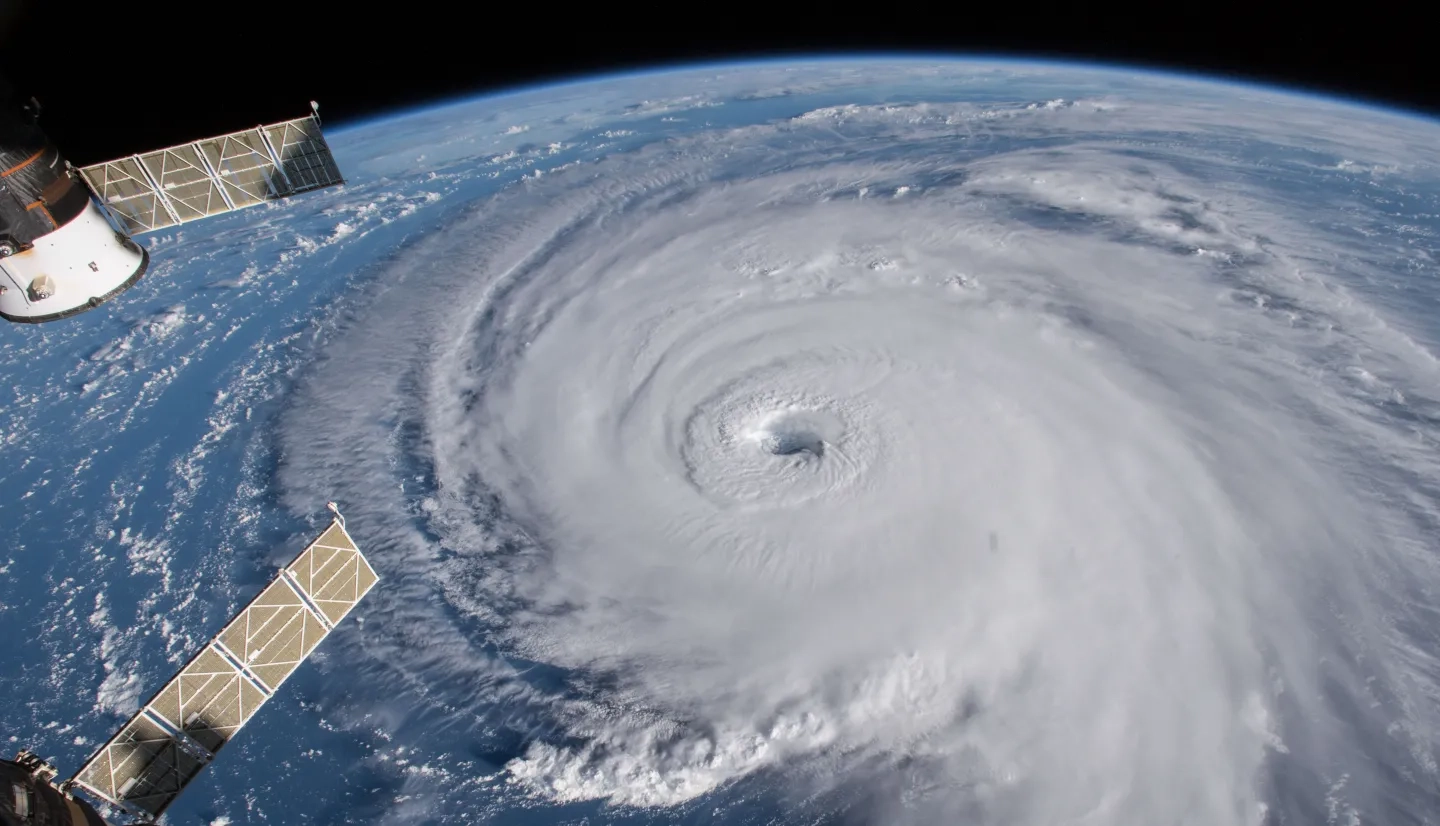

The increasing frequency of so-called '1-in-a-1000-year' weather events highlights how global warming is disrupting rather more typical weather patterns beyond what scientific models can reliably predict. A recent paper proposes a three-tier scientific approach for addressing these unprecedented climate challenges: improving rapid response capabilities, making incremental infrastructure adaptations, and pursuing transformational system changes to manage escalating climate chaos.
