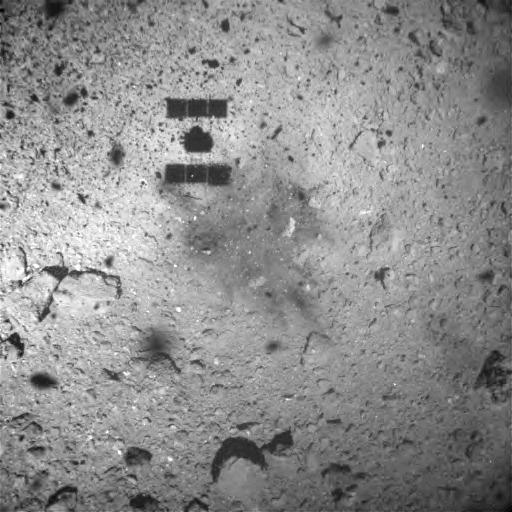

The Hayabusa2 spacecraft left its mark on asteroid Ryugu, which mission controllers noticed after the spacecraft touched down on the surface and left a dark patch behind.
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

A new study has placed new constraints on the emergence of complex life, which effectively narrows what what we would consider to be a star's "habitable zone"
Continue reading
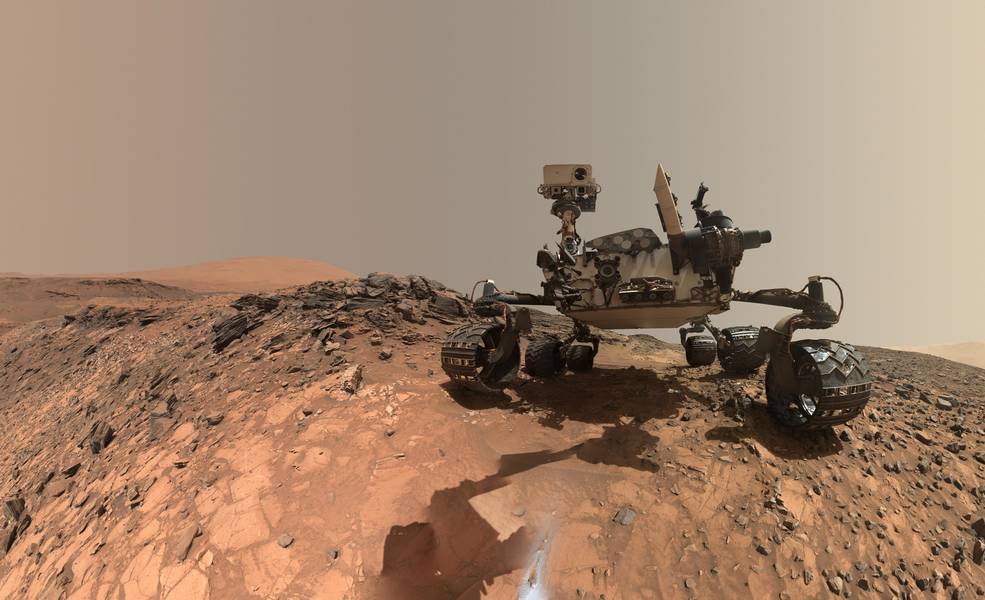

A few weeks after Curiosity suffered a glitch that put it in safe mode, the rover is once again operating normally.
Continue reading
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading
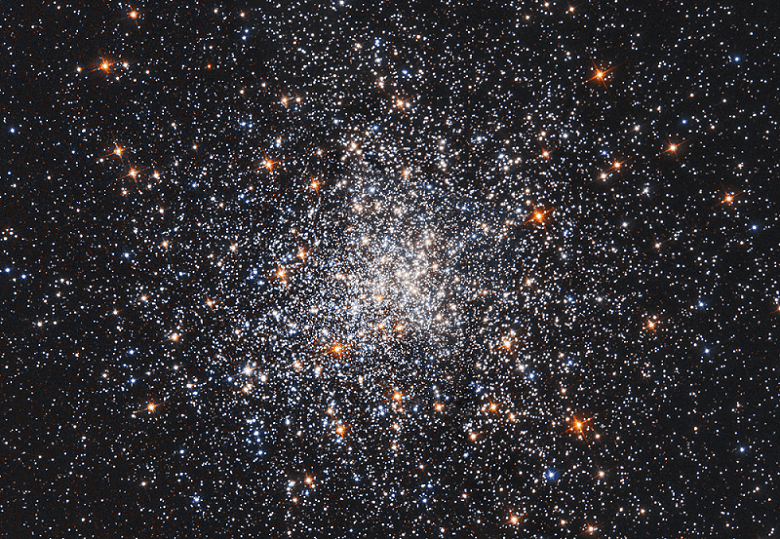
Located 42,000 light-years from Earth is the globular cluster known as Messier 79, which may have originated outside of our galaxy.
Continue reading
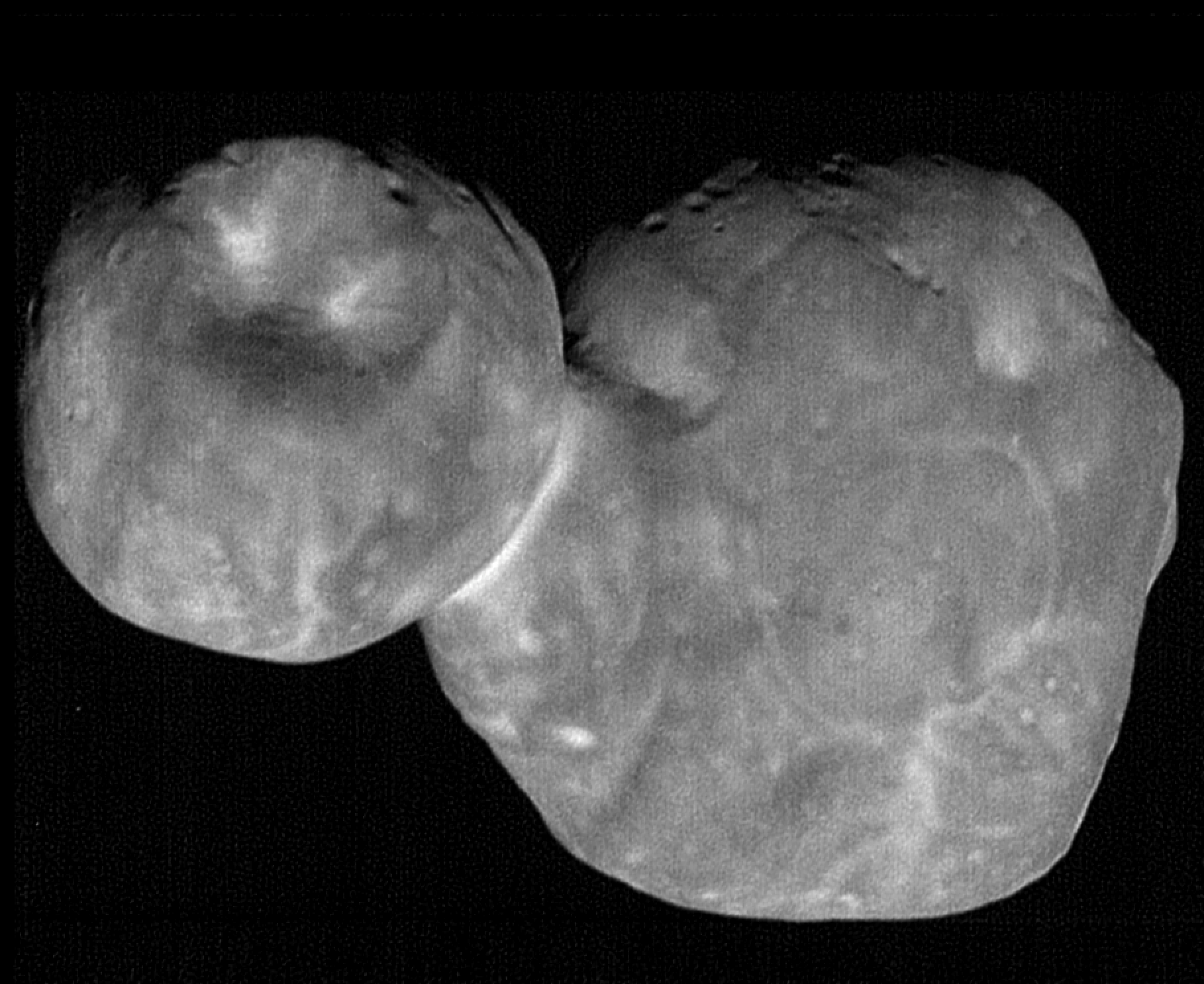
The latest images taken by New Horizons of Ultima Thule are the most detailed to date, and are providing new clues about the objects origin and evolution.
Continue reading
Continue reading
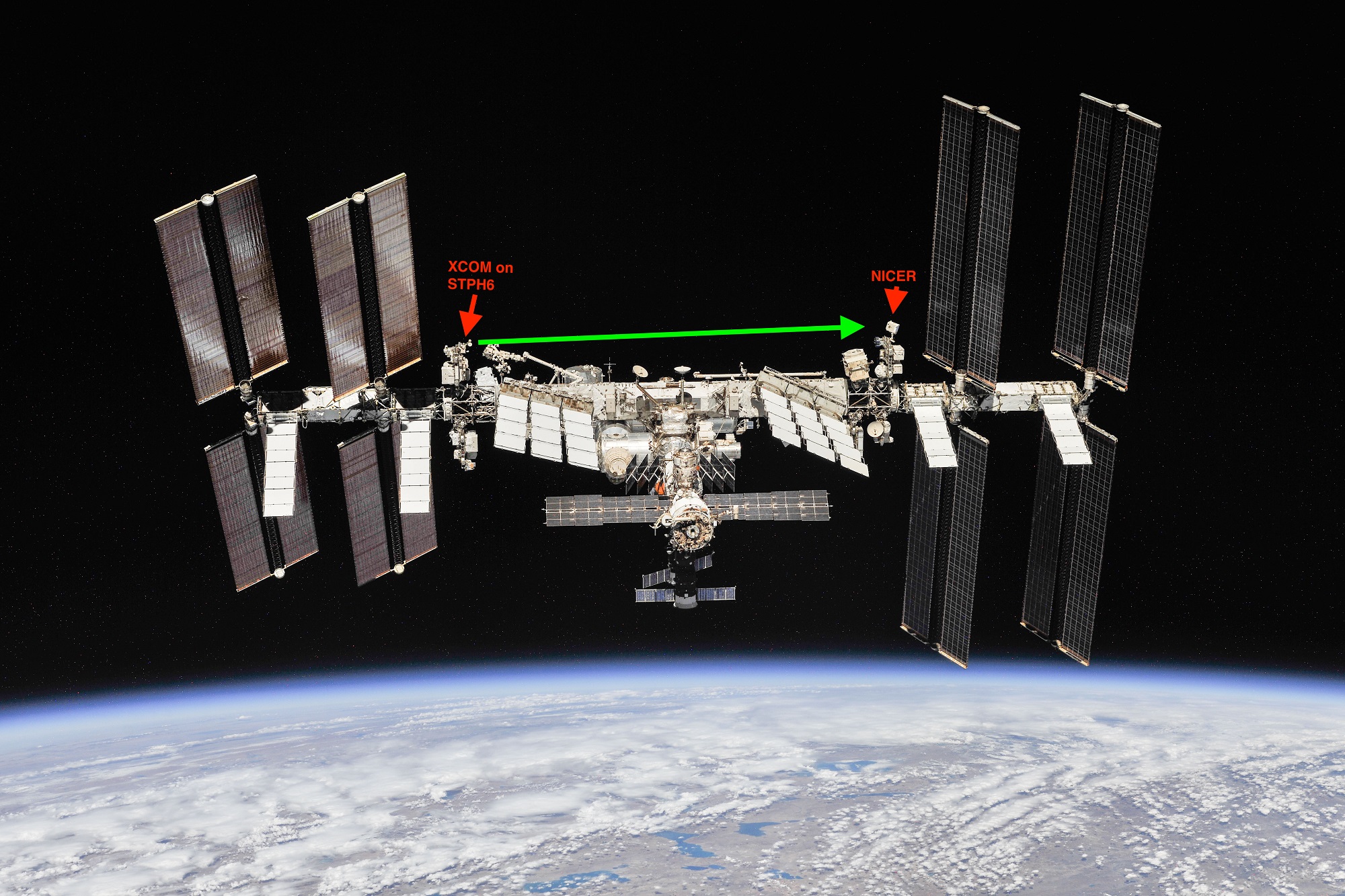

