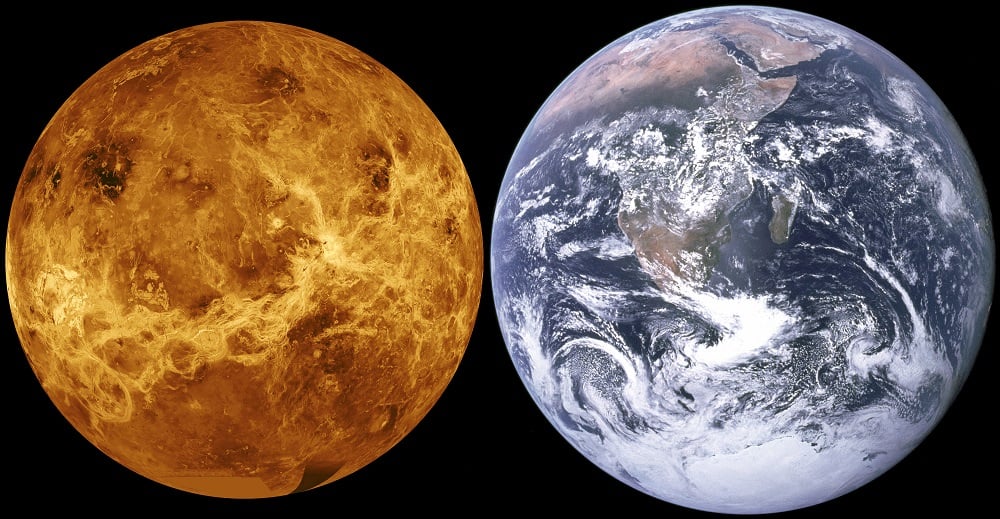
For many reasons, Venus is sometimes referred to as "
Earth's Twin
" (or "Sister Planet", depending on who you ask). Like Earth, it is terrestrial (i.e. rocky) in nature, composed of silicate minerals and metals that are differentiated between an iron-nickel core and silicate mantle and crust. But when it comes to their respective atmospheres and magnetic fields, our two planets could not be more different.
For some time, astronomers have struggled to answer why Earth has a magnetic field (which allows it to retain a thick atmosphere) and Venus do not. According to a
new study
conducted by an international team of scientists, it may have something to do with a massive impact that occurred in the past. Since Venus appears to have never suffered such an impact, its never developed the dynamo needed to generate a magnetic field.
The study, titled "
Formation, stratification, and mixing of the cores of Earth and Venus ", recently appeared in the scientific journal *Earth and Science Planetary Letters*. The study was led by Seth A. Jacobson of Northwestern University, and included members from the Observatory de la
Côte d'Azur,
the University of Bayreuth,
the Tokyo Institute of Technology, and the Carnegie Institution of Washington.
[caption id="attachment_120189" align="aligncenter" width="580"]
The Earth's layers, showing the Inner and Outer Core, the Mantle, and Crust. Credit: discovermagazine.com
[/caption]
For the sake of their study, Jacobson and his colleagues began considering how terrestrial planets form in the first place. According to the most widely-accepted models of planet formation, terrestrial planets are not formed in a single stage, but from a series of accretion events characterized by collisions with planetesimals and planetary embryos - most of which have cores of their own.
Recent studies on high-pressure mineral physics and on orbital dynamics have also indicated that planetary cores develop a stratified structure as they accrete. The reason for this has to do with how a higher abundance of light elements are incorporated in with liquid metal during the process, which would then sink to form the core of the planet as temperatures and pressure increased.
Such a stratified core would be incapable of convection, which is believed to be what allows for Earth's magnetic field. What's more, such models are incompatible with seismological studies that indicate that Earth's core consists mostly of iron and nickel, while approximately 10% of its weight is made up of light elements - such as silicon, oxygen, sulfur, and others. It's outer core is similarly homogeneous, and composed of much the same elements.
As Dr. Jacobson explained to Universe Today via email:
To add to this state of confusion, paleomagnetic studies have been conducted that indicate that Earth's magnetic field has existed for at least 4.2 billion years (roughly 340 million years after it formed). As such, the question naturally arises as to what could account for the current state of convection and how it came about. For the sake of their study, Jacobson and his team considering the possibility that a massive impact could account for this. As Jacobson indicated:
Basically, the energy of this impact would have shaken up the core, creating a single homogeneous region within which a long-lasting geodynamo could operate. Given the age of Earth's magnetic field, this is consistent with the Theia impact theory, where a Mars-sized object is believed to have collided with Earth 4.51 billion years ago and led to the formation of the
Earth-Moon system
.
This impact could have caused Earth's core to go from being stratified to homogeneous, and over the course of the next 300 million years, pressure and temperature conditions could have caused it to differentiate between a solid inner core and liquid outer core. Thanks to rotation in the outer core, the result was a dynamo effect that protected our atmosphere as it formed.
[caption id="attachment_63584" align="aligncenter" width="580"]
Artist's concept of a collision between proto-Earth and Theia, believed to happened 4.5 billion years ago. Credit: NASA
[/caption]
The seeds of this theory were presented last year at the
47th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference
in The Woodlands, Texas. During a presentation titled "
Dynamical Mixing of Planetary Cores by Giant Impacts
", Dr. Miki Nakajima of Caltech - one of the co-authors on this latest study - and David J. Stevenson of the Carnegie Institution of Washington. At the time, they indicated that the stratification of Earth's core may have been reset by the same impact that formed the Moon.
It was Nakajima and Stevenson's study that showed how the most violent impacts could stir the core of planets late in their accretion. Building on this, Jacobson and the other co-authors applied models of how Earth and Venus accreted from a disk of solids and gas about a proto-Sun. They also applied calculations of how Earth and Venus grew, based on the chemistry of the mantle and core of each planet through each accretion event.
The significance of this study, in terms of how it relates to the evolution of Earth and the emergence of life, cannot be understated. If Earth's magnetosphere is the result of a late energetic impact, then such impacts could very well be the difference between our planet being habitable or being either too cold and arid (like Mars) or too hot and hellish (like Venus). As Jacobson concluded:
Looking beyond our Solar System, this paper also has implications in the study of extra-solar planets. Here too, the difference between a planet being habitable or not may come down to high-energy impacts being a part of the system's early history. In the future, when studying extra-solar planets and looking for signs of habitability, scientists may very well be forced to ask one simple question: "Was it hit hard enough?"
Further Reading: Earth Science and Planetary Letters
 Universe Today
Universe Today