Continue reading
Continue reading

Continue reading
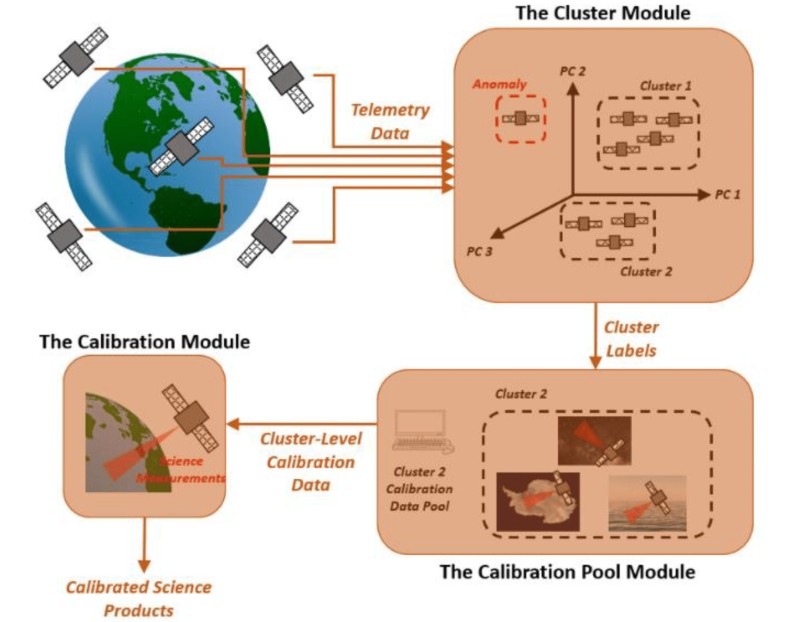
CubeSats have a lot of advantages. They are small, inexpensive, and easily reproducible. But those advantages also come with significant disadvantages - they have trouble linking into broader constellations that allow them to be more effective at their observational or communication tasks. A team from the University of Albany thinks they might have solved that problem by using a customized calibration algorithm to ensure the right CubeSats link up together.
Continue reading
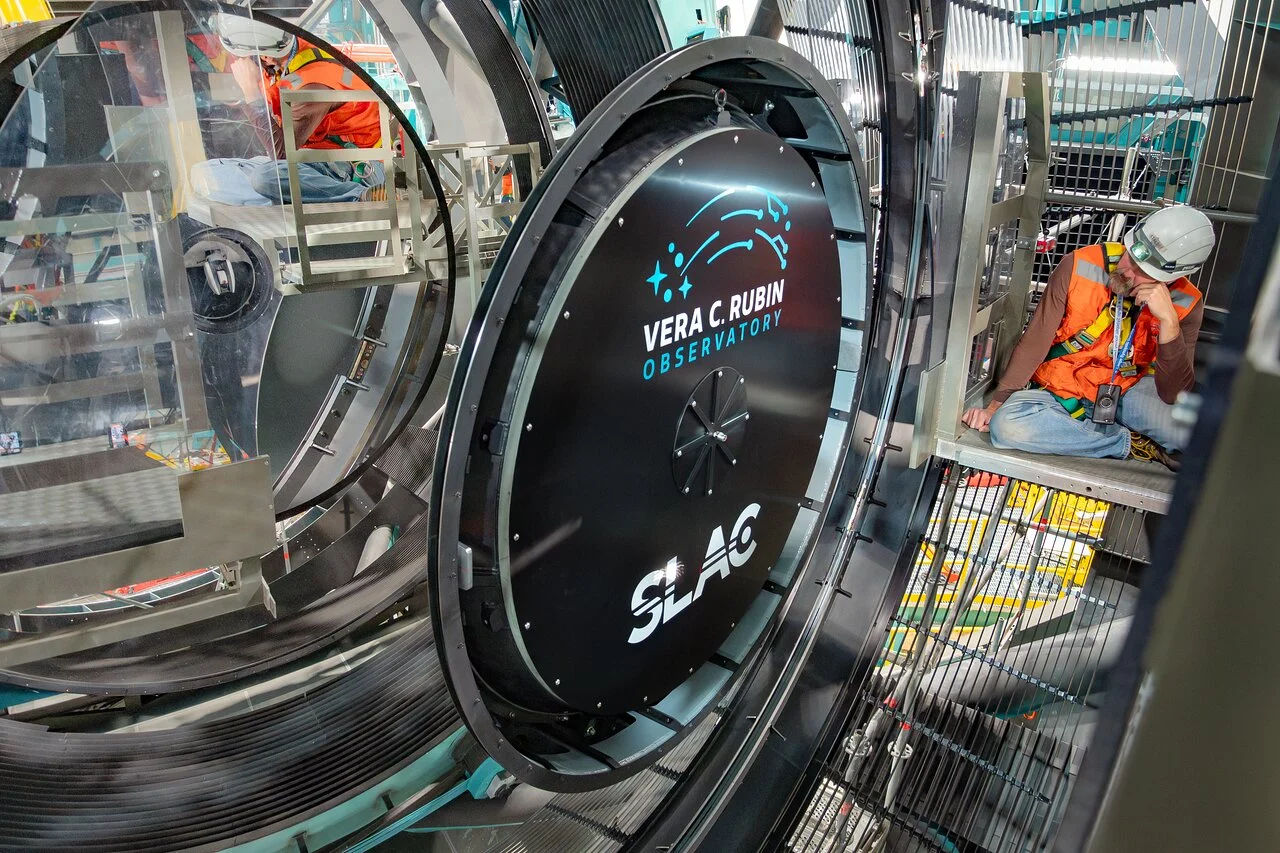

Located on a mountaintop in Chile, the nearly complete Vera C. Rubin Observatory will capture the Universe in incredible detail. This week saw another huge step for the observatory with the installation of the car sized - yes car sized - LSST camera onto the Simonyi Survey Telescope. The camera is the largest ever built, weighing in at over 3,000 kilograms with an impressive 3,200 megapixels. Coupled to the 8.4 metre optics of the Rubin will allow it to capture everything that happens in the southern sky, night after night.