In the coming years, NASA plans to test x-ray technology aboard the ISS as a way of creating more robust communication systems.
Continue reading
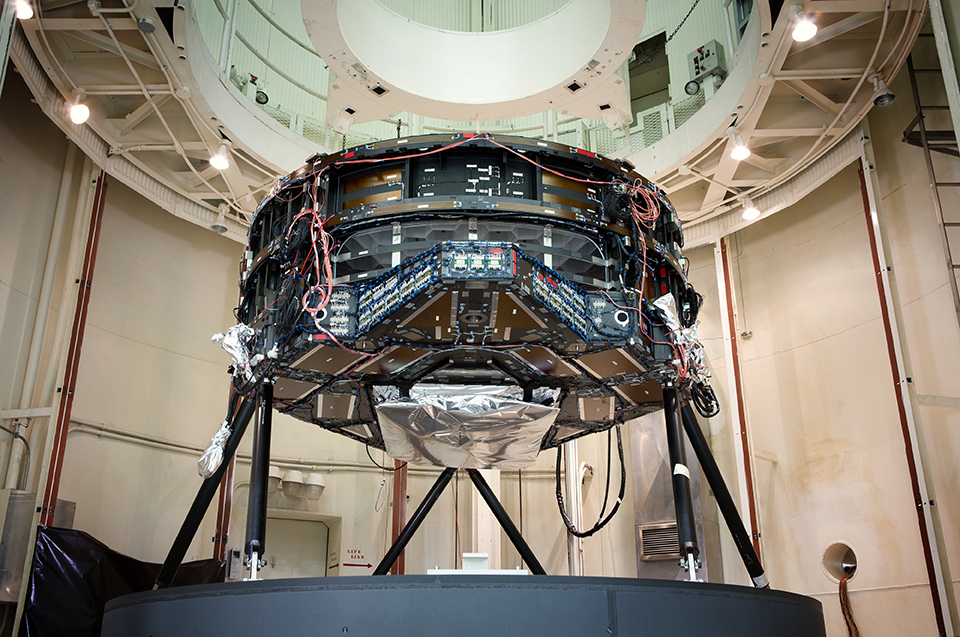

