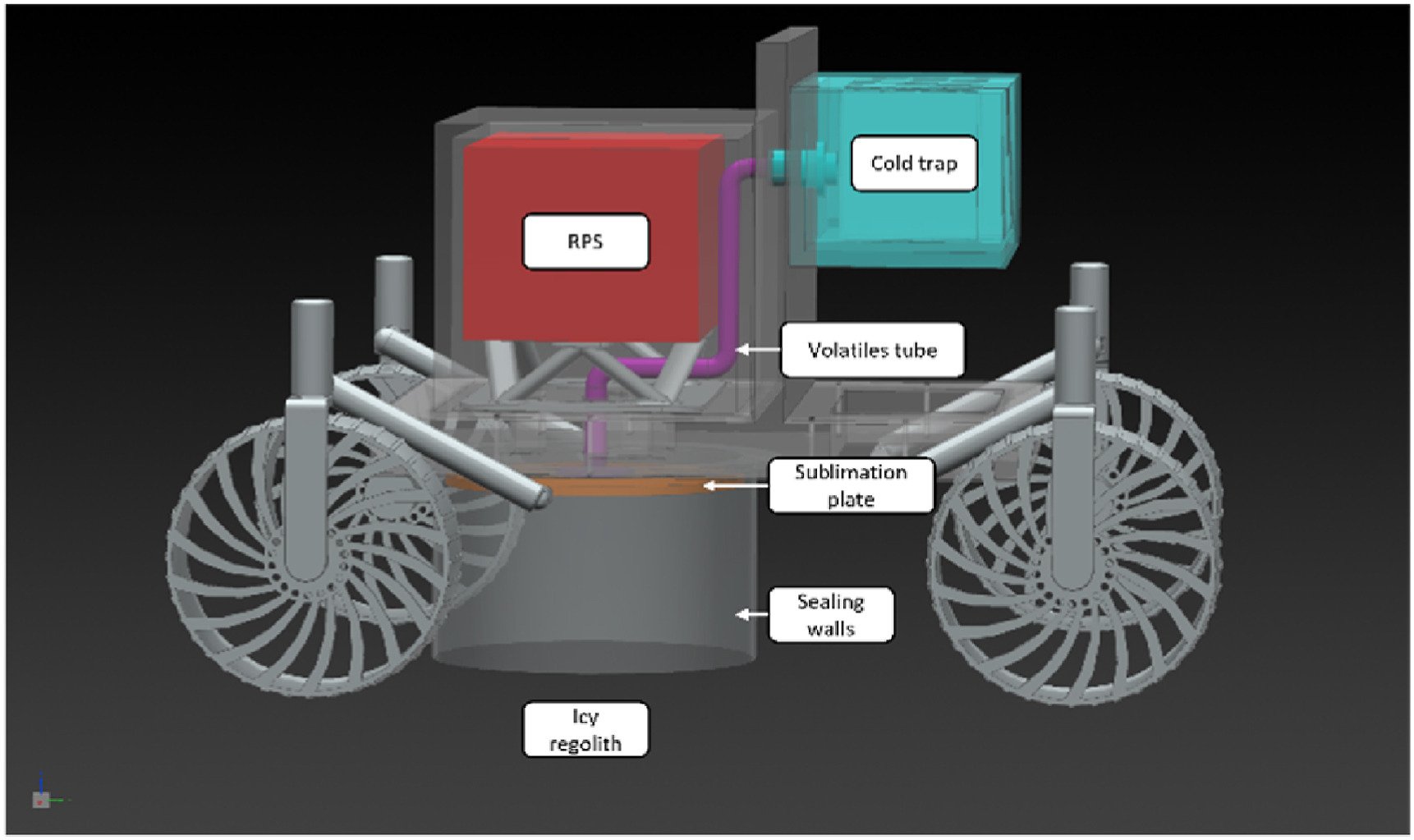
Continue reading

Continue reading
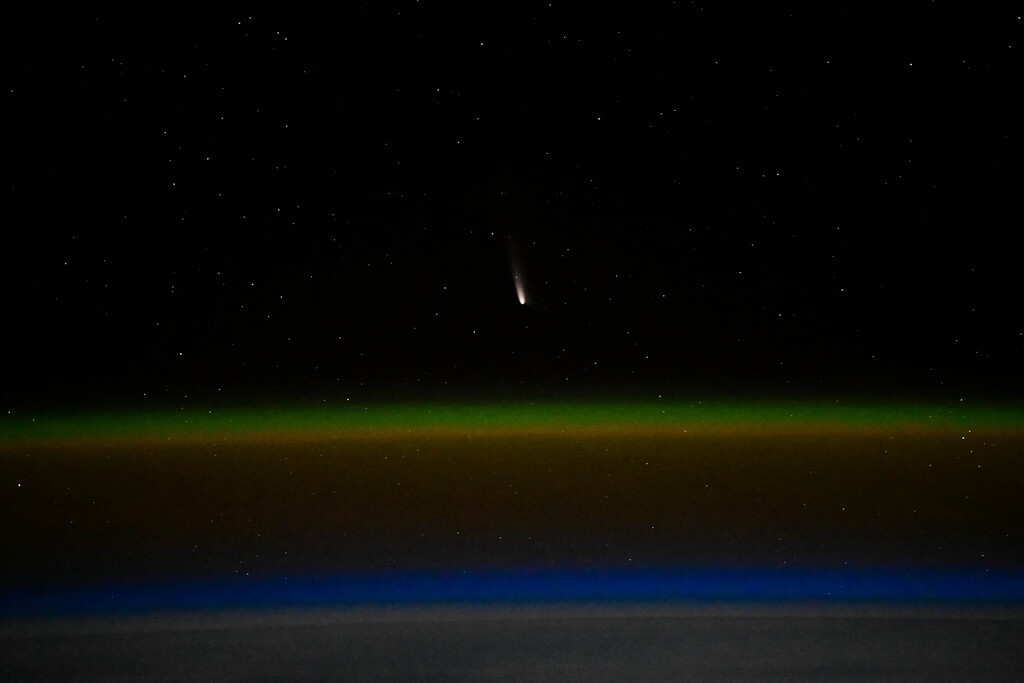

Now is the time to catch Comet A3-Tsuchinshan-ATLAS at dawn.
Continue reading

Astrobiologists continue to search for their ideal biosignatures. A chemical or collection of chemicals that would give a clear indication of life on an exoplanet. The problem is that natural processes can produce all the same chemicals that life can generate. Now, researchers have produced dimethyl sulfide in the lab, a chemical made by marine microbes. They used light and gases found in many planetary atmospheres. The search for biosignatures continues.
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading


















