Continue reading
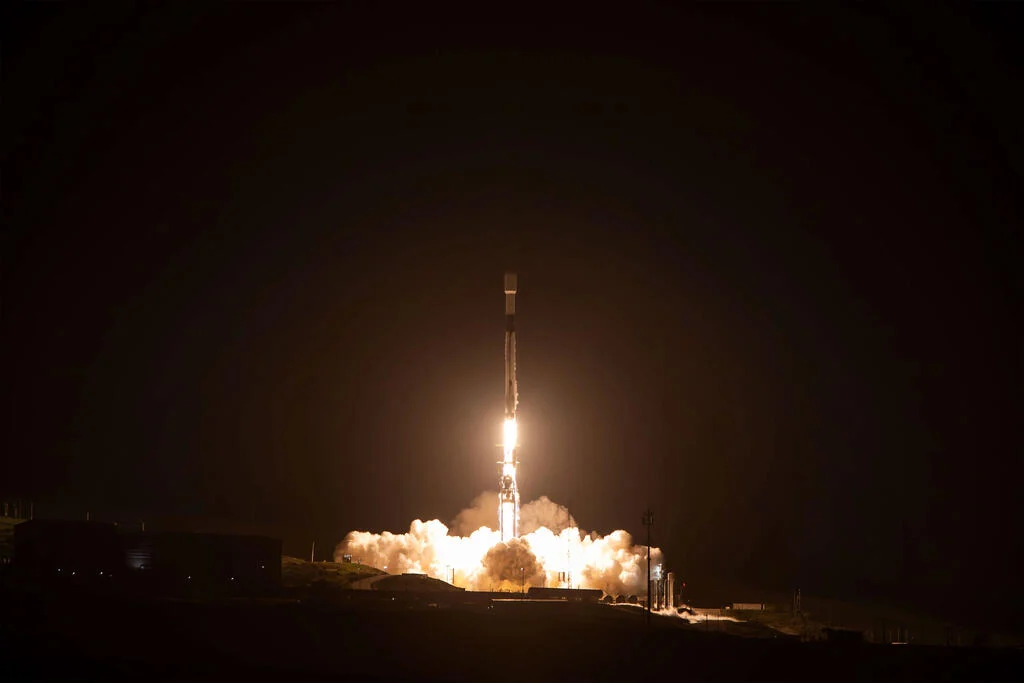

On March 11, the California skyline was once again treated to the launch of the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from the Vandenberg Space Force Base. It carried two missions into space; SPHEREx to study the origins of the Universe and the molecular clouds of the Milky Way and four other satellites making up PUNCH. This latter mission is tasked with exploring how the Sun's outer atmosphere causes the solar wind.
Continue reading
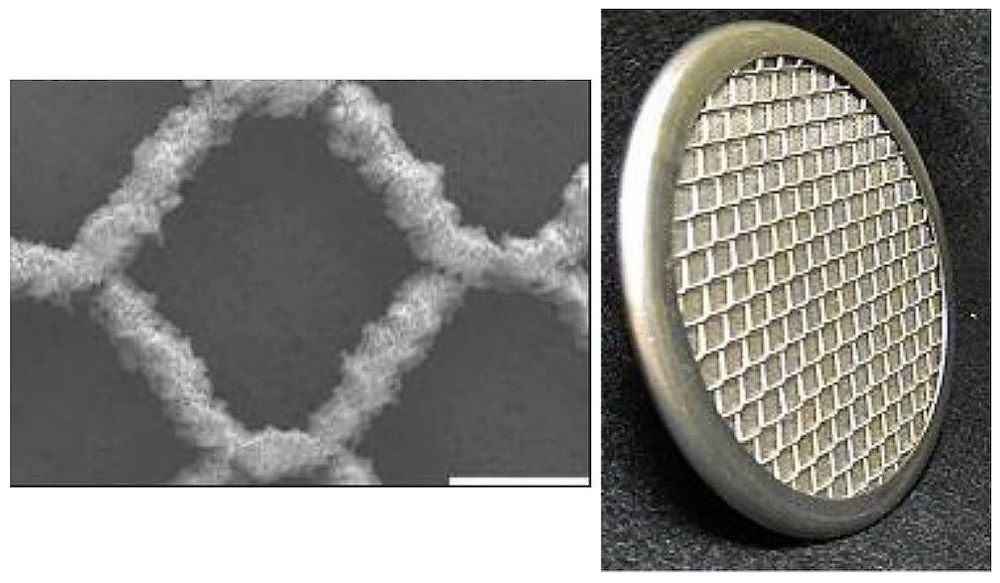
Electrolysis has been a mainstay of crewed mission designs for the outer solar system for decades. It is the most commonly used methodology to split oxygen from water, creating a necessary gas from a necessary liquid. However, electrolysis systems are bulky and power-intensive, so NASA has decided to look into alternative solutions. They supported a company called Precision Combustion, Inc (PCI) via their Institutes for Advanced Concepts (NIAC) grant to work on a system of thermo-photo-catalytic conversion that could dramatically outperform existing electrolysis reactors.