Continue reading
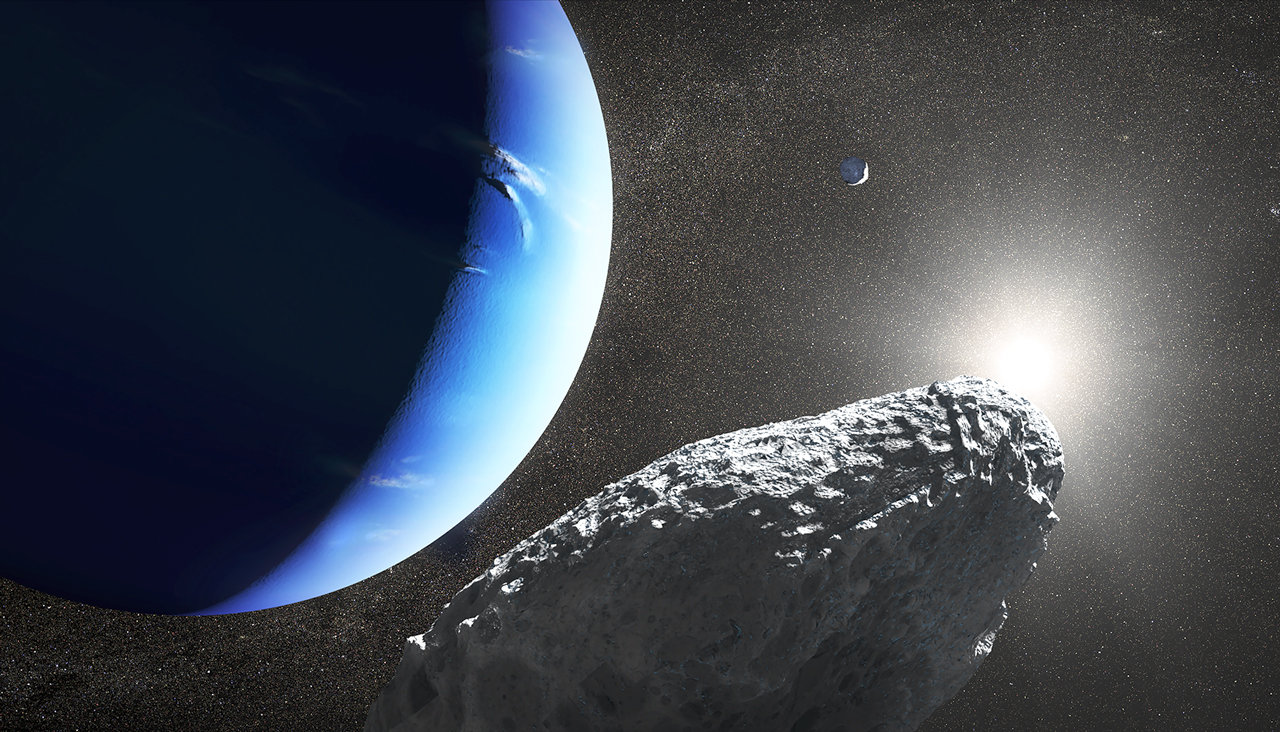

Continue reading
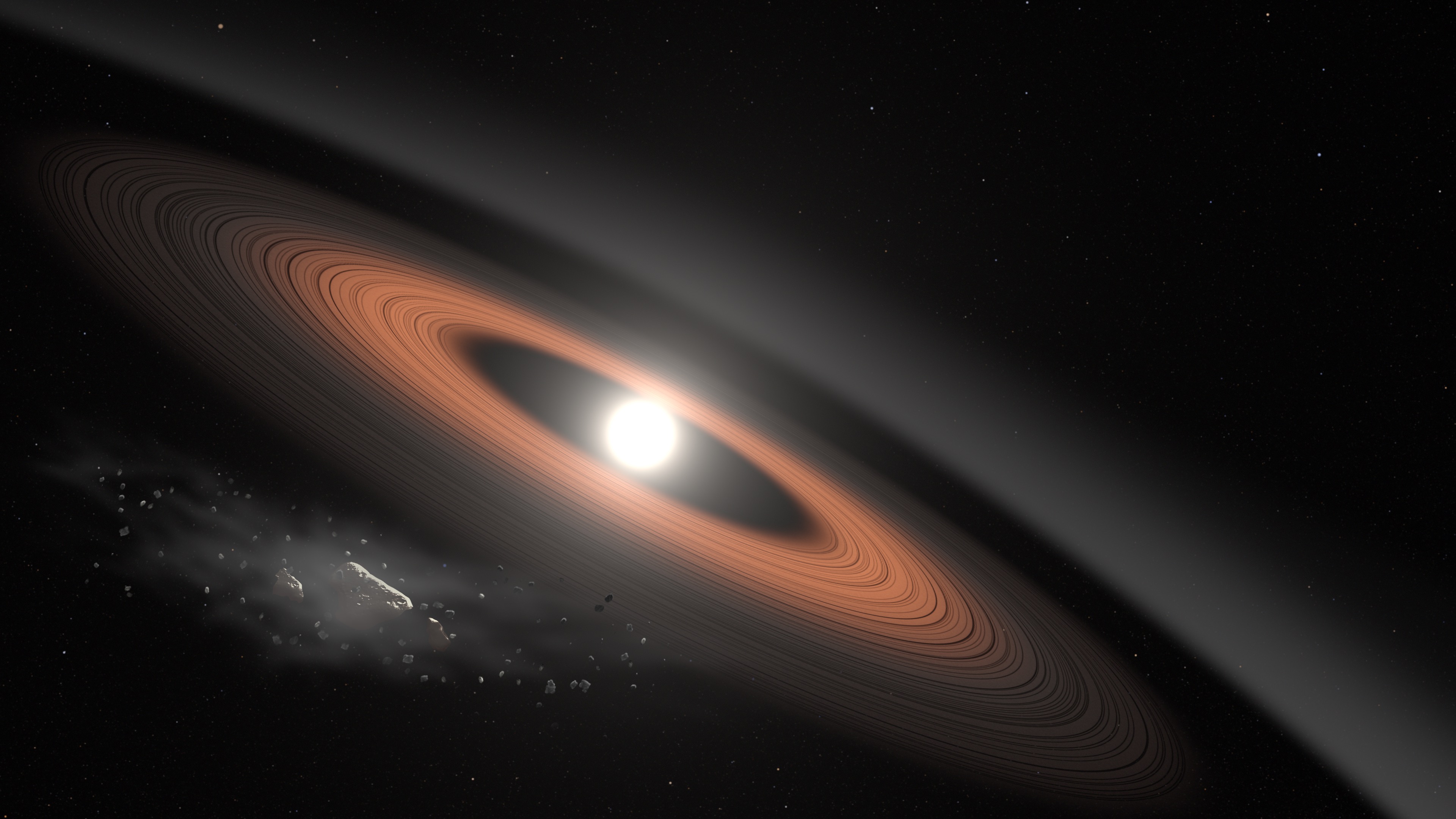

A citizen scientist recently discovered a white dwarf star that has multiple dust rings, a finding which could force a rethink of how planetary systems evolve.
Continue reading
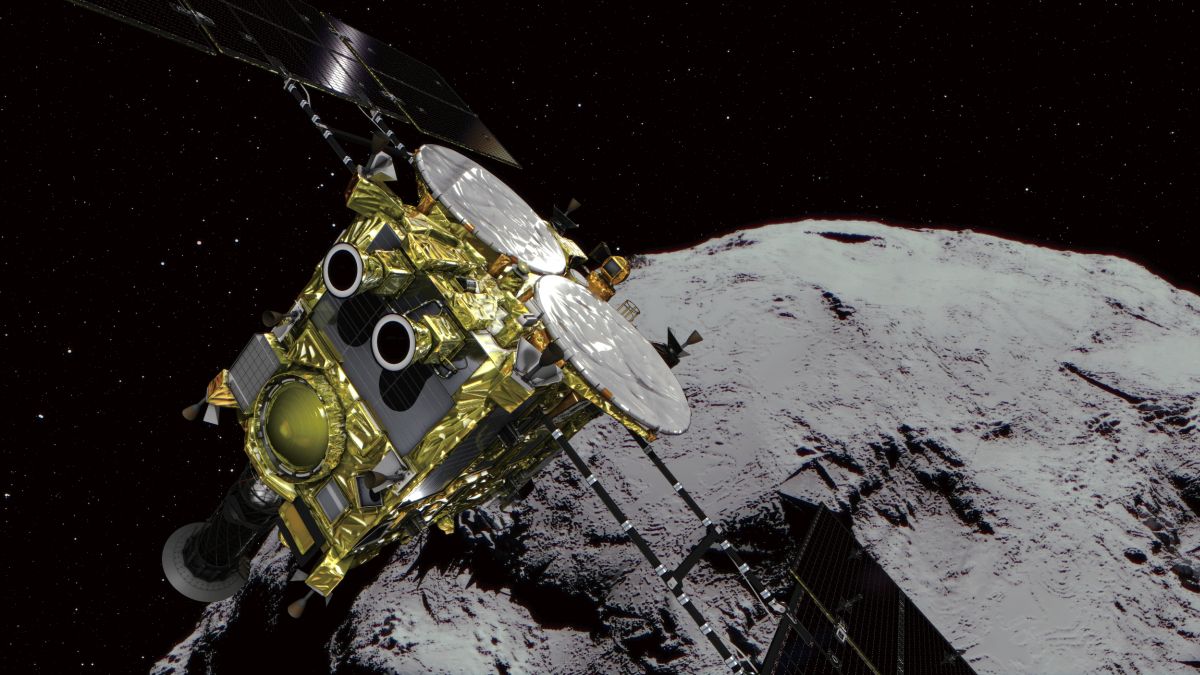

Continue reading

Continue reading
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading
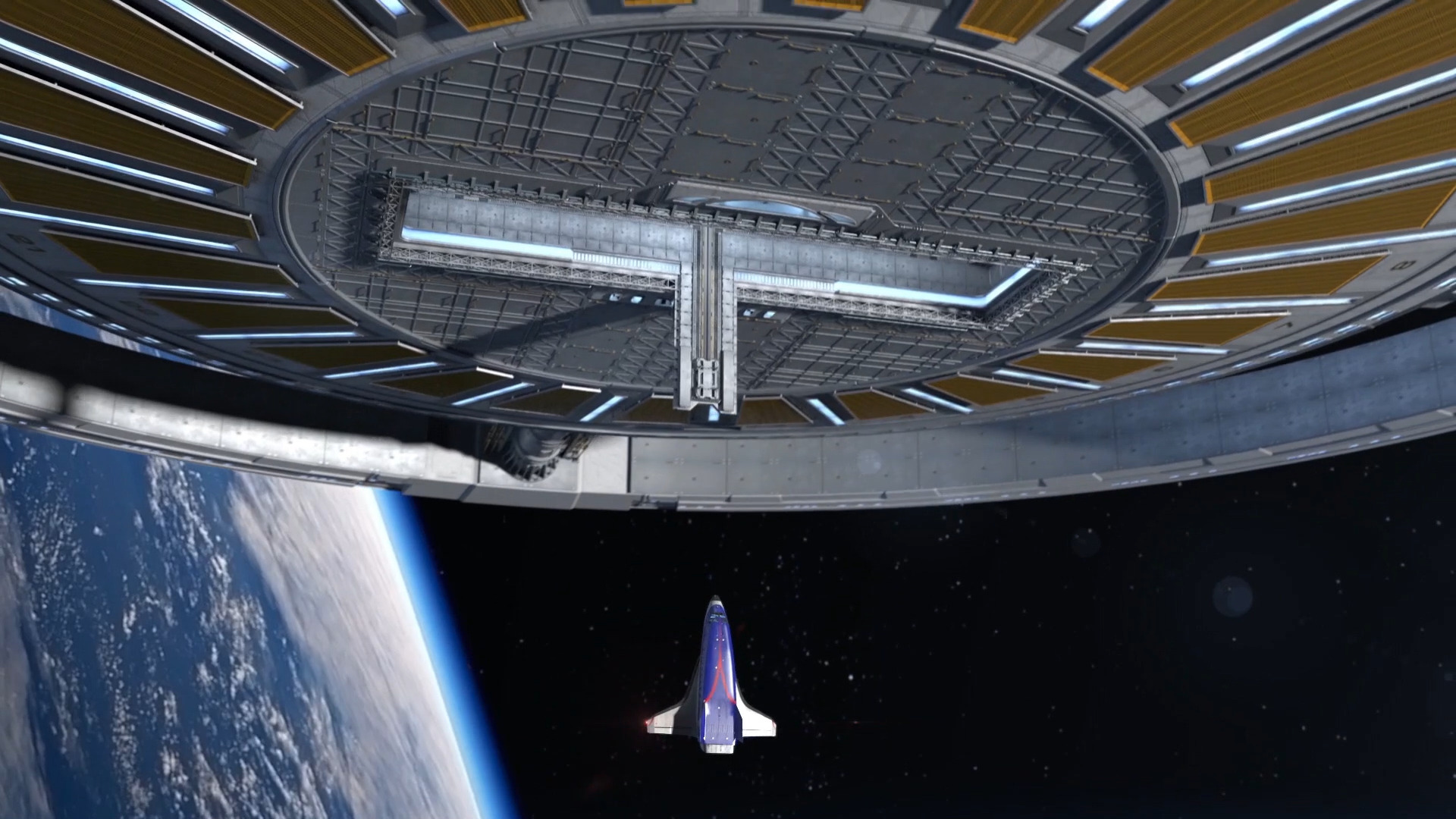

The Gateway Foundation is looking to build a rotating space station in orbit. And thanks to Elon Musk and his plans for the BFR, it might just be affordable!
Continue reading
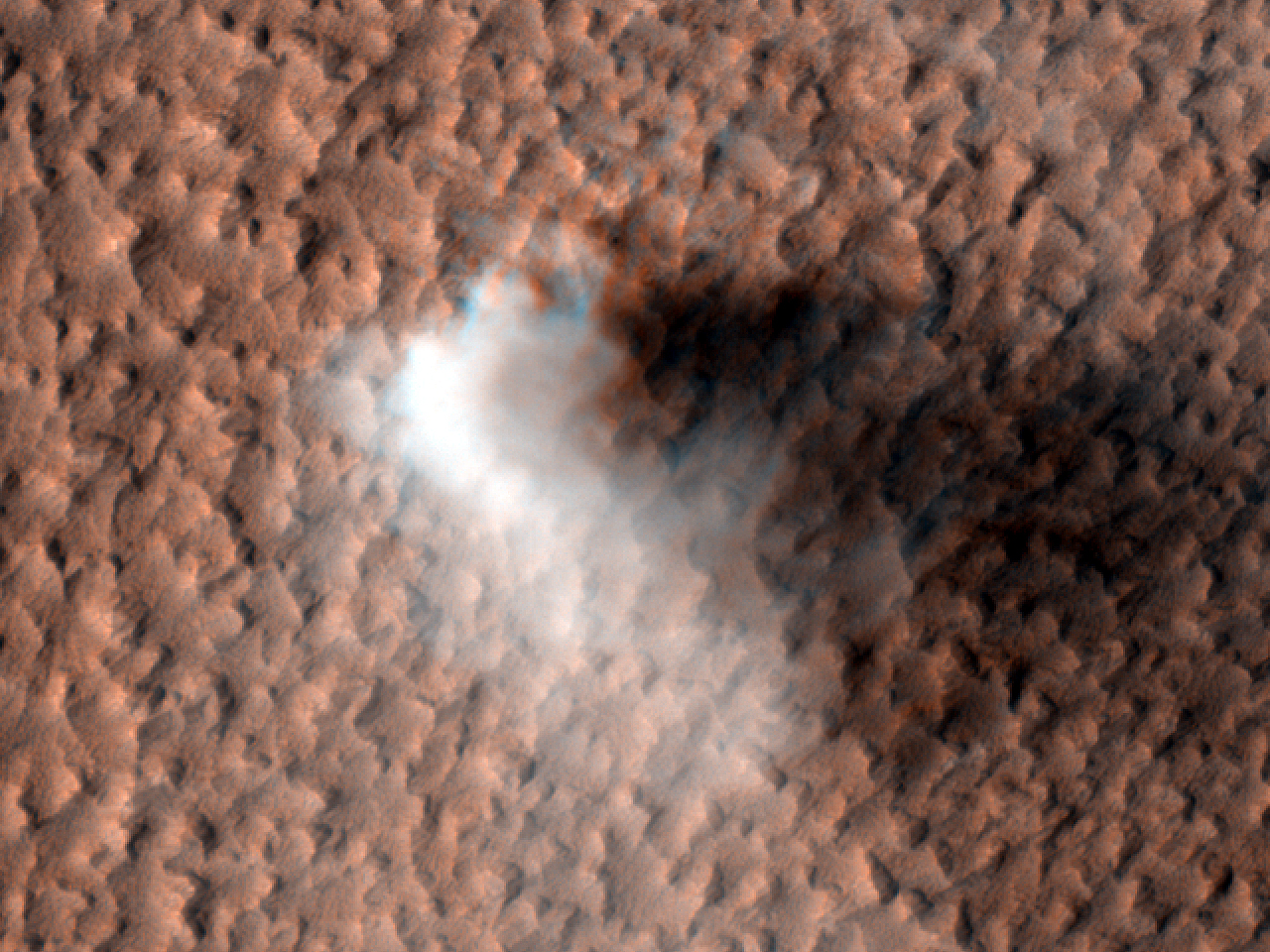

Continue reading
Continue reading

Continue reading
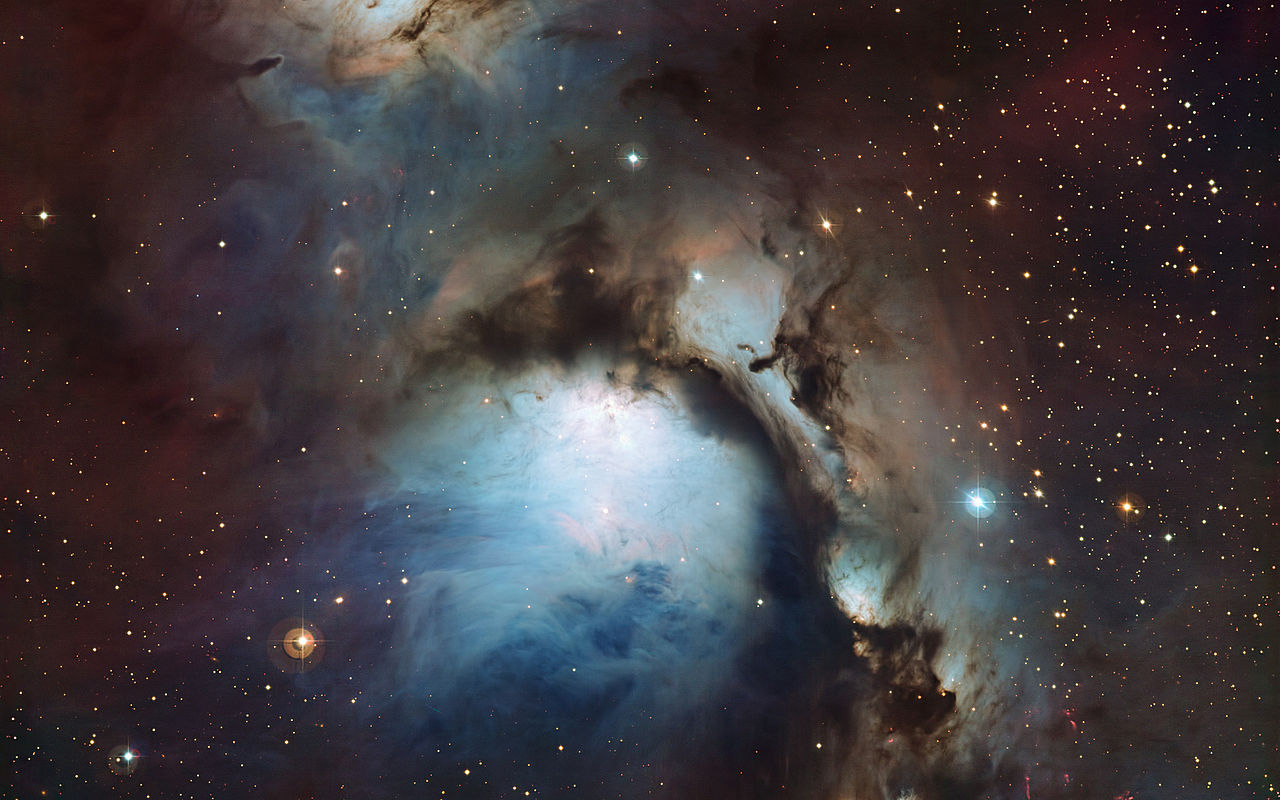

Located in the Orion Constellation, roughly 13,500 light years from Earth, is the bright reflection nebula known as Messier 78.
Continue reading
Continue reading