Continue reading
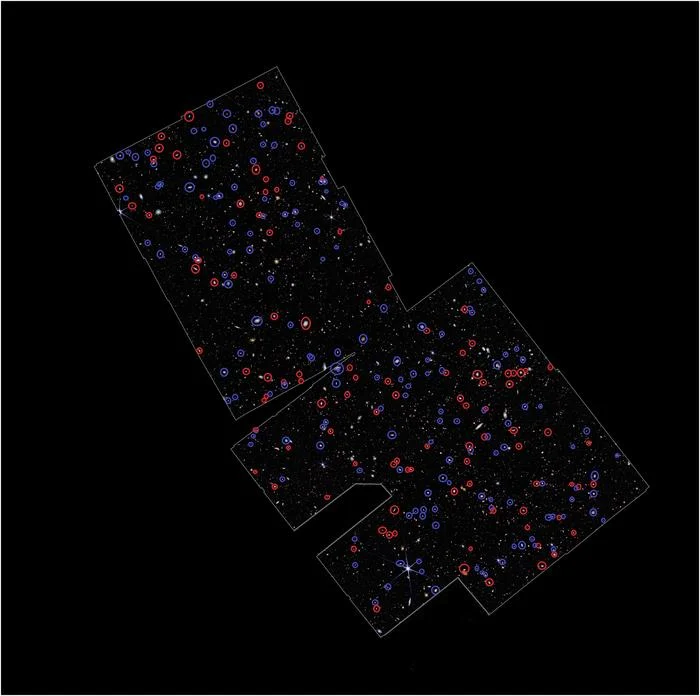
Astronomers using the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) have completed a survey of galaxies that reveals their rotation directions with unprecedented clarity. Contrary to expectations that galaxy rotations would be randomly distributed, they discovered a surprising pattern, that most galaxies appear to rotate in a similar direction! One hypothesis suggests the universe itself might have an overall rotation, researchers believe a more plausible explanation though is that Earth's motion through space creates an observational bias, making galaxies rotating in certain directions more detectable than others.
Continue reading
Continue reading

Dark matter - that mysterious, unknown stuff that's detectable only by its effect on other matter - seems to be sparking strong emissions at the heart of the Milky Way Galaxy.
Continue reading
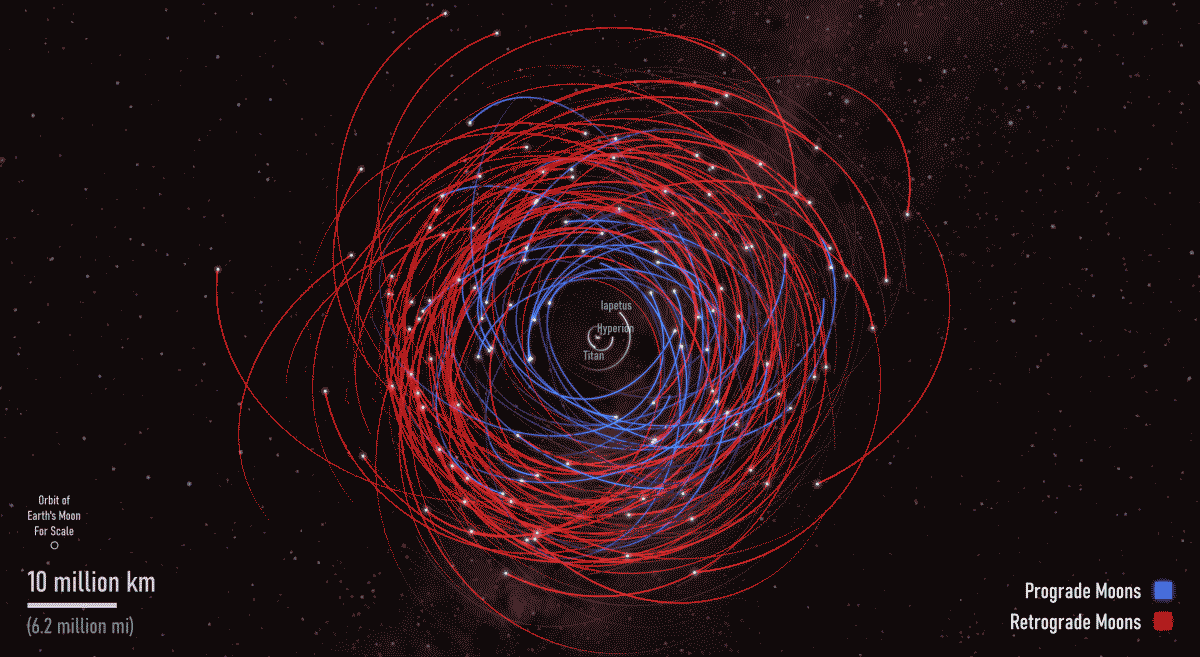
Dutch astronomer Christiaan Huygens was the first to discover a Saturnian moon way back in 1655. Thanks to his skill as a lens grinder and polisher, he was the first person to see Titan. Over the centuries, we've discovered many more moons orbiting the ringed planet. In a surprising announcement on March 11th, the Minor Planet Center announced the discovery of 128 more moons, almost doubling the previous number.