Continue reading
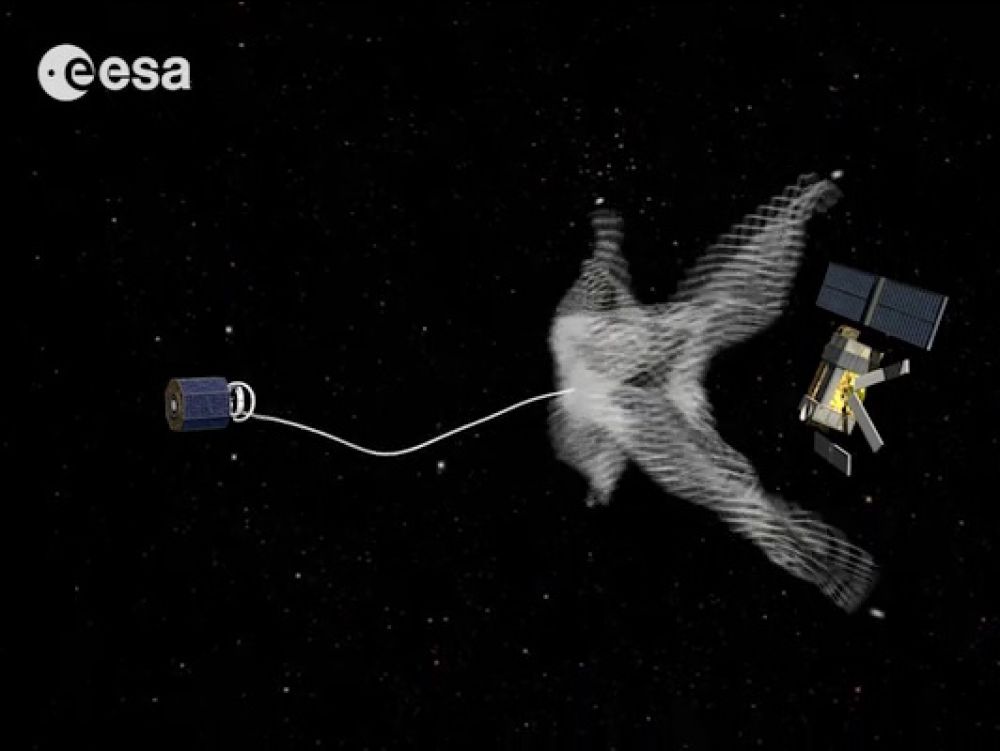

The RemoveDebris spacecraft recently tested out its harpoon, one of the tools it will use to remove space debris from Earth's orbit.
Continue reading
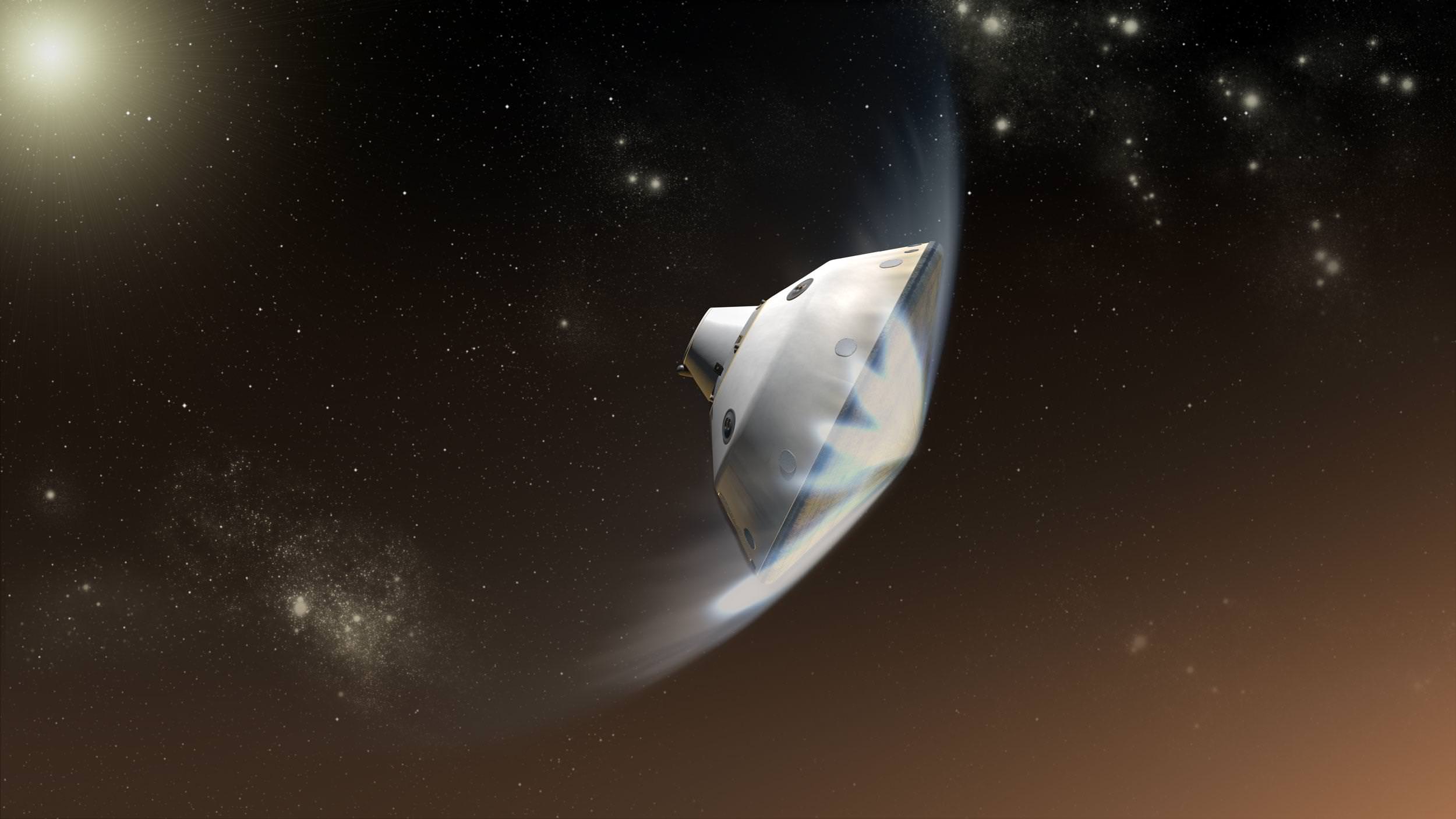

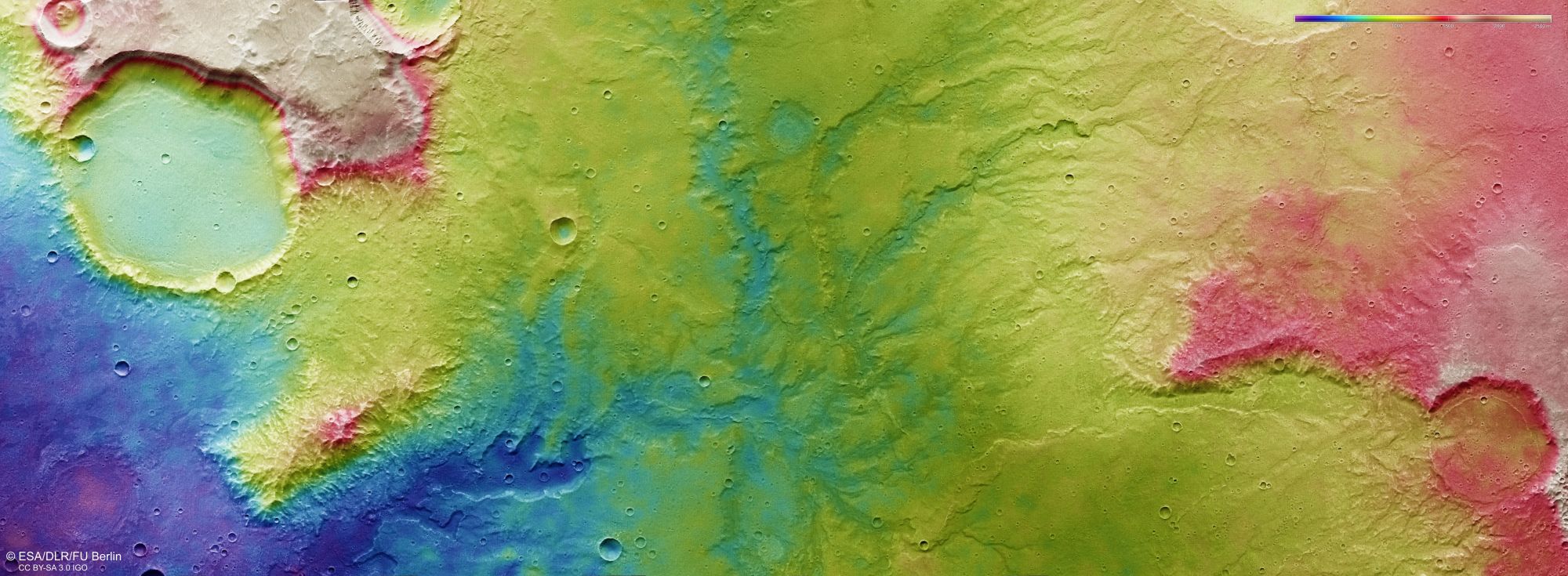
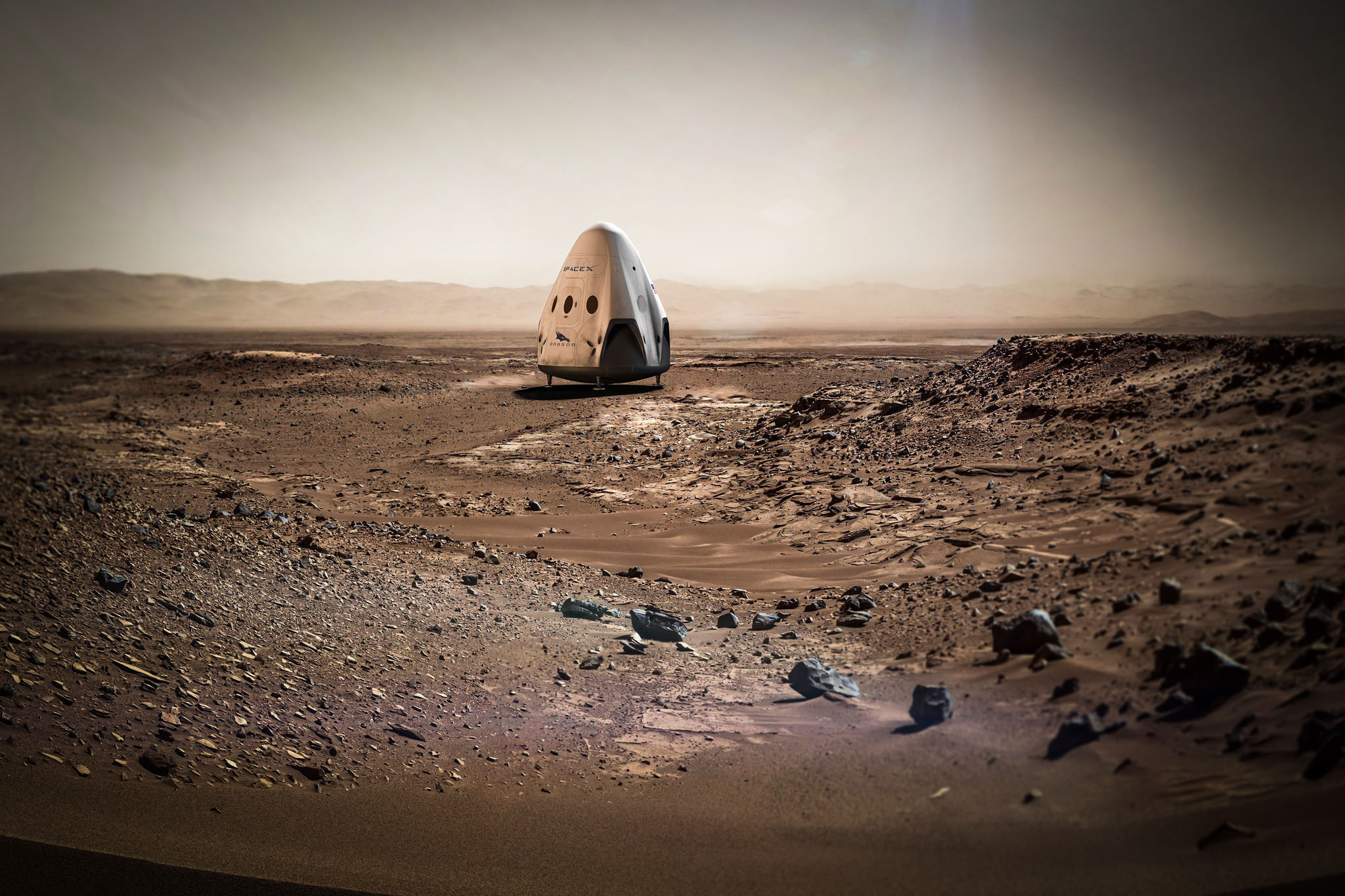
A team of researchers has devised a new strategy for landing heavier craft on Mars, which could allow for crewed missions to the Red Planet.
Continue reading
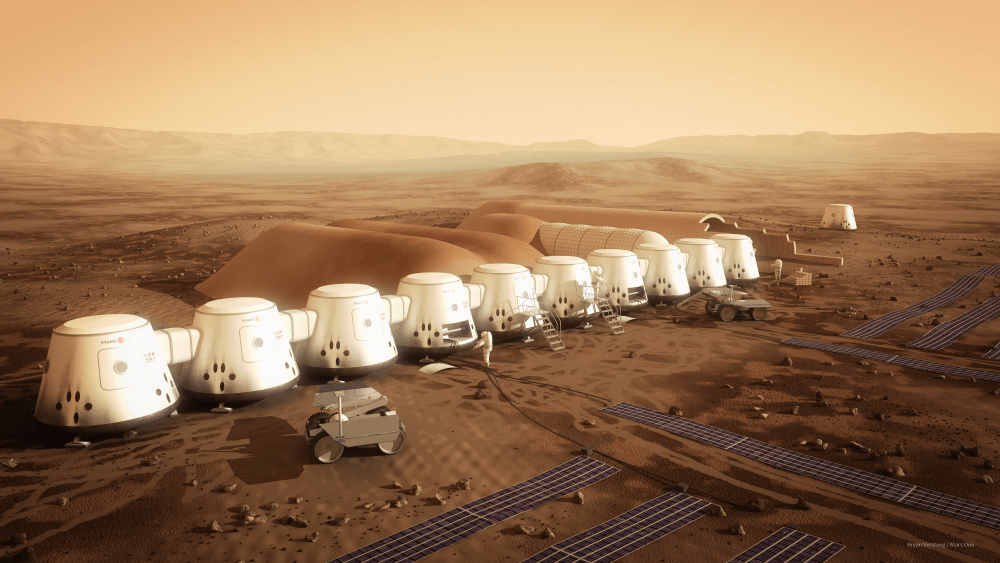

According to multiple sources, Mars One - the organization intent on crowdsourcing the colonization of Mars - is apparently bankrupt.
Continue reading
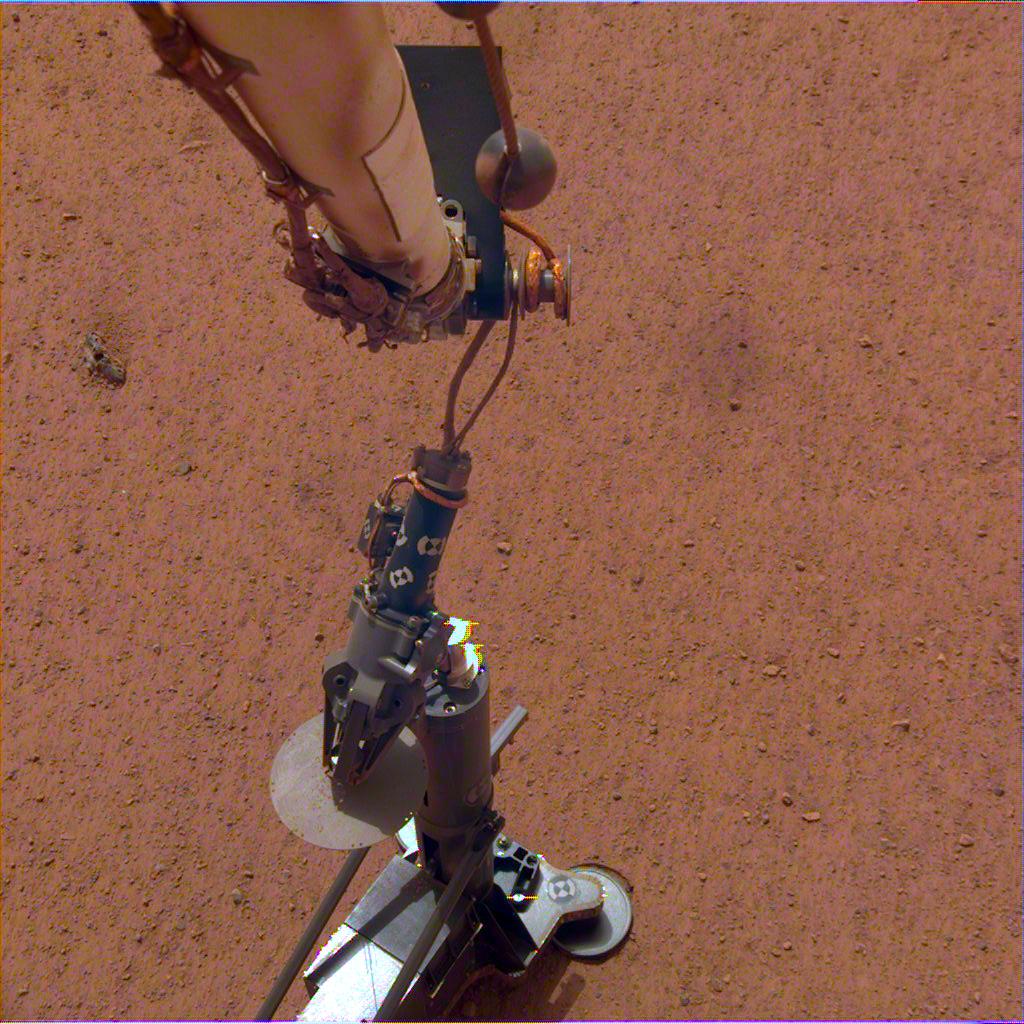
Continue reading
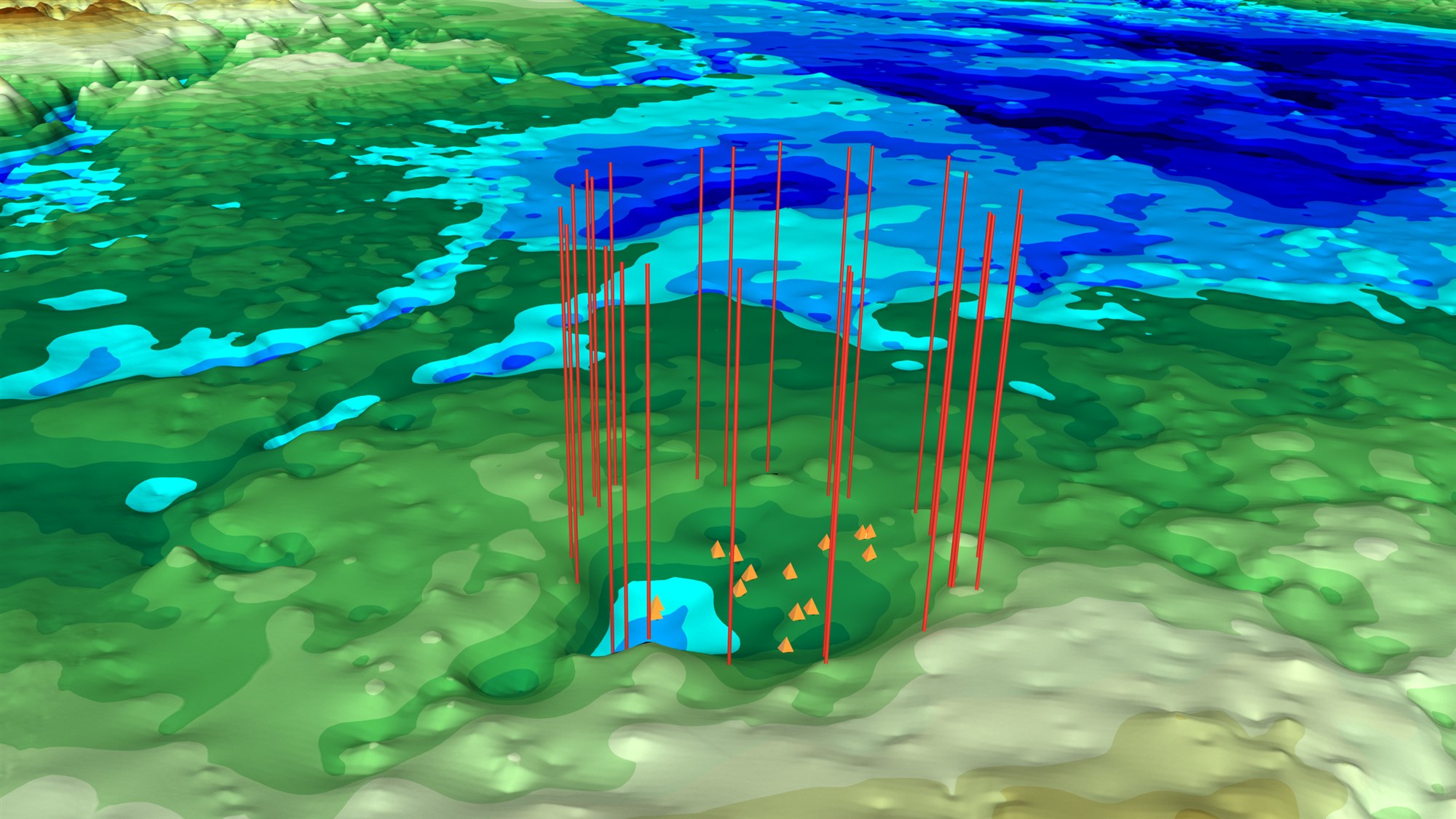
Continue reading
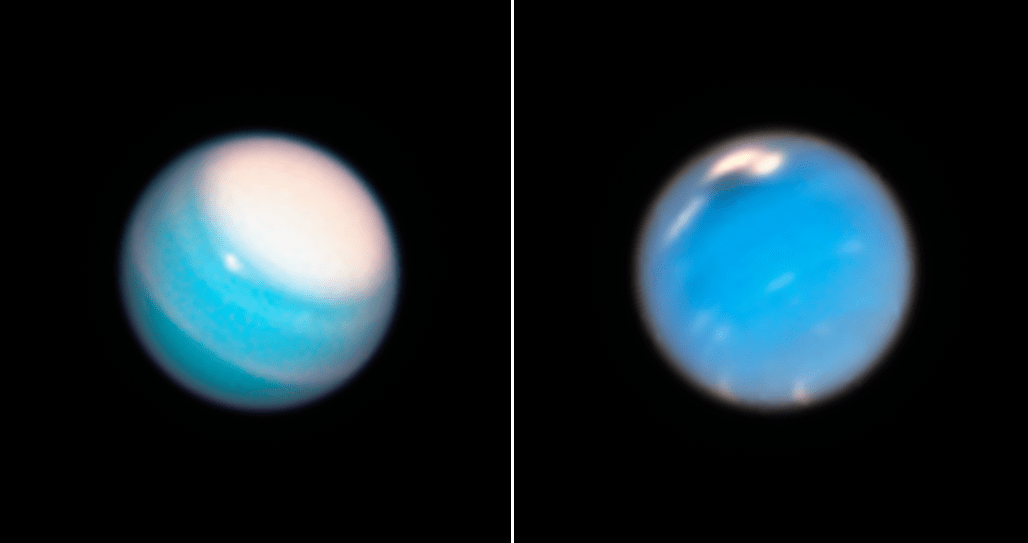
New images from Hubble have shown some interesting seasonal developments on Neptune and Uranus
Continue reading