Continue reading
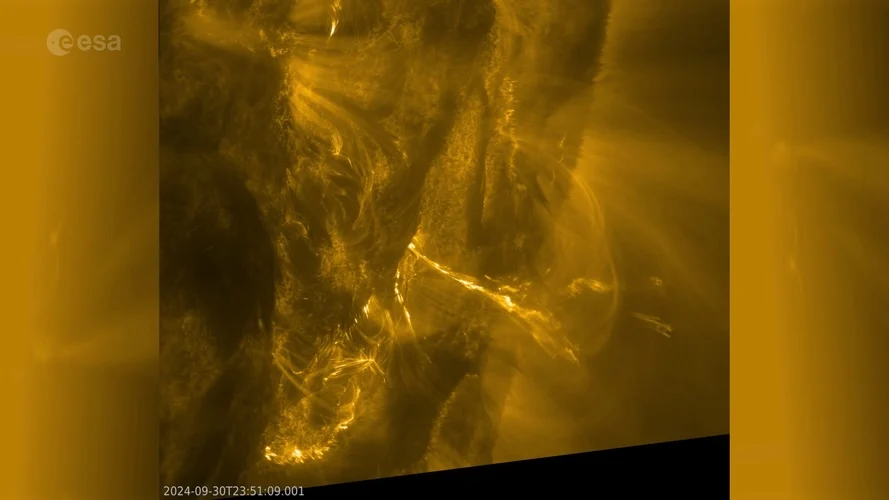
Our local star, the Sun has been under the watchful gaze of ESA's Solar Orbiter since its launch in 2020. It's been slowly getting closer and grabbing images using its Extreme Ultraviolet Imager (EUI) which citizen scientists have been stitching together into wonderful time-lapse videos. A recent video covers just 15 minutes of real time but within, you can see an M-Class flare that was unleashed by the Sun. The flares can produce brief radio blackouts here on Earth.
Continue reading

If you're a regular visitor to Universe Today, you've probably noticed that the website looks dramatically different. Simpler, cleaner, without all those pesky intrusive ads. We're in a new era, now. Here's what happened, why I decided to remove the ads from the site, and what you can expect going forward.
Continue reading
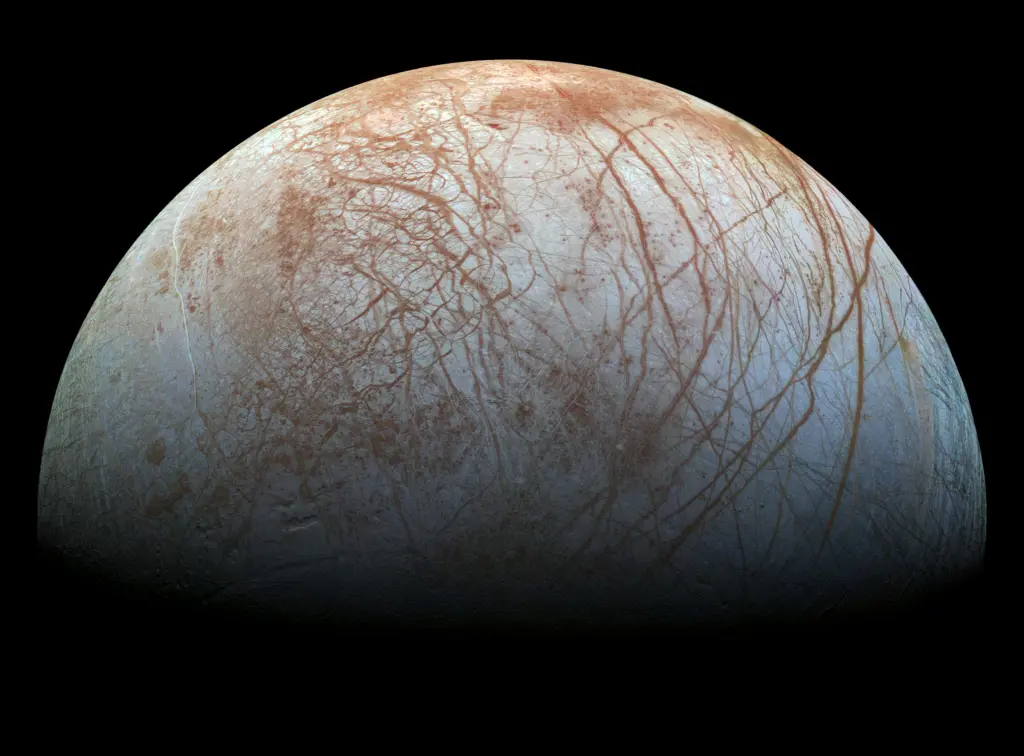

Of all the moons in the Solar System, Europa is perhaps one of the most fascinating. With a thick ice shell surrounding a subsurface ocean, astrobiologists hope maybe there is life down there! Finding a way through the ice to explore what's below is one of the biggest challenges. It's possible however that the vital chemicals from life could find their way to the surface and through out into space. A new paper proposes an ultraviolet laser could be used to cause amino acids to fluoresce giving away their presence.