Continue reading
Continue reading

Continue reading
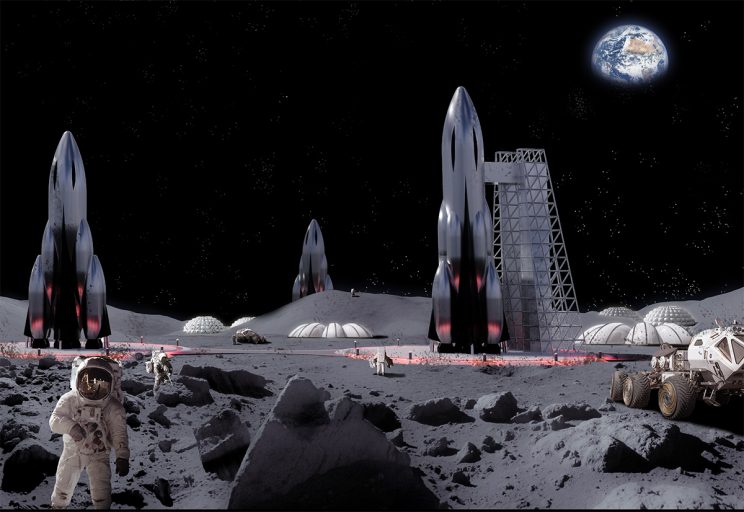

A student team associated with the ESA recently developed a concept for a Moon base that would rely on lunar regolith to provide protection.
Continue reading
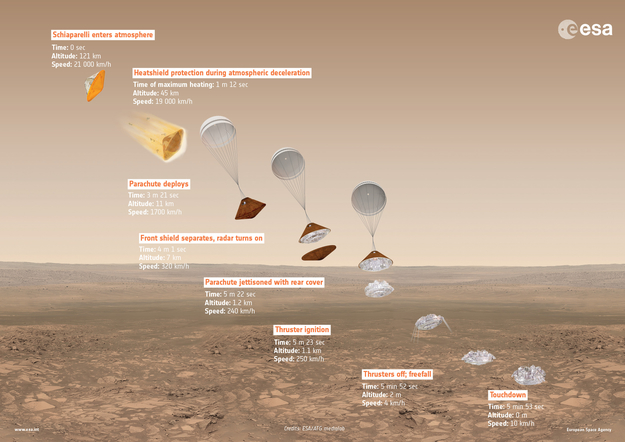
Continue reading
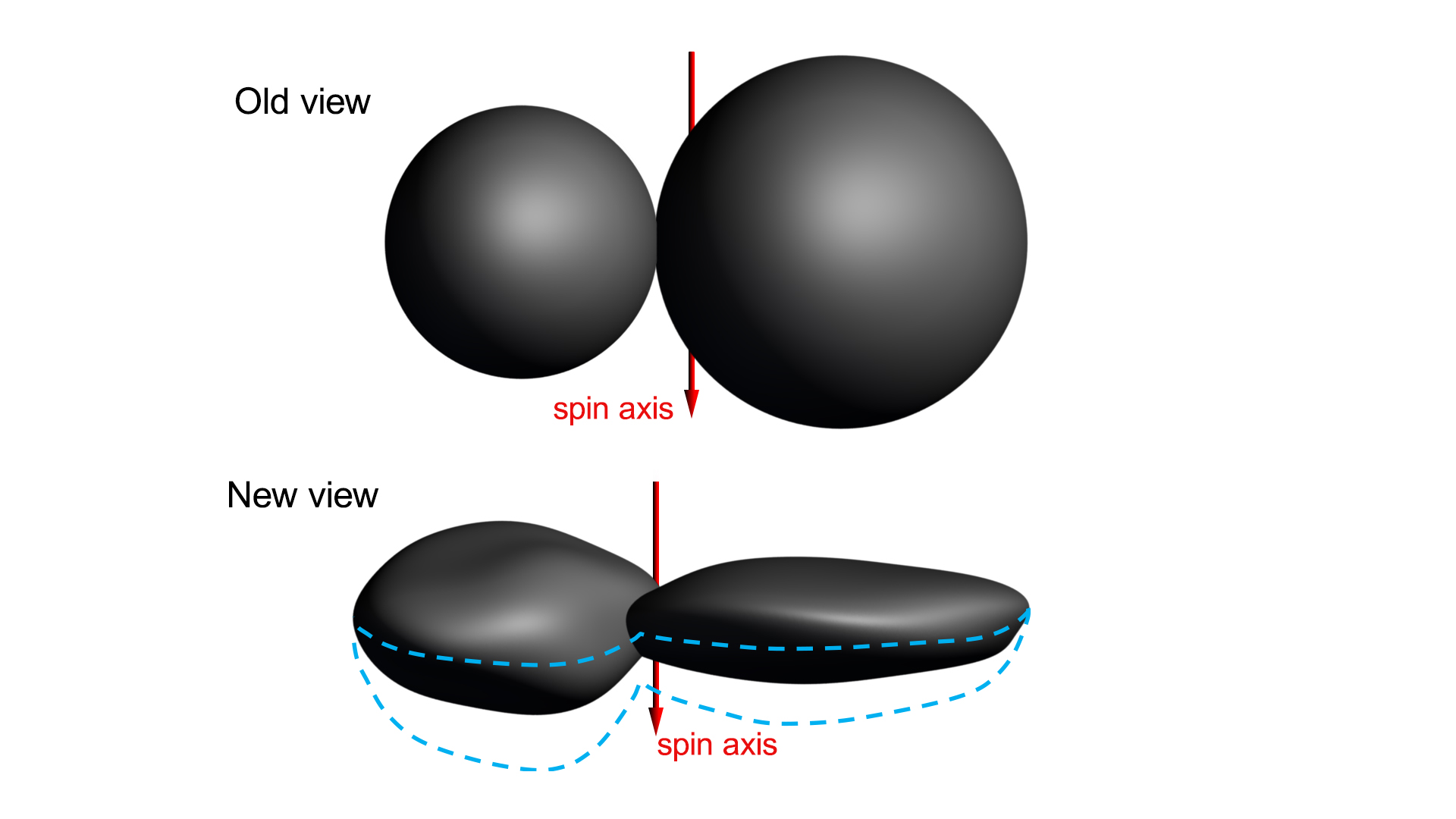
The latest images to come from the New Horizons mission show that Ultima Thule (the first KBO to be studied up close) has an unusual shape.
Continue reading
Continue reading