Continue reading
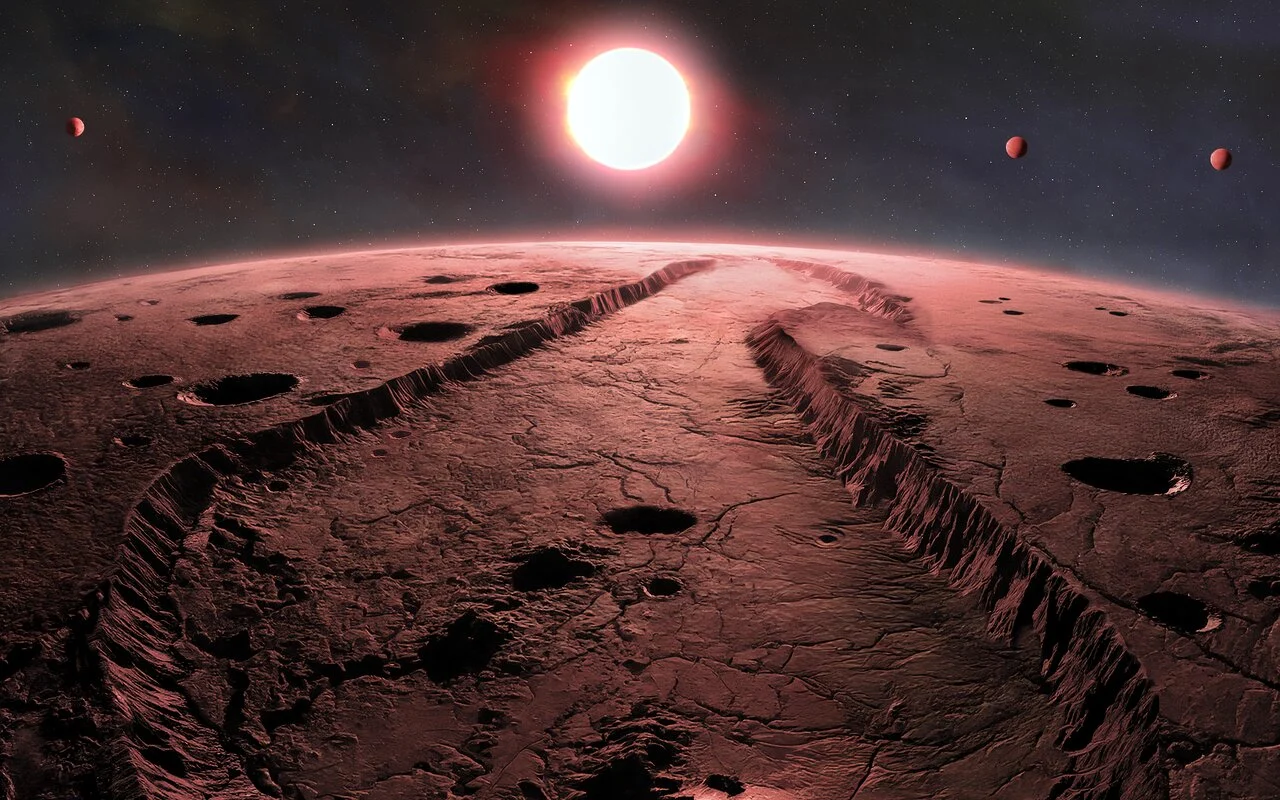

The closest single star to our own Solar System is Barnard's Star. It's 6 light years away and astronomers have just found four new mini-Earth planets in orbit around this red dwarf star. The discovery was made with the MAROON-X instrument on the Gemini North telescope which makes use of the radial velocity method to detect exoplanets. One planet was found in August 2024, the other three were only just added.
Continue reading
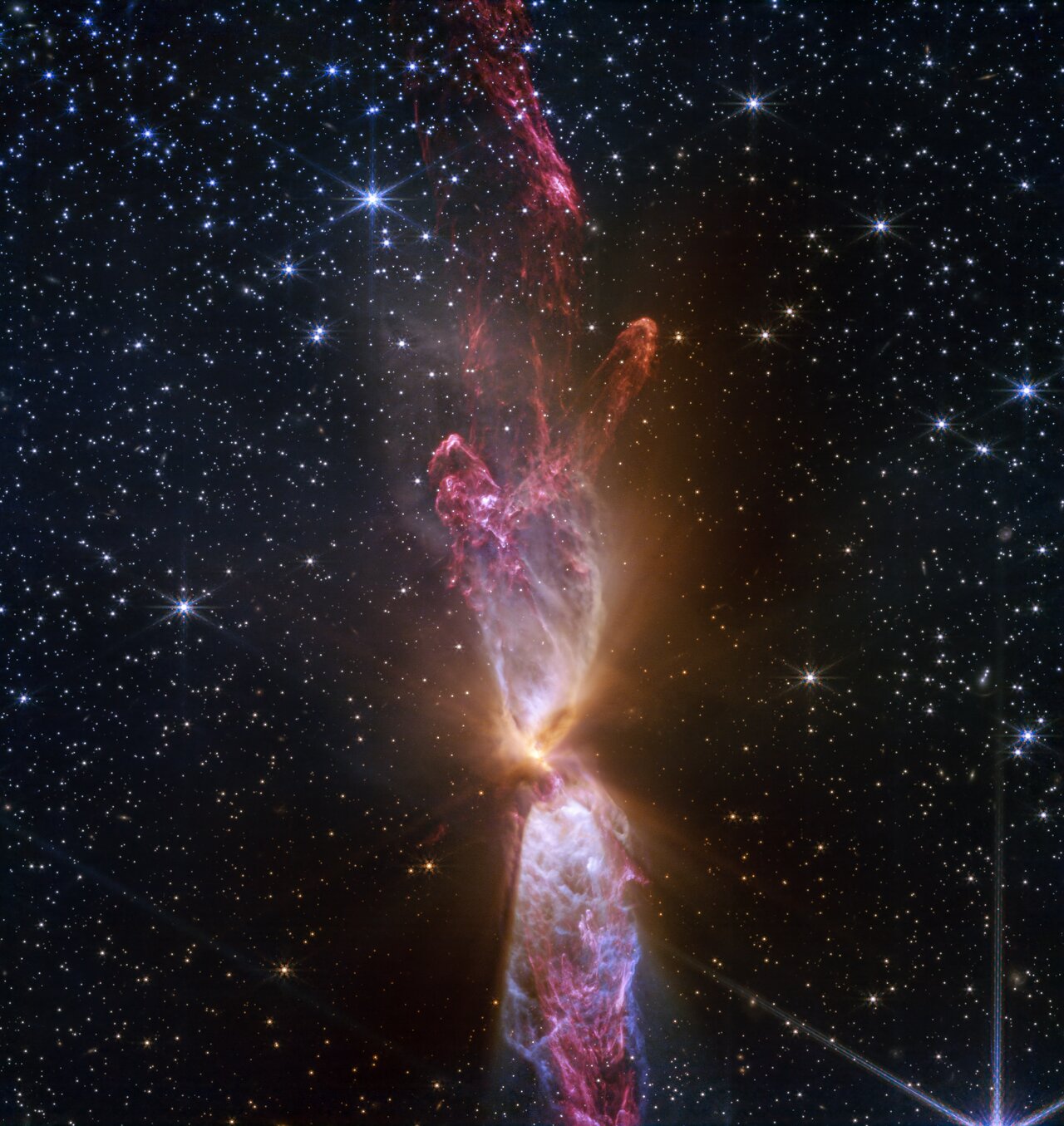

Young stars grow by gobbling up nearby gas and dust. Over time, they can become extremely massive. The most massive stars we know of have up to 200 solar masses. But the flow of matter isn't a one-way street. Instead, young protostars eject some of the matter back into space with powerful jets.
Continue reading

Looking back in time can seem like a sci-fi fantasy. But the nature of the Universe allows us to do it if we have the right telescope. The JWST is the right telescope, and as part of its observations, it frequently examines ancient galaxies whose light is only reaching us now. One of those ancient galaxies is both bright and enriched with metals, both signs of maturity.