Continue reading
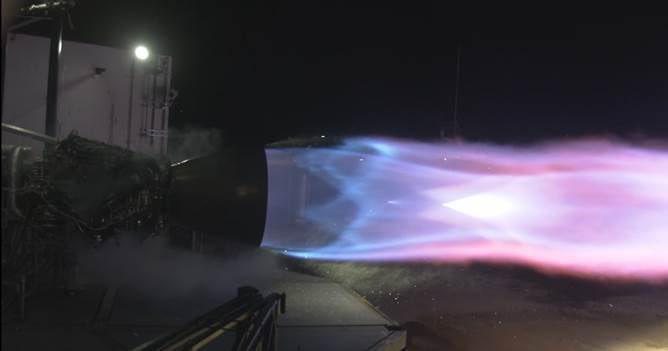
Elon Musk posted the results of the Raptor engine's recent test-firing, and claims it broke an almost 20-year old record!
Continue reading
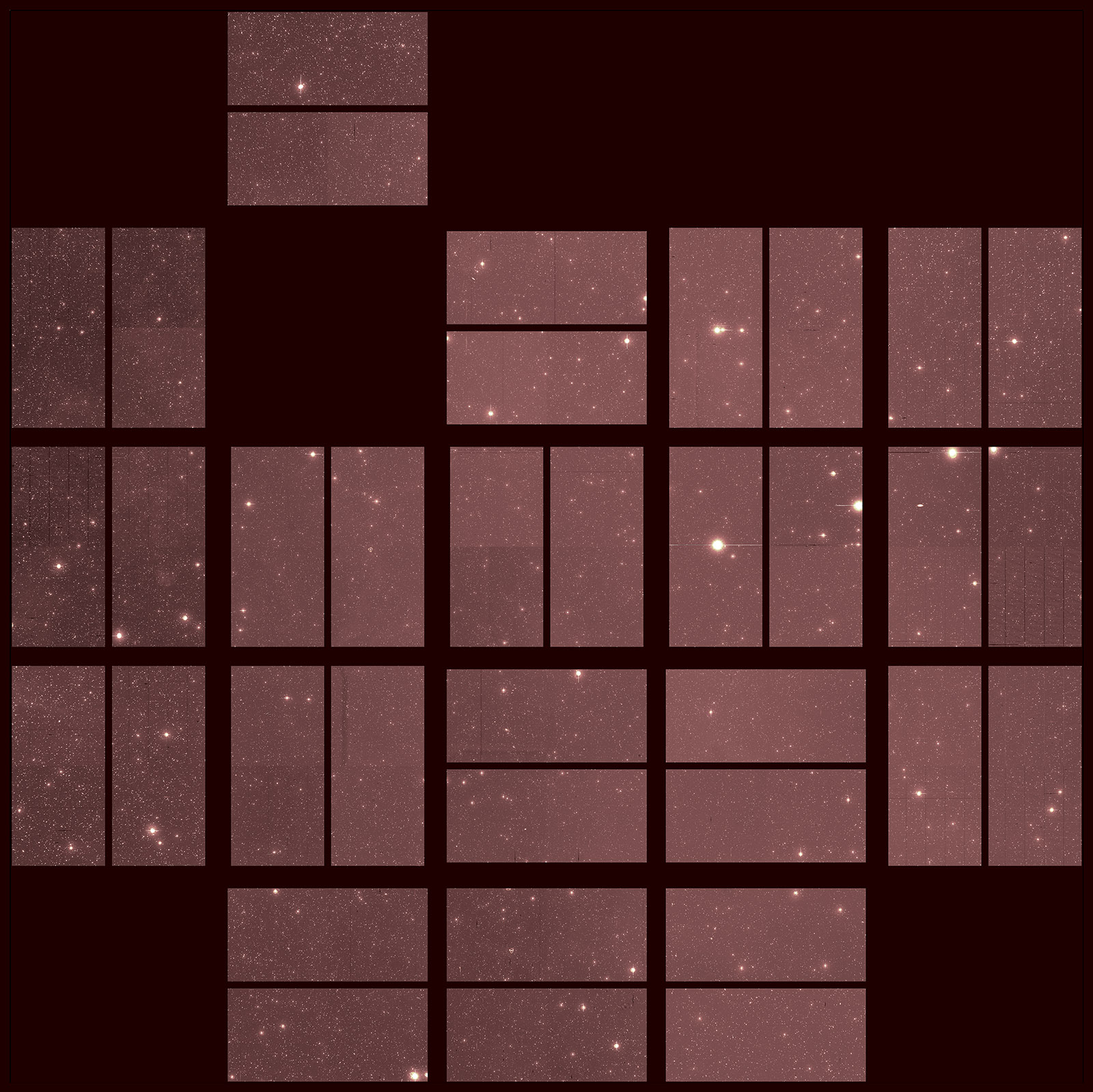

Even in retirement, the Kepler space telescope is still allowing for discoveries, which include it's "last light" images and recordings.
Continue reading
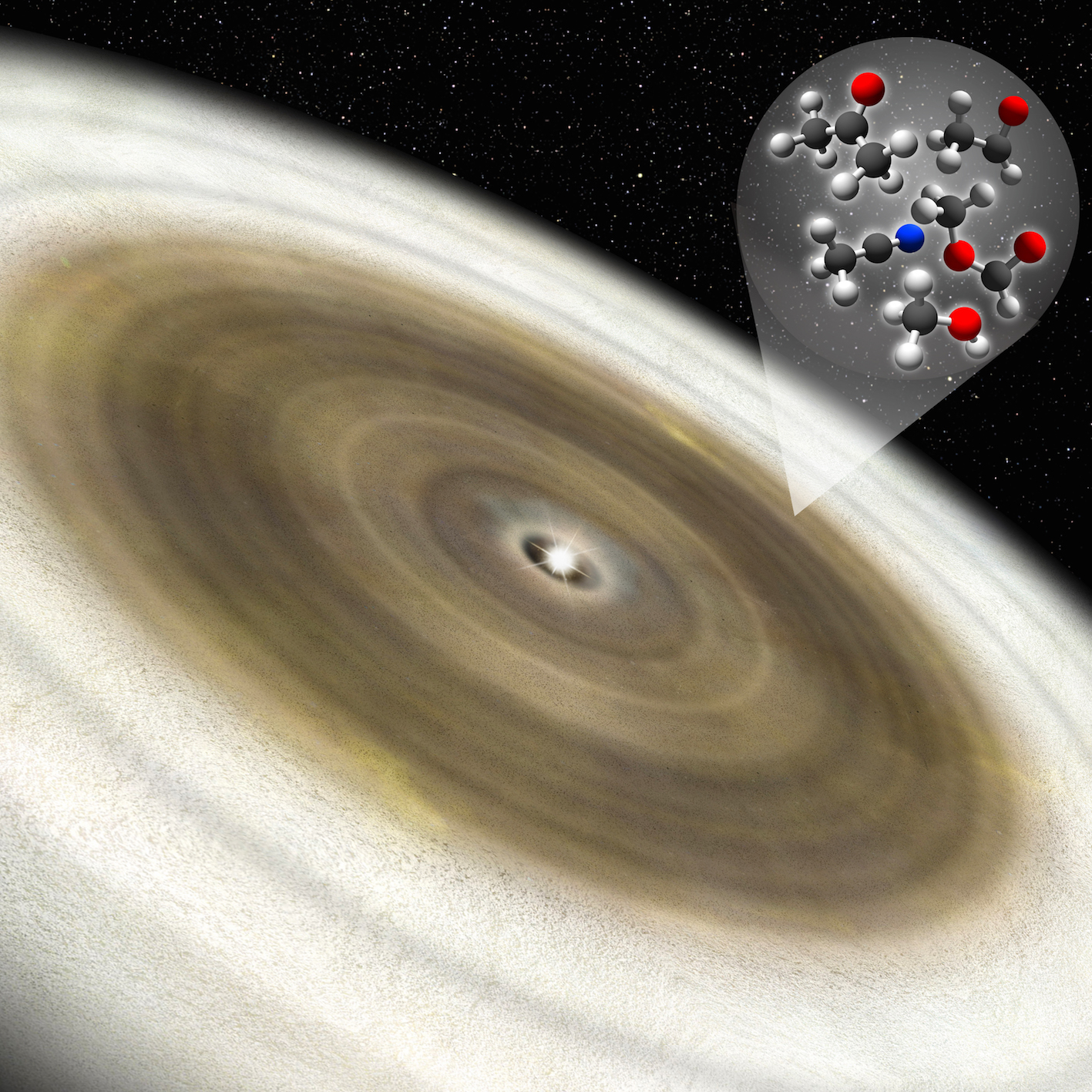

A new study by an international team of astronomers has discovered the presence of organic molecules in the disk of a young star.
Continue reading

Continue reading
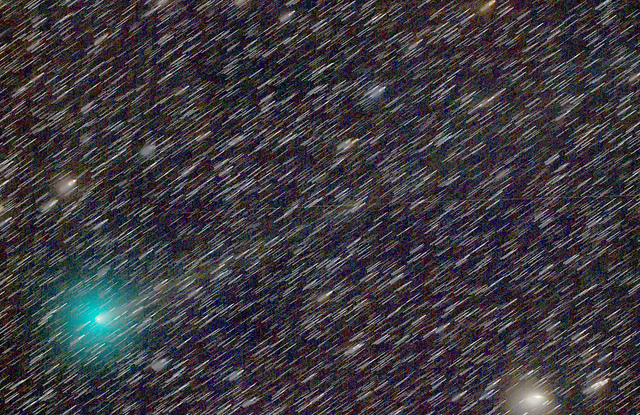

Every year produces a handful of binocular comets, and the first one for 2019 is coming right up, with a fine apparition for Comet C/2018 Y1 Iwamoto.
Continue reading

 Universe Today
Universe Today








