Continue reading
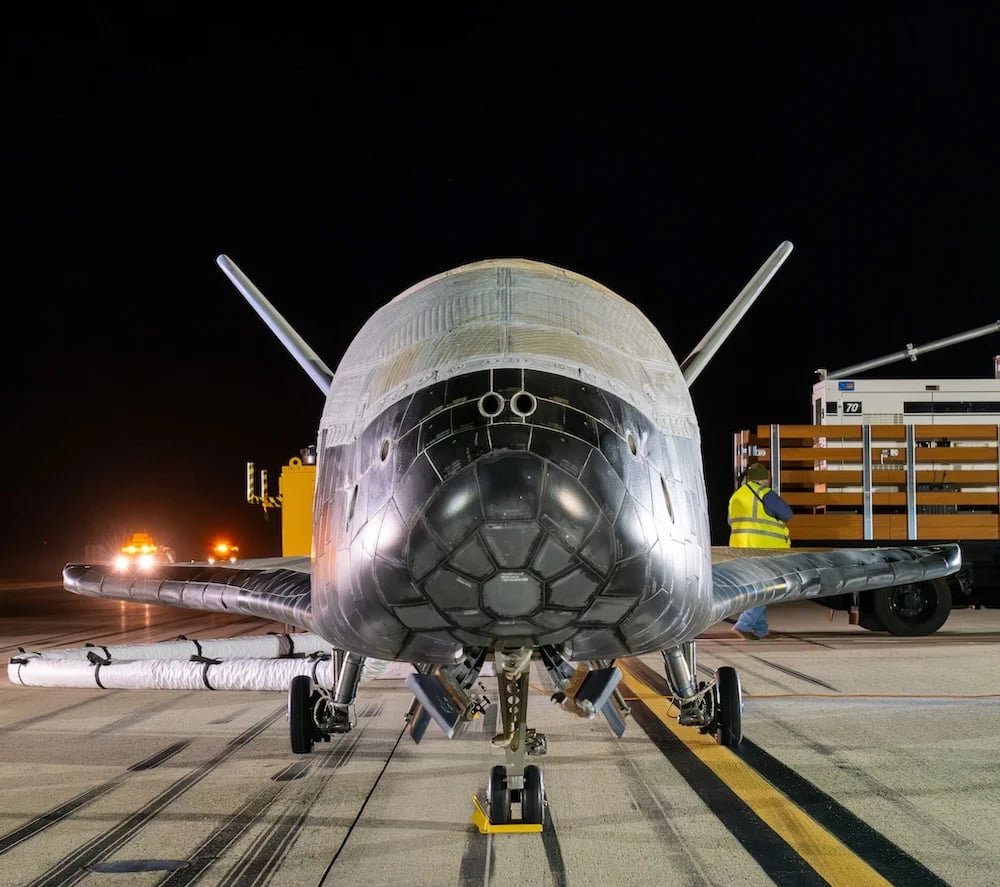

The U.S. Space Force's X-37B spaceplane (which looks remarkably like a Space Shuttle that someone forgot to put the windows in!) completed its seventh mission this week, touching down at Vandenberg Space Force Base after 434 days in orbit. Although the mission is classified, Space Force officials, said that it followed a highly elliptical orbital path while conducting various tests and experiments. They also described the mission as operating "across orbital regimes," whatever that means…is classified!
Continue reading
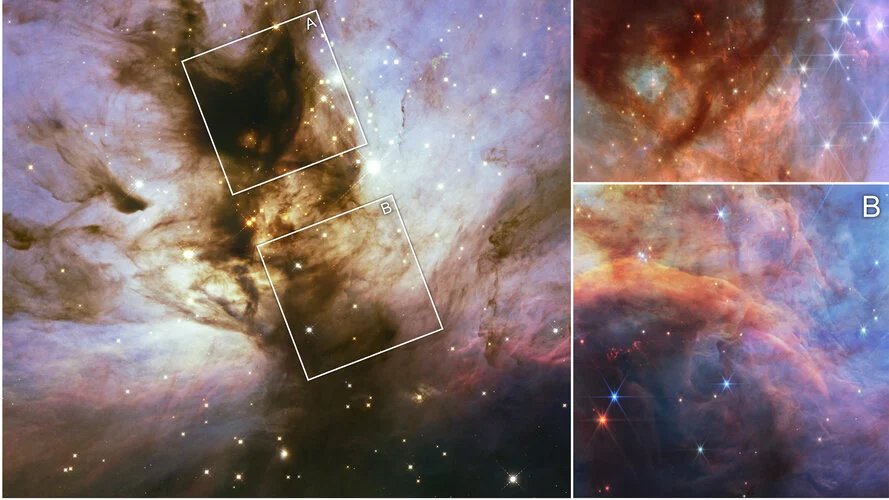

Astronomers know the Flame Nebula well—a stellar nursery around 1,400 light years away. It's less than a million years old and is teeming with brown dwarfs, objects that never quite accumulated enough mass to begin fusing elements in their core. When comparing the James Webb Space Telescope's (JWST) infrared observations with Hubble's visible light images of the Flame Nebula, the difference is, ahem - astronomical! The infrared wavelengths penetrate the obscuring gas and dust, revealing clusters where young stars and brown dwarfs are taking shape.
Continue reading

Firefly Aerospace's Blue Ghost Mission has successfully touched down on the lunar surface and is now undertaking various experiments. Two of these experiments have been captured on video; the first is the LISTER drill, capable of penetrating the lunar regolith to depths of up to 3 meters. It will provide scientists with data to measure the Moon's cooling rate. Additionally, footage has been obtained of the PlanetVac experiment, which is evaluating regolith sample collection methods under the Moon's vacuum conditions.
Continue reading

 Universe Today
Universe Today

